Abstract
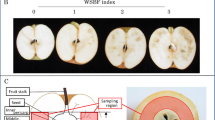
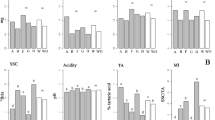
Penicillium funiculosum Thom. was consistently isolated from pineapple-infected fruitlet (black spots). Polyphenol oxidase, peroxidase, and laccase activities were determined in extracts from contiguous and infected fruitlets. Healthy fruitlets showed a rather high level of polyphenol oxidase (optimum pH 7.0), and this activity was tremendously increased (×10) in contiguous infected fruitlets. Furthermore, infected fruitlets also exhibited laccase activity (optimum pH 4.0), while peroxidase was rather constant in both fruitlets. Browning reactions were attributed to qualitative and quantitative modifications of the enzymatic equipment (polyphenol oxidase and laccase) (p<0.0001). In infected fruiltets, sucrose and L-malic acid were present at significantly lower amounts than in healthy ones, likely owing to fungal metabolism (p<0.0001), whereas cell wall material was three times higher, which could be viewed as a defense mechanism to limit expansion of the mycelium. RID=”” ID=”” <E5>Correspondence to: </E5>S. Avallone; <E5>email:</E5> avallone@siarc.cnearc.fr
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 September 2002 / Accepted: 25 September 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avallone, S., Guiraud, JP., Brillouet, JM. et al. Enzymatic Browning and Biochemical Alterations in Black Spots of Pineapple [Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.]. Curr Microbiol 47, 0113–0118 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3958-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3958-4