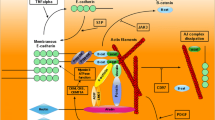
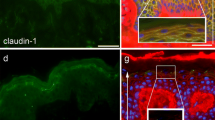
Abstract
Mucosal surfaces are lined by epithelial cells that form a physical barrier protecting the body against external noxious substances and pathogens. At a molecular level, the mucosal barrier is regulated by tight junctions (TJs) that seal the paracellular space between adjacent epithelial cells. Transmembrane proteins within TJs include junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) that belong to the cortical thymocyte marker for Xenopus family of proteins. JAM family encompasses three classical members (JAM-A, JAM-B, and JAM-C) and related molecules including JAM4, JAM-like protein, Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR), CAR-like membrane protein and endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule. JAMs have multiple functions that include regulation of endothelial and epithelial paracellular permeability, leukocyte recruitment during inflammation, angiogenesis, cell migration, and proliferation. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge regarding the roles of the JAM family members in the regulation of mucosal homeostasis and leukocyte trafficking with a particular emphasis on barrier function and its perturbation during pathological inflammation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams AF, Barclay AN (1988) The immunoglobulin superfamily—domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 6:381–405
Malergue F, Galland F, Martin F, Mansuelle P, Aurrand-Lions M et al (1998) A novel immunoglobulin superfamily junctional molecule expressed by antigen presenting cells, endothelial cells and platelets. Mol Immunol 35:1111–1119
Martin-Padura I, Lostaglio S, Schneemann M, Williams L, Romano M et al (1998) Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. J Cell Biol 142:117–127
Cunningham SA, Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, Bjercke RJ, Vanderslice P et al (2000) A novel protein with homology to the junctional adhesion molecule. Characterization of leukocyte interactions. J Biol Chem 275:34750–34756
Palmeri D, van Zante A, Huang CC, Hemmerich S, Rosen SD (2000) Vascular endothelial junction-associated molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is localized to intercellular boundaries of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 275:19139–19145
Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, Tran TM, Brock TA, Cunningham SA (2001) Cloning of human junctional adhesion molecule 3 (JAM3) and its identification as the JAM2 counter-receptor. J Biol Chem 276:45826–45832
Aurrand-Lions M, Duncan L, Ballestrem C, Imhof BA (2001) JAM-2, a novel immunoglobulin superfamily molecule, expressed by endothelial and lymphatic cells. J Biol Chem 276:2733–2741
Ebnet K, Suzuki A, Ohno S, Vestweber D (2004) Junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs): more molecules with dual functions? J Cell Sci 117:19–29
Hirabayashi S, Tajima M, Yao I, Nishimura W, Mori H et al (2003) JAM4, a junctional cell adhesion molecule interacting with a tight junction protein, MAGI-1. Mol Cell Biol 23:4267–4282
Moog-Lutz C, Cave-Riant F, Guibal FC, Breau MA, Di Gioia Y et al (2003) JAML, a novel protein with characteristics of a junctional adhesion molecule, is induced during differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 102:3371–3378
Tomko RP, Xu R, Philipson L (1997) HCAR and MCAR: the human and mouse cellular receptors for subgroup C adenoviruses and group B Coxsackieviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:3352–3356
Raschperger E, Engstrom U, Pettersson RF, Fuxe J (2004) CLMP, a novel member of the CTX family and a new component of epithelial tight junctions. J Biol Chem 279:796–804
Hirata K, Ishida T, Penta K, Rezaee M, Yang E et al (2001) Cloning of an immunoglobulin family adhesion molecule selectively expressed by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 276:16223–16231
Bradfield PF, Nourshargh S, Aurrand-Lions M, Imhof BA (2007) JAM family and related proteins in leukocyte migration (Vestweber series). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2104–2112
Naik TU, Naik MU, Naik UP (2008) Junctional adhesion molecules in angiogenesis. Front Biosci 13:258–262
Bazzoni G (2011) Pathobiology of junctional adhesion molecules. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1221–1234
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M (2001) Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:285–293
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S et al (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
Koval M (2006) Claudins–key pieces in the tight junction puzzle. Cell Commun Adhes 13:127–138
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K, Saitou M et al (1999) Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins. J Cell Biol 147:1351–1363
Fanning AS, Jameson BJ, Jesaitis LA, Anderson JM (1998) The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 273:29745–29753
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2006) Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol 68:403–429
Saitou M, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Schulzke JD, Fromm M et al (2000) Complex phenotype of mice lacking occludin, a component of tight junction strands. Mol Biol Cell 11:4131–4142
Schulzke JD, Gitter AH, Mankertz J, Spiegel S, Seidler U et al (2005) Epithelial transport and barrier function in occludin-deficient mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1669:34–42
Wang Z, Mandell KJ, Parkos CA, Mrsny RJ, Nusrat A (2005) The second loop of occludin is required for suppression of Raf1-induced tumor growth. Oncogene 24:4412–4420
Wong V, Gumbiner BM (1997) A synthetic peptide corresponding to the extracellular domain of occludin perturbs the tight junction permeability barrier. J Cell Biol 136:399–409
Betanzos A, Schnoor M, Severson EA, Liang TW, Parkos CA (2009) Evidence for cross-reactivity of JAM-C antibodies: implications for cellular localization studies. Biol Cell 101:441–453
Liu Y, Nusrat A, Schnell FJ, Reaves TA, Walsh S et al (2000) Human junction adhesion molecule regulates tight junction resealing in epithelia. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 13):2363–2374
Itoh M, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Ozaki H, Kita T et al (2001) Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) binds to PAR-3: a possible mechanism for the recruitment of PAR-3 to tight junctions. J Cell Biol 154:491–497
Furuse M, Sasaki H, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) A single gene product, claudin-1 or -2, reconstitutes tight junction strands and recruits occludin in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 143:391–401
Laukoetter MG, Nava P, Lee WY, Severson EA, Capaldo CT et al (2007) JAM-A regulates permeability and inflammation in the intestine in vivo. J Exp Med 204:3067–3076
Vetrano S, Rescigno M, Cera MR, Correale C, Rumio C et al (2008) Unique role of junctional adhesion molecule—a in maintaining mucosal homeostasis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 135:173–184
Kostrewa D, Brockhaus M, D’Arcy A, Dale GE, Nelboeck P et al (2001) X-ray structure of junctional adhesion molecule: structural basis for homophilic adhesion via a novel dimerization motif. EMBO J 20:4391–4398
Prota AE, Campbell JA, Schelling P, Forrest JC, Watson MJ et al (2003) Crystal structure of human junctional adhesion molecule 1: implications for reovirus binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:5366–5371
Mandell KJ, McCall IC, Parkos CA (2004) Involvement of the junctional adhesion molecule-1 (JAM1) homodimer interface in regulation of epithelial barrier function. J Biol Chem 279:16254–16262
Mandell KJ, Berglin L, Severson EA, Edelhauser HF, Parkos CA (2007) Expression of JAM-A in the human corneal endothelium and retinal pigment epithelium: localization and evidence for role in barrier function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:3928–3936
Rehder D, Iden S, Nasdala I, Wegener J, Brickwedde MK et al (2006) Junctional adhesion molecule—a participates in the formation of apico-basal polarity through different domains. Exp Cell Res 312:3389–3403
Ebnet K, Suzuki A, Horikoshi Y, Hirose T, Meyer Zu Brickwedde MK et al (2001) The cell polarity protein ASIP/PAR-3 directly associates with junctional adhesion molecule (JAM). EMBO J 20:3738–3748
Suzuki A, Ishiyama C, Hashiba K, Shimizu M, Ebnet K et al (2002) aPKC kinase activity is required for the asymmetric differentiation of the premature junctional complex during epithelial cell polarization. J Cell Sci 115:3565–3573
Iden S, Misselwitz S, Peddibhotla SS, Tuncay H, Rehder D et al (2012) aPKC phosphorylates JAM-A at Ser285 to promote cell contact maturation and tight junction formation. J Cell Biol 196:623–639
Bazzoni G, Martinez-Estrada OM, Orsenigo F, Cordenonsi M, Citi S et al (2000) Interaction of junctional adhesion molecule with the tight junction components ZO-1, cingulin, and occludin. J Biol Chem 275:20520–20526
Monteiro AC, Sumagin R, Rankin CR, Leoni G, Mina MJ et al (2013) JAM-A associates with ZO-2, afadin, and PDZ-GEF1 to activate Rap2c and regulate epithelial barrier function. Mol Biol Cell 24:2849–2860
Nomme J, Fanning AS, Caffrey M, Lye MF, Anderson JM et al (2011) The Src homology 3 domain is required for junctional adhesion molecule binding to the third PDZ domain of the scaffolding protein ZO-1. J Biol Chem 286:43352–43360
Ebnet K, Schulz CU, Meyer Zu Brickwedde MK, Pendl GG, Vestweber D (2000) Junctional adhesion molecule interacts with the PDZ domain-containing proteins AF-6 and ZO-1. J Biol Chem 275:27979–27988
Severson EA, Lee WY, Capaldo CT, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2009) Junctional adhesion molecule A interacts with Afadin and PDZ-GEF2 to activate Rap1A, regulate beta1 integrin levels, and enhance cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 20:1916–1925
Hamazaki Y, Itoh M, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2002) Multi-PDZ domain protein 1 (MUPP1) is concentrated at tight junctions through its possible interaction with claudin-1 and junctional adhesion molecule. J Biol Chem 277:455–461
Martinez-Estrada OM, Villa A, Breviario F, Orsenigo F, Dejana E et al (2001) Association of junctional adhesion molecule with calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (CASK/LIN-2) in human epithelial caco-2 cells. J Biol Chem 276:9291–9296
Ivanov AI, Parkos CA, Nusrat A (2010) Cytoskeletal regulation of epithelial barrier function during inflammation. Am J Pathol 177:512–524
Miyata M, Rikitake Y, Takahashi M, Nagamatsu Y, Yamauchi Y et al (2009) Regulation by afadin of cyclical activation and inactivation of Rap1, Rac1, and RhoA small G proteins at leading edges of moving NIH3T3 cells. J Biol Chem 284:24595–24609
Tanaka-Okamoto M, Hori K, Ishizaki H, Itoh Y, Onishi S et al (2011) Involvement of afadin in barrier function and homeostasis of mouse intestinal epithelia. J Cell Sci 124:2231–2240
Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM (2009) Physiology and function of the tight junction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a002584
Chiba H, Gotoh T, Kojima T, Satohisa S, Kikuchi K et al (2003) Hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)-4alpha triggers formation of functional tight junctions and establishment of polarized epithelial morphology in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res 286:288–297
Darsigny M, Babeu JP, Dupuis AA, Furth EE, Seidman EG et al (2009) Loss of hepatocyte-nuclear-factor-4alpha affects colonic ion transport and causes chronic inflammation resembling inflammatory bowel disease in mice. PLoS One 4:e7609
Satohisa S, Chiba H, Osanai M, Ohno S, Kojima T et al (2005) Behavior of tight-junction, adherens-junction and cell polarity proteins during HNF-4alpha-induced epithelial polarization. Exp Cell Res 310:66–78
Tajima M, Hirabayashi S, Yao I, Shirasawa M, Osuga J et al (2003) Roles of immunoglobulin-like loops of junctional cell adhesion molecule 4; involvement in the subcellular localization and the cell adhesion. Genes Cells 8:759–768
Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, Kurt-Jones EA, Krithivas A et al (1997) Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science 275:1320–1323
Tomko RP, Johansson CB, Totrov M, Abagyan R, Frisen J et al (2000) Expression of the adenovirus receptor and its interaction with the fiber knob. Exp Cell Res 255:47–55
Cohen CJ, Shieh JT, Pickles RJ, Okegawa T, Hsieh JT et al (2001) The Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor is a transmembrane component of the tight junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:15191–15196
Coyne CB, Voelker T, Pichla SL, Bergelson JM (2004) The Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor interacts with the multi-PDZ domain protein-1 (MUPP-1) within the tight junction. J Biol Chem 279:48079–48084
Raschperger E, Thyberg J, Pettersson S, Philipson L, Fuxe J et al (2006) The coxsackie- and adenovirus receptor (CAR) is an in vivo marker for epithelial tight junctions, with a potential role in regulating permeability and tissue homeostasis. Exp Cell Res 312:1566–1580
Ebnet K, Aurrand-Lions M, Kuhn A, Kiefer F, Butz S et al (2003) The junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) family members JAM-2 and JAM-3 associate with the cell polarity protein PAR-3: a possible role for JAMs in endothelial cell polarity. J Cell Sci 116:3879–3891
Patzke C, Max KE, Behlke J, Schreiber J, Schmidt H et al (2010) The Coxsackievirus–adenovirus receptor reveals complex homophilic and heterophilic interactions on neural cells. J Neurosci 30:2897–2910
van Raaij MJ, Chouin E, van der Zandt H, Bergelson JM, Cusack S (2000) Dimeric structure of the Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor D1 domain at 1.7 A resolution. Structure 8:1147–1155
Hussain F, Morton PE, Snippe M, Sullivan J, Farmer C et al (2011) CAR modulates E-cadherin dynamics in the presence of adenovirus type 5. PLoS One 6:e23056
Morton PE, Hicks A, Nastos T, Santis G, Parsons M (2013) CAR regulates epithelial cell junction stability through control of E-cadherin trafficking. Sci Rep 3:2889
Pazirandeh A, Sultana T, Mirza M, Rozell B, Hultenby K et al (2011) Multiple phenotypes in adult mice following inactivation of the Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (Car) gene. PLoS One 6:1–6
Van Der Werf CS, Wabbersen TD, Hsiao NH, Paredes J, Etchevers HC et al (2012) CLMP is required for intestinal development, and loss-of-function mutations cause congenital short-bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 142(453–462):e453
Artis D (2008) Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol 8:411–420
Hooper LV, Macpherson AJ (2010) Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nat Rev Immunol 10:159–169
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S (2007) Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol 7:678–689
Aurrand-Lions M, Johnson-Leger C, Wong C, Du Pasquier L, Imhof BA (2001) Heterogeneity of endothelial junctions is reflected by differential expression and specific subcellular localization of the three JAM family members. Blood 98:3699–3707
Carson SD, Hobbs JT, Tracy SM, Chapman NM (1999) Expression of the Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells: regulation in response to cell density. J Virol 73:7077–7079
Dejana E (2004) Endothelial cell–cell junctions: happy together. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:261–270
Nasdala I, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Wolburg H, Kuhn A, Ebnet K et al (2002) A transmembrane tight junction protein selectively expressed on endothelial cells and platelets. J Biol Chem 277:16294–16303
Wegmann F, Ebnet K, Du Pasquier L, Vestweber D, Butz S (2004) Endothelial adhesion molecule ESAM binds directly to the multidomain adaptor MAGI-1 and recruits it to cell contacts. Exp Cell Res 300:121–133
Ozaki H, Ishii K, Horiuchi H, Arai H, Kawamoto T et al (1999) Cutting edge: combined treatment of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma causes redistribution of junctional adhesion molecule in human endothelial cells. J Immunol 163:553–557
Fraemohs L, Koenen RR, Ostermann G, Heinemann B, Weber C (2004) The functional interaction of the beta 2 integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 with junctional adhesion molecule-A is mediated by the I domain. J Immunol 173:6259–6264
Ostermann G, Weber KS, Zernecke A, Schroder A, Weber C (2002) JAM-1 is a ligand of the beta(2) integrin LFA-1 involved in transendothelial migration of leukocytes. Nat Immunol 3:151–158
Wojcikiewicz EP, Koenen RR, Fraemohs L, Minkiewicz J, Azad H et al (2009) LFA-1 binding destabilizes the JAM-A homophilic interaction during leukocyte transmigration. Biophys J 96:285–293
Del Maschio A, De Luigi A, Martin-Padura I, Brockhaus M, Bartfai T et al (1999) Leukocyte recruitment in the cerebrospinal fluid of mice with experimental meningitis is inhibited by an antibody to junctional adhesion molecule (JAM). J Exp Med 190:1351–1356
Corada M, Chimenti S, Cera MR, Vinci M, Salio M et al (2005) Junctional adhesion molecule-A-deficient polymorphonuclear cells show reduced diapedesis in peritonitis and heart ischemia–reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10634–10639
Khandoga A, Kessler JS, Meissner H, Hanschen M, Corada M et al (2005) Junctional adhesion molecule-A deficiency increases hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury despite reduction of neutrophil transendothelial migration. Blood 106:725–733
Woodfin A, Reichel CA, Khandoga A, Corada M, Voisin MB et al (2007) JAM-A mediates neutrophil transmigration in a stimulus-specific manner in vivo: evidence for sequential roles for JAM-A and PECAM-1 in neutrophil transmigration. Blood 110:1848–1856
Woodfin A, Voisin MB, Imhof BA, Dejana E, Engelhardt B et al (2009) Endothelial cell activation leads to neutrophil transmigration as supported by the sequential roles of ICAM-2, JAM-A, and PECAM-1. Blood 113:6246–6257
Cera MR, Fabbri M, Molendini C, Corada M, Orsenigo F et al (2009) JAM-A promotes neutrophil chemotaxis by controlling integrin internalization and recycling. J Cell Sci 122:268–277
Cera MR, Del Prete A, Vecchi A, Corada M, Martin-Padura I et al (2004) Increased DC trafficking to lymph nodes and contact hypersensitivity in junctional adhesion molecule-A-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 114:729–738
Liang TW, Chiu HH, Gurney A, Sidle A, Tumas DB et al (2002) Vascular endothelial-junctional adhesion molecule (VE-JAM)/JAM 2 interacts with T, NK, and dendritic cells through JAM 3. J Immunol 168:1618–1626
Cunningham SA, Rodriguez JM, Arrate MP, Tran TM, Brock TA (2002) JAM2 interacts with alpha4beta1. Facilitation by JAM3. J Biol Chem 277:27589–27592
Lamagna C, Meda P, Mandicourt G, Brown J, Gilbert RJ et al (2005) Dual interaction of JAM-C with JAM-B and alpha(M)beta2 integrin: function in junctional complexes and leukocyte adhesion. Mol Biol Cell 16:4992–5003
Ludwig RJ, Zollner TM, Santoso S, Hardt K, Gille J et al (2005) Junctional adhesion molecules (JAM)-B and -C contribute to leukocyte extravasation to the skin and mediate cutaneous inflammation. J Invest Dermatol 125:969–976
Ludwig RJ, Hardt K, Hatting M, Bistrian R, Diehl S et al (2009) Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM)-B supports lymphocyte rolling and adhesion through interaction with alpha4beta1 integrin. Immunology 128:196–205
Santoso S, Sachs UJ, Kroll H, Linder M, Ruf A et al (2002) The junctional adhesion molecule 3 (JAM-3) on human platelets is a counterreceptor for the leukocyte integrin Mac-1. J Exp Med 196:679–691
Aurrand-Lions M, Lamagna C, Dangerfield JP, Wang S, Herrera P et al (2005) Junctional adhesion molecule-C regulates the early influx of leukocytes into tissues during inflammation. J Immunol 174:6406–6415
Chavakis T, Keiper T, Matz-Westphal R, Hersemeyer K, Sachs UJ et al (2004) The junctional adhesion molecule-C promotes neutrophil transendothelial migration in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 279:55602–55608
Imhof BA, Zimmerli C, Gliki G, Ducrest-Gay D, Juillard P et al (2007) Pulmonary dysfunction and impaired granulocyte homeostasis result in poor survival of Jam-C-deficient mice. J Pathol 212:198–208
Johnson-Leger CA, Aurrand-Lions M, Beltraminelli N, Fasel N, Imhof BA (2002) Junctional adhesion molecule-2 (JAM-2) promotes lymphocyte transendothelial migration. Blood 100:2479–2486
Scheiermann C, Colom B, Meda P, Patel NS, Voisin MB et al (2009) Junctional adhesion molecule-C mediates leukocyte infiltration in response to ischemia reperfusion injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1509–1515
Vonlaufen A, Aurrand-Lions M, Pastor CM, Lamagna C, Hadengue A et al (2006) The role of junctional adhesion molecule C (JAM-C) in acute pancreatitis. J Pathol 209:540–548
Bradfield PF, Scheiermann C, Nourshargh S, Ody C, Luscinskas FW et al (2007) JAM-C regulates unidirectional monocyte transendothelial migration in inflammation. Blood 110:2545–2555
Woodfin A, Voisin MB, Beyrau M, Colom B, Caille D et al (2011) The junctional adhesion molecule JAM-C regulates polarized transendothelial migration of neutrophils in vivo. Nat Immunol 12:761–769
Orlova VV, Economopoulou M, Lupu F, Santoso S, Chavakis T (2006) Junctional adhesion molecule-C regulates vascular endothelial permeability by modulating VE-cadherin-mediated cell-cell contacts. J Exp Med 203:2703–2714
Khandoga A, Huettinger S, Khandoga AG, Li H, Butz S et al (2009) Leukocyte transmigration in inflamed liver: a role for endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule. J Hepatol 50:755–765
Wegmann F, Petri B, Khandoga AG, Moser C, Khandoga A et al (2006) ESAM supports neutrophil extravasation, activation of Rho, and VEGF-induced vascular permeability. J Exp Med 203:1671–1677
Inoue M, Ishida T, Yasuda T, Toh R, Hara T et al (2010) Endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule modulates atherosclerosis through plaque angiogenesis and monocyte-endothelial interaction. Microvasc Res 80:179–187
Hara T, Ishida T, Cangara HM, Hirata K (2009) Endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule regulates albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. Microvasc Res 77:348–355
Luissint AC, Lutz PG, Calderwood DA, Couraud PO, Bourdoulous S (2008) JAM-L-mediated leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells is regulated in cis by alpha4beta1 integrin activation. J Cell Biol 183:1159–1173
Vincent T, Pettersson RF, Crystal RG, Leopold PL (2004) Cytokine-mediated downregulation of Coxsackievirus–adenovirus receptor in endothelial cells. J Virol 78:8047–8058
Guo YL, Bai R, Chen CX, Liu DQ, Liu Y et al (2009) Role of junctional adhesion molecule-like protein in mediating monocyte transendothelial migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:75–83
Mirza M, Hreinsson J, Strand ML, Hovatta O, Soder O et al (2006) Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) is expressed in male germ cells and forms a complex with the differentiation factor JAM-C in mouse testis. Exp Cell Res 312:817–830
Mirza M, Pang MF, Zaini MA, Haiko P, Tammela T et al (2012) Essential role of the coxsackie- and adenovirus receptor (CAR) in development of the lymphatic system in mice. PLoS One 7:e37523
Parkos CA, Delp C, Arnaout MA, Madara JL (1991) Neutrophil migration across a cultured intestinal epithelium. Dependence on a CD11b/CD18-mediated event and enhanced efficiency in physiological direction. J Clin Invest 88:1605–1612
Zen K, Liu Y, Cairo D, Parkos CA (2002) CD11b/CD18-dependent interactions of neutrophils with intestinal epithelium are mediated by fucosylated proteoglycans. J Immunol 169:5270–5278
Heit B, Tavener S, Raharjo E, Kubes P (2002) An intracellular signaling hierarchy determines direction of migration in opposing chemotactic gradients. J Cell Biol 159:91–102
Blake KM, Carrigan SO, Issekutz AC, Stadnyk AW (2004) Neutrophils migrate across intestinal epithelium using beta2 integrin (CD11b/CD18)-independent mechanisms. Clin Exp Immunol 136:262–268
Hawkins HK, Heffelfinger SC, Anderson DC (1992) Leukocyte adhesion deficiency: clinical and postmortem observations. Pediatr Pathol 12:119–130
Lee WY, Weber DA, Laur O, Stowell SR, McCall I et al (2010) The role of cis dimerization of signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) in binding to CD47. J Biol Chem 285:37953–37963
Liu Y, Merlin D, Burst SL, Pochet M, Madara JL et al (2001) The role of CD47 in neutrophil transmigration. Increased rate of migration correlates with increased cell surface expression of CD47. J Biol Chem 276:40156–40166
Parkos CA, Colgan SP, Liang TW, Nusrat A, Bacarra AE et al (1996) CD47 mediates post-adhesive events required for neutrophil migration across polarized intestinal epithelia. J Cell Biol 132:437–450
de Vries HE, Hendriks JJ, Honing H, De Lavalette CR, van der Pol SM et al (2002) Signal-regulatory protein alpha-CD47 interactions are required for the transmigration of monocytes across cerebral endothelium. J Immunol 168:5832–5839
Stefanidakis M, Newton G, Lee WY, Parkos CA, Luscinskas FW (2008) Endothelial CD47 interaction with SIRPgamma is required for human T-cell transendothelial migration under shear flow conditions in vitro. Blood 112:1280–1289
Ginzberg HH, Cherapanov V, Dong Q, Cantin A, McCulloch CA et al (2001) Neutrophil-mediated epithelial injury during transmigration: role of elastase. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G705–G717
Zen K, Liu Y, McCall IC, Wu T, Lee W et al (2005) Neutrophil migration across tight junctions is mediated by adhesive interactions between epithelial coxsackie and adenovirus receptor and a junctional adhesion molecule-like protein on neutrophils. Mol Biol Cell 16:2694–2703
Chin AC, Parkos CA (2007) Pathobiology of neutrophil transepithelial migration: implications in mediating epithelial injury. Annu Rev Pathol 2:111–143
Nash S, Stafford J, Madara JL (1987) Effects of polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration on the barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest 80:1104–1113
Nusrat A, Parkos CA, Liang TW, Carnes DK, Madara JL (1997) Neutrophil migration across model intestinal epithelia: monolayer disruption and subsequent events in epithelial repair. Gastroenterology 113:1489–1500
Huang GT, Eckmann L, Savidge TC, Kagnoff MF (1996) Infection of human intestinal epithelial cells with invasive bacteria upregulates apical intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM)-1) expression and neutrophil adhesion. J Clin Invest 98:572–583
Parkos CA, Colgan SP, Diamond MS, Nusrat A, Liang TW et al (1996) Expression and polarization of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human intestinal epithelia: consequences for CD11b/CD18-mediated interactions with neutrophils. Mol Med 2:489–505
Sumagin R, Robin AZ, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2013) Transmigrated neutrophils in the intestinal lumen engage ICAM-1 to regulate the epithelial barrier and neutrophil recruitment. Mucosal Immunol.
Brazil JC, Lee WY, Kolegraff KN, Nusrat A, Parkos CA et al (2010) Neutrophil migration across intestinal epithelium: evidence for a role of CD44 in regulating detachment of migrating cells from the luminal surface. J Immunol 185:7026–7036
Lawrence DW, Bruyninckx WJ, Louis NA, Lublin DM, Stahl GL et al (2003) Antiadhesive role of apical decay-accelerating factor (CD55) in human neutrophil transmigration across mucosal epithelia. J Exp Med 198:999–1010
Colgan SP, Serhan CN, Parkos CA, Delp-Archer C, Madara JL (1993) Lipoxin A4 modulates transmigration of human neutrophils across intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest 92:75–82
Fournier BM, Parkos CA (2012) The role of neutrophils during intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 5:354–366
Serhan CN, Petasis NA (2011) Resolvins and protectins in inflammation resolution. Chem Rev 111:5922–5943
Yang H, Antony PA, Wildhaber BE, Teitelbaum DH (2004) Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte gamma delta-T cell-derived keratinocyte growth factor modulates epithelial growth in the mouse. J Immunol 172:4151–4158
Byrne FR, Farrell CL, Aranda R, Rex KL, Scully S et al (2002) rHuKGF ameliorates symptoms in DSS and CD4(+)CD45RB(Hi) T cell transfer mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282:G690–G701
Witherden DA, Verdino P, Rieder SE, Garijo O, Mills RE et al (2010) The junctional adhesion molecule JAML is a costimulatory receptor for epithelial gammadelta T cell activation. Science 329:1205–1210
Chen Y, Chou K, Fuchs E, Havran WL, Boismenu R (2002) Protection of the intestinal mucosa by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:14338–14343
Weber DA, Sumagin R, McCall IC, Leoni G, Neumann PA, Andargachew R, Brazil JC, Medina-Contreras O, Denning TL, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2014) Neutrophil-derived JAML inhibits repair of intestinal epithelial injury during acute inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. doi:10.1038/mi.2014.12
Brannigan AE, O’Connell PR, Hurley H, O’Neill A, Brady HR et al (2000) Neutrophil apoptosis is delayed in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Shock 13:361–366
Brazil JC, Louis NA, Parkos CA (2013) The role of polymorphonuclear leukocyte trafficking in the perpetuation of inflammation during inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 19:1556–1565
Koenen RR, Pruessmeyer J, Soehnlein O, Fraemohs L, Zernecke A et al (2009) Regulated release and functional modulation of junctional adhesion molecule A by disintegrin metalloproteinases. Blood 113:4799–4809
Rabquer BJ, Amin MA, Teegala N, Shaheen MK, Tsou PS et al (2010) Junctional adhesion molecule-C is a soluble mediator of angiogenesis. J Immunol 185:1777–1785
Cesaro A, Abakar-Mahamat A, Brest P, Lassalle S, Selva E et al (2009) Differential expression and regulation of ADAM17 and TIMP3 in acute inflamed intestinal epithelia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:G1332–G1343
Nava P, Capaldo CT, Koch S, Kolegraff K, Rankin CR et al (2011) JAM-A regulates epithelial proliferation through Akt/beta-catenin signalling. EMBO Rep 12:314–320
Bruewer M, Utech M, Ivanov AI, Hopkins AM, Parkos CA et al (2005) Interferon-gamma induces internalization of epithelial tight junction proteins via a macropinocytosis-like process. FASEB J 19:923–933
Kucharzik T, Walsh SV, Chen J, Parkos CA, Nusrat A (2001) Neutrophil transmigration in inflammatory bowel disease is associated with differential expression of epithelial intercellular junction proteins. Am J Pathol 159:2001–2009
Clayburgh DR, Barrett TA, Tang Y, Meddings JB, Van Eldik LJ et al (2005) Epithelial myosin light chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. J Clin Invest 115:2702–2715
Capaldo CT, Nusrat A (2009) Cytokine regulation of tight junctions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:864–871
Gassler N, Rohr C, Schneider A, Kartenbeck J, Bach A et al (2001) Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with changes of enterocytic junctions. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G216–G228
Raddatz D, Bockemuhl M, Ramadori G (2005) Quantitative measurement of cytokine mRNA in inflammatory bowel disease: relation to clinical and endoscopic activity and outcome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:547–557
Schmitz H, Barmeyer C, Fromm M, Runkel N, Foss HD et al (1999) Altered tight junction structure contributes to the impaired epithelial barrier function in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 116:301–309
Fais S, Capobianchi MR, Silvestri M, Mercuri F, Pallone F et al (1994) Interferon expression in Crohn’s disease patients: increased interferon-gamma and -alpha mRNA in the intestinal lamina propria mononuclear cells. J Interferon Res 14:235–238
MacDonald TT, Hutchings P, Choy MY, Murch S, Cooke A (1990) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma production measured at the single cell level in normal and inflamed human intestine. Clin Exp Immunol 81:301–305
Murch SH, Braegger CP, Walker-Smith JA, MacDonald TT (1993) Location of tumour necrosis factor alpha by immunohistochemistry in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 34:1705–1709
Bruewer M, Luegering A, Kucharzik T, Parkos CA, Madara JL et al (2003) Proinflammatory cytokines disrupt epithelial barrier function by apoptosis-independent mechanisms. J Immunol 171:6164–6172
Poritz LS, Garver KI, Tilberg AF, Koltun WA (2004) Tumor necrosis factor alpha disrupts tight junction assembly. J Surg Res 116:14–18
Utech M, Ivanov AI, Samarin SN, Bruewer M, Turner JR et al (2005) Mechanism of IFN-gamma-induced endocytosis of tight junction proteins: myosin II-dependent vacuolarization of the apical plasma membrane. Mol Biol Cell 16:5040–5052
Wang F, Graham WV, Wang Y, Witkowski ED, Schwarz BT et al (2005) Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergize to induce intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by up-regulating myosin light chain kinase expression. Am J Pathol 166:409–419
Korn WM, Macal M, Christian C, Lacher MD, McMillan A et al (2006) Expression of the Coxsackievirus- and adenovirus receptor in gastrointestinal cancer correlates with tumor differentiation. Cancer Gene Ther 13:792–797
Okegawa T, Pong RC, Li Y, Bergelson JM, Sagalowsky AI et al (2001) The mechanism of the growth-inhibitory effect of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR) on human bladder cancer: a functional analysis of car protein structure. Cancer Res 61:6592–6600
Stecker K, Koschel A, Wiedenmann B, Anders M (2009) Loss of Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor downregulates alpha-catenin expression. Br J Cancer 101:1574–1579
Mandicourt G, Iden S, Ebnet K, Aurrand-Lions M, Imhof BA (2007) JAM-C regulates tight junctions and integrin-mediated cell adhesion and migration. J Biol Chem 282:1830–1837
Naik MU, Mousa SA, Parkos CA, Naik UP (2003) Signaling through JAM-1 and alphavbeta3 is required for the angiogenic action of bFGF: dissociation of the JAM-1 and alphavbeta3 complex. Blood 102:2108–2114
Naik MU, Naik UP (2006) Junctional adhesion molecule-A-induced endothelial cell migration on vitronectin is integrin alpha v beta 3 specific. J Cell Sci 119:490–499
McSherry EA, McGee SF, Jirstrom K, Doyle EM, Brennan DJ et al (2009) JAM-A expression positively correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer 125:1343–1351
Mandell KJ, Babbin BA, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2005) Junctional adhesion molecule 1 regulates epithelial cell morphology through effects on beta1 integrins and Rap1 activity. J Biol Chem 280:11665–11674
Severson EA, Jiang L, Ivanov AI, Mandell KJ, Nusrat A et al (2008) Cis-dimerization mediates function of junctional adhesion molecule A. Mol Biol Cell 19:1862–1872
Khounlotham M, Kim W, Peatman E, Nava P, Medina-Contreras O et al (2012) Compromised intestinal epithelial barrier induces adaptive immune compensation that protects from colitis. Immunity 37:563–573
Naik MU, Naik TU, Suckow AT, Duncan MK, Naik UP (2008) Attenuation of junctional adhesion molecule-A is a contributing factor for breast cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res 68:2194–2203
Fuse C, Ishida Y, Hikita T, Asai T, Oku N (2007) Junctional adhesion molecule-C promotes metastatic potential of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma. J Biol Chem 282:8276–8283
Liang TW, DeMarco RA, Mrsny RJ, Gurney A, Gray A et al (2000) Characterization of huJAM: evidence for involvement in cell-cell contact and tight junction regulation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C1733–C1743
Gliki G, Ebnet K, Aurrand-Lions M, Imhof BA, Adams RH (2004) Spermatid differentiation requires the assembly of a cell polarity complex downstream of junctional adhesion molecule-C. Nature 431:320–324
Shao M, Ghosh A, Cooke VG, Naik UP, Martin-DeLeon PA (2008) JAM-A is present in mammalian spermatozoa where it is essential for normal motility. Dev Biol 313:246–255
Sugano Y, Takeuchi M, Hirata A, Matsushita H, Kitamura T et al (2008) Junctional adhesion molecule-A, JAM-A, is a novel cell-surface marker for long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 111:1167–1172
Sakaguchi T, Nishimoto M, Miyagi S, Iwama A, Morita Y et al (2006) Putative "stemness" gene jam-B is not required for maintenance of stem cell state in embryonic, neural, or hematopoietic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 26:6557–6570
Praetor A, McBride JM, Chiu H, Rangell L, Cabote L et al (2009) Genetic deletion of JAM-C reveals a role in myeloid progenitor generation. Blood 113:1919–1928
Colom B, Poitelon Y, Huang W, Woodfin A, Averill S et al (2012) Schwann cell-specific JAM-C-deficient mice reveal novel expression and functions for JAM-C in peripheral nerves. FASEB J 26:1064–1076
Scheiermann C, Meda P, Aurrand-Lions M, Madani R, Yiangou Y et al (2007) Expression and function of junctional adhesion molecule-C in myelinated peripheral nerves. Science 318:1472–1475
Morris AP, Tawil A, Berkova Z, Wible L, Smith CW et al (2006) Junctional Adhesion Molecules (JAMs) are differentially expressed in fibroblasts and co-localize with ZO-1 to adherens-like junctions. Cell Commun Adhes 13:233–247
Nagamatsu G, Ohmura M, Mizukami T, Hamaguchi I, Hirabayashi S et al (2006) A CTX family cell adhesion molecule, JAM4, is expressed in stem cell and progenitor cell populations of both male germ cell and hematopoietic cell lineages. Mol Cell Biol 26:8498–8506
Vigl B, Zgraggen C, Rehman N, Banziger-Tobler NE, Detmar M et al (2009) Coxsackie- and adenovirus receptor (CAR) is expressed in lymphatic vessels in human skin and affects lymphatic endothelial cell function in vitro. Exp Cell Res 315:336–347
Eguchi J, Wada J, Hida K, Zhang H, Matsuoka T et al (2005) Identification of adipocyte adhesion molecule (ACAM), a novel CTX gene family, implicated in adipocyte maturation and development of obesity. Biochem J 387:343–353
Ishida T, Kundu RK, Yang E, Hirata K, Ho YD et al (2003) Targeted disruption of endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule inhibits angiogenic processes in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 278:34598–34604
Yokota T, Oritani K, Butz S, Kokame K, Kincade PW et al (2009) The endothelial antigen ESAM marks primitive hematopoietic progenitors throughout life in mice. Blood 113:2914–2923
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge funding from The NIH (DK072564, DK061379, DK079392, DK064399, DK059888, and DK055679) and DOD (PR121194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the special issue on New paradigms in leukocyte trafficking, lessons for therapeutics - Guest Editors: F. W. Luscinskas and B. A. Imhof
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luissint, AC., Nusrat, A. & Parkos, C.A. JAM-related proteins in mucosal homeostasis and inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 36, 211–226 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-014-0421-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-014-0421-0