Abstract
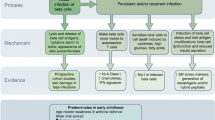
The question if enteroviruses could cause beta-cell damage and type 1 diabetes has become more and more relevant when recent studies have provided new evidence supporting this scenario. One important observation is the recent discovery of IFIH1 as a risk gene for type 1 diabetes. This gene is an innate immune system receptor for enteroviruses offering one possible mechanism for the diabetogenic effect of enteroviruses. This is further emphasized by the observations suggesting that the innate immune system is activated in the pancreatic islets of type 1 diabetic patients and that the innate immune system is important for the defense against the virus and for the regulation of adaptive immune system. Important progress has also been gained in studies analyzing pancreas tissue for possible presence of enteroviruses. Several studies have found enteroviruses in the pancreatic islets of type 1 diabetic patients using various methods. The virus seems to be located in the islets while exocrine pancreas is mostly uninfected. One recent study found the virus in the intestinal mucosa in the majority of diabetic patients. Enteroviruses can also infect cultured human pancreatic islets causing either rapid cell destruction or a persistent-like noncytolytic infection. Combined with all previous, epidemiological findings indicating the risk effect of enteroviruses in cross-sectional and prospective studies, these observations fit to a scenario where certain diabetogenic enterovirus variants establish persistent infection in gut mucosa and in the pancreatic islets. This in turn could lead to a local inflammation and the breakdown of tolerance in genetically susceptible individuals. This is also supported by mouse experiments showing that enteroviruses can establish prolonged infection in the pancreas and intestine, and some virus strains cause beta-cell damage and diabetes. In conclusion, recent studies have strengthened the hypothesis that enteroviruses play a role in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. These findings open also new opportunities to explore the underlying mechanism and get closer to causal relationship.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreoletti L, Hober D, Hober-Vandenberghe C, Belaich S, Vantyghem MC, Lefebvre J, Wattre P (1997) Detection of coxsackie B virus RNA sequences in whole blood samples from adult patients at the onset of type I diabetes mellitus. J Med Virol 52:121–127
Beck MA, Levander OA, Handy J (2003) Selenium deficiency and viral infection. J Nutr 133:1463S–1467S
Cerutis DR, Bruner RH, Thomas DC, Giron DJ (1989) Tropism and histopathology of the D, B, K, and MM variants of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Med Virol 29:63–69
Chapman NM, Kim KS (2008) Persistent coxsackievirus infection: enterovirus persistence in chronic myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 323:275–292
Chapman NM, Kim KS, Drescher KM, Oka K, Tracy S (2008) 5′ terminal deletions in the genome of a coxsackievirus B2 strain occurred naturally in human heart. Virology 375:480–491
Chehadeh W, Kerr-Conte J, Pattou F, Alm G, Lefebvre J, Wattre P, Hober D (2000) Persistent infection of human pancreatic islets by coxsackievirus B is associated with alpha interferon synthesis in beta cells. J Virol 74:10153–10164
Chehadeh W, Weill J, Vantyghem MC, Alm G, Lefebvre J, Wattre P, Hober D (2000) Increased level of interferon-alpha in blood of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: relationship with coxsackievirus B infection. J Infect Dis 181:1929–1939
Clements GB, Galbraith DN, Taylor KW (1995) Coxsackie B virus infection and onset of childhood diabetes. Lancet 346:221–223
Craig ME, Howard NJ, Silink M, Rawlinson WD (2003) Reduced frequency of HLA DRB1*03-DQB1*02 in children with type 1 diabetes associated with enterovirus RNA. J Infect Dis 187:1562–1570
Dahlquist GG, Ivarsson S, Lindberg B, Forsgren M (1995) Maternal enteroviral infection during pregnancy as a risk factor for childhood IDDM. A population-based case-control study. Diabetes 44:408–413
Dahlquist GG, Boman JE, Juto P (1999) Enteroviral RNA and IgM antibodies in early pregnancy and risk for childhood-onset IDDM in offspring. Diabetes Care 22:364–365
Dahlquist GG, Forsberg J, Hagenfeldt L, Boman J, Juto P (2004) Increased prevalence of enteroviral RNA in blood spots from newborn children who later developed type 1 diabetes: a population-based case-control study. Diabetes Care 27:285–286
Dotta F, Censini S, van Halteren AG, Marselli L, Masini M, Dionisi S, Mosca F, Boggi U, Muda AO, Prato SD, Elliott JF, Covacci A, Rappuoli R, Roep BO, Marchetti P (2007) Coxsackie B4 virus infection of beta cells and natural killer cell insulitis in recent-onset type 1 diabetic patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5115–5120
Dotta F, Fondelli C, Falorni A (2008) Can NK cells be a therapeutic target in human type 1 diabetes? Eur J Immunol 38:2961–2963
Drescher KM, Sosnowska D (2008) Being a mouse in a man’s world: what TMEV has taught us about human disease. Front Biosci 13:3775–3785
Elshebani A, Olsson A, Westman J, Tuvemo T, Korsgren O, Frisk G (2007) Effects on isolated human pancreatic islet cells after infection with strains of enterovirus isolated at clinical presentation of type 1 diabetes. Virus Res 124:193–203
Feuer R, Ruller CM, An N, Tabor-Godwin JM, Rhoades RE, Maciejewski S, Pagarigan RR, Cornell CT, Crocker SJ, Kiosses WB, Pham-Mitchell N, Campbell IL, Whitton JL (2009) Viral persistence and chronic immunopathology in the adult central nervous system following Coxsackievirus infection during the neonatal period. J Virol 83:9356–9369
Filippi CM, Estes EA, Oldham JE, von Herrath MG (2009) Immunoregulatory mechanisms triggered by viral infections protect from type 1 diabetes in mice. J Clin Invest 119:1515–1523
Foulis AK, Farquharson MA, Cameron SO, McGill M, Schonke H, Kandolf R (1990) A search for the presence of the enteroviral capsid protein VP1 in pancreases of patients with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes and pancreases and hearts of infants who died of coxsackieviral myocarditis. Diabetologia 33:290–298
Foulis AK, McGill M, Farquharson MA, Hilton DA (1997) A search for evidence of viral infection in pancreases of newly diagnosed patients with IDDM. Diabetologia 40:53–61
Foy CA, Quirke P, Lewis FA, Futers TS, Bodansky HJ (1995) Detection of common viruses using the polymerase chain reaction to assess levels of viral presence in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabet Med 12:1002–1008
Fuchtenbusch M, Irnstetter A, Jager G, Ziegler AG (2001) No evidence for an association of coxsackie virus infections during pregnancy and early childhood with development of islet autoantibodies in offspring of mothers or fathers with type 1 diabetes. J Autoimmun 17:333–340
Gamble DR, Kinsley ML, FitzGerald MG, Bolton R, Taylor KW (1969) Viral antibodies in diabetes mellitus. Br Med J 3:627–630
Gamble DR, Taylor KW (1969) Seasonal incidence of diabetes mellitus. Br Med J 3:631–633
Gianani R, Putnam A, Still T, Yu L, Miao D, Gill RG, Beilke J, Supon P, Valentine A, Iveson A, Dunn S, Eisenbarth GS, Hutton J, Gottlieb P, Wiseman A (2006) Initial results of screening of non-diabetic organ donors for expression of islet autoantibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:1855–1861
Gladisch R, Hofmann W, Waldherr R (1976) Myocarditis and insulitis following coxsackie virus infection. Z Kardiol 65:837–849
Graves PM, Rotbart HA, Nix WA, Pallansch MA, Erlich HA, Norris JM, Hoffman M, Eisenbarth GS, Rewers M (2003) Prospective study of enteroviral infections and development of beta-cell autoimmunity. Diabetes autoimmunity study in the young (DAISY). Diabetes Res Clin Pract 59:51–61
Harkonen T, Puolakkainen M, Sarvas M, Airaksinen U, Hovi T, Roivainen M (2000) Picornavirus proteins share antigenic determinants with heat shock proteins 60/65. J Med Virol 62:383–391
Harkonen T, Lankinen H, Davydova B, Hovi T, Roivainen M (2002) Enterovirus infection can induce immune responses that cross-react with beta-cell autoantigen tyrosine phosphatase IA-2/IAR. J Med Virol 66:340–350
Harkonen T, Paananen A, Lankinen H, Hovi T, Vaarala O, Roivainen M (2003) Enterovirus infection may induce humoral immune response reacting with islet cell autoantigens in humans. J Med Virol 69:426–440
Hermitte L, Vialettes B, Naquet P, Atlan C, Payan MJ, Vague P (1990) Paradoxical lessening of autoimmune processes in non-obese diabetic mice after infection with the diabetogenic variant of encephalomyocarditis virus. Eur J Immunol 20:1297–1303
Hiltunen M, Hyoty H, Knip M, Ilonen J, Reijonen H, Vahasalo P, Roivainen M, Lonnrot M, Leinikki P, Hovi T, Akerblom HK (1997) Islet cell antibody seroconversion in children is temporally associated with enterovirus infections. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. J Infect Dis 175:554–560
Horwitz MS, Bradley LM, Harbertson J, Krahl T, Lee J, Sarvetnick N (1998) Diabetes induced by Coxsackie virus: initiation by bystander damage and not molecular mimicry. Nat Med 4:781–785
Huhn MH, McCartney SA, Lind K, Svedin E, Colonna M, Flodstrom-Tullberg M Melanoma differentiation-associated protein-5 (MDA-5) limits early viral replication but is not essential for the induction of type 1 interferons after Coxsackievirus infection. Virology
Hyoty H, Hiltunen M, Knip M, Laakkonen M, Vahasalo P, Karjalainen J, Koskela P, Roivainen M, Leinikki P, Hovi T et al (1995) A prospective study of the role of coxsackie B and other enterovirus infections in the pathogenesis of IDDM. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. Diabetes 44:652–657
Hyoty H (2004) Environmental causes: viral causes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 33:27–44, viii
Iwasaki T, Monma N, Satodate R, Kawana R, Kurata T (1985) An immunofluorescent study of generalized Coxsackie virus B3 infection in a newborn infant. Acta Pathol Jpn 35:741–748
Jun HS, Kang Y, Notkins AL, Yoon JW (1997) Gain or loss of diabetogenicity resulting from a single point mutation in recombinant encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol 71:9782–9785
Kawashima H, Ihara T, Ioi H, Oana S, Sato S, Kato N, Takami T, Kashiwagi Y, Takekuma K, Hoshika A, Mori T (2004) Enterovirus-related type 1 diabetes mellitus and antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase in Japan. J Infect 49:147–151
Khetsuriani N, Lamonte-Fowlkes A, Oberst S, Pallansch MA (2006) Enterovirus surveillance—United States, 1970–2005. MMWR Surveill Summ 55:1–20
Kim KS, Tracy S, Tapprich W, Bailey J, Lee CK, Kim K, Barry WH, Chapman NM (2005) 5′-Terminal deletions occur in coxsackievirus B3 during replication in murine hearts and cardiac myocyte cultures and correlate with encapsidation of negative-strand viral RNA. J Virol 79:7024–7041
Kruppenbacher JP, Mertens T, Muntefering H, Eggers HJ (1985) Encephalomyocarditis virus and diabetes mellitus: studies on virus mutants in susceptible and non-susceptible mice. J Gen Virol 66(Pt 4):727–732
Lonnrot M, Korpela K, Knip M, Ilonen J, Simell O, Korhonen S, Savola K, Muona P, Simell T, Koskela P, Hyoty H (2000) Enterovirus infection as a risk factor for beta-cell autoimmunity in a prospectively observed birth cohort: the Finnish Diabetes Prediction and Prevention Study. Diabetes 49:1314–1318
Lonnrot M, Salminen K, Knip M, Savola K, Kulmala P, Leinikki P, Hyypia T, Akerblom HK, Hyoty H (2000) Enterovirus RNA in serum is a risk factor for beta-cell autoimmunity and clinical type 1 diabetes: a prospective study. Childhood Diabetes in Finland (DiMe) Study Group. J Med Virol 61:214–220
Makela M, Vaarala O, Hermann R, Salminen K, Vahlberg T, Veijola R, Hyoty H, Knip M, Simell O, Ilonen J (2006) Enteral virus infections in early childhood and an enhanced type 1 diabetes-associated antibody response to dietary insulin. J Autoimmun 27:54–61
Moya-Suri V, Schlosser M, Zimmermann K, Rjasanowski I, Gurtler L, Mentel R (2005) Enterovirus RNA sequences in sera of schoolchildren in the general population and their association with type 1-diabetes-associated autoantibodies. J Med Microbiol 54:879–883
Nairn C, Galbraith DN, Taylor KW, Clements GB (1999) Enterovirus variants in the serum of children at the onset of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 16:509–513
Nejentsev S, Walker N, Riches D, Egholm M, Todd JA (2009) Rare variants of IFIH1, a gene implicated in antiviral responses, protect against type 1 diabetes. Science 324:387–389
Oikarinen M, Tauriainen S, Honkanen T, Oikarinen S, Vuori K, Kaukinen K, Rantala I, Maki M, Hyoty H (2008) Detection of enteroviruses in the intestine of type 1 diabetic patients. Clin Exp Immunol 151:71–75
Oikarinen M, Tauriainen S, Honkanen T, Vuori K, Karhunen P, Vasama-Nolvi C, Oikarinen S, Verbeke C, Blair GE, Rantala I, Ilonen J, Simell O, Knip M, Hyoty H (2008) Analysis of pancreas tissue in a child positive for islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia 51:1796–1802
Parkkonen P, Hyoty H, Koskinen L, Leinikki P (1992) Mumps virus infects beta cells in human fetal islet cell cultures upregulating the expression of HLA class I molecules. Diabetologia 35:63–69
Richardson SJ, Willcox A, Bone AJ, Foulis AK, Morgan NG (2009) The prevalence of enteroviral capsid protein vp1 immunostaining in pancreatic islets in human type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 52:1143–1151
Richer MJ, Horwitz MS (2009) Coxsackievirus infection as an environmental factor in the etiology of type 1 diabetes. Autoimmun Rev 8:611–615
Roivainen M, Ylipaasto P, Savolainen C, Galama J, Hovi T, Otonkoski T (2002) Functional impairment and killing of human beta cells by enteroviruses: the capacity is shared by a wide range of serotypes, but the extent is a characteristic of individual virus strains. Diabetologia 45:693–702
Ross ME, Onodera T, Brown KS, Notkins AL (1976) Virus-induced diabetes mellitus. IV. Genetic and environmental factors influencing the development of diabetes after infection with the M variant of encephalomyocarditis virus. Diabetes 25:190–197
Sadeharju K, Lonnrot M, Kimpimaki T, Savola K, Erkkila S, Kalliokoski T, Savolainen P, Koskela P, Ilonen J, Simell O, Knip M, Hyoty H (2001) Enterovirus antibody levels during the first two years of life in prediabetic autoantibody-positive children. Diabetologia 44:818–823
Sadeharju K, Hamalainen AM, Knip M, Lonnrot M, Koskela P, Virtanen SM, Ilonen J, Akerblom HK, Hyoty H (2003) Enterovirus infections as a risk factor for type I diabetes: virus analyses in a dietary intervention trial. Clin Exp Immunol 132:271–277
Sadeharju K, Knip M, Hiltunen M, Akerblom HK, Hyoty H (2003) The HLA-DR phenotype modulates the humoral immune response to enterovirus antigens. Diabetologia 46:1100–1105
Sadeharju K, Knip M, Virtanen SM, Savilahti E, Tauriainen S, Koskela P, Akerblom HK, Hyoty H (2007) Maternal antibodies in breast milk protect the child from enterovirus infections. Pediatrics 119:941–946
Salminen K, Sadeharju K, Lonnrot M, Vahasalo P, Kupila A, Korhonen S, Ilonen J, Simell O, Knip M, Hyoty H (2003) Enterovirus infections are associated with the induction of beta-cell autoimmunity in a prospective birth cohort study. J Med Virol 69:91–98
Salminen KK, Vuorinen T, Oikarinen S, Helminen M, Simell S, Knip M, Ilonen J, Simell O, Hyoty H (2004) Isolation of enterovirus strains from children with preclinical Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med 21:156–164
Sauter P, Hober D (2009) Mechanisms and results of the antibody-dependent enhancement of viral infections and role in the pathogenesis of coxsackievirus B-induced diseases. Microbes Infect 11:443–451
Sayama K, Imagawa A, Okita K, Uno S, Moriwaki M, Kozawa J, Iwahashi H, Yamagata K, Tamura S, Matsuzawa Y, Hanafusa T, Miyagawa J, Shimomura I (2005) Pancreatic beta and alpha cells are both decreased in patients with fulminant type 1 diabetes: a morphometrical assessment. Diabetologia 48:1560–1564
Seiskari T, Kondrashova A, Viskari H, Kaila M, Haapala AM, Aittoniemi J, Virta M, Hurme M, Uibo R, Knip M, Hyoty H (2007) Allergic sensitization and microbial load—a comparison between Finland and Russian Karelia. Clin Exp Immunol 148:47–52
Shibasaki S, Imagawa A, Tauriainen S, Iino M, Oikarinen M, Abiru H, Tamaki K, Seino H, Nishi K, Takase I, Okada Y, Uno S, Murase-Mishiba Y, Terasaki J, Makino H, Shimomura I, Hyoty H, Hanafusa T (2009) Expression of toll-like receptors in the pancreas of recent-onset fulminant type 1 diabetes. Endocr J
Shigemoto T, Kageyama M, Hirai R, Zheng J, Yoneyama M, Fujita T (2009) Identification of loss of function mutations in human genes encoding RIG-I and MDA5: implications for resistance to type I diabetes. J Biol Chem 284:13348–13354
Smyth DJ, Cooper JD, Bailey R, Field S, Burren O, Smink LJ, Guja C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, Widmer B, Dunger DB, Savage DA, Walker NM, Clayton DG, Todd JA (2006) A genome-wide association study of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a type 1 diabetes locus in the interferon-induced helicase (IFIH1) region. Nat Genet 38:617–619
Tanaka S, Nishida Y, Aida K, Maruyama T, Shimada A, Suzuki M, Shimura H, Takizawa S, Takahashi M, Akiyama D, Arai-Yamashita S, Furuya F, Kawaguchi A, Kaneshige M, Katoh R, Endo T, Kobayashi T (2009) Enterovirus infection, CXC chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10), and CXCR3 circuit: a mechanism of accelerated beta-cell failure in fulminant type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 58:2285–2291
Tauriainen S, Oikarinen M, Keim J, Oikarinen S, Hyöty H, group ns (2009) Detection of enterovirus in pancreatic tissues of cadaver organ donors—results from nPOD study. In: Annual meeting of Immunology of Diabetes Society, Malmö, Sweden
Tracy S, Drescher KM (2007) Coxsackievirus infections and NOD mice: relevant models of protection from, and induction of, type 1 diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1103:143–151
Viskari H, Ludvigsson J, Uibo R, Salur L, Marciulionyte D, Hermann R, Soltesz G, Fuchtenbusch M, Ziegler AG, Kondrashova A, Romanov A, Knip M, Hyoty H (2004) Relationship between the incidence of type 1 diabetes and enterovirus infections in different European populations: results from the EPIVIR project. J Med Virol 72:610–617
Viskari H, Ludvigsson J, Uibo R, Salur L, Marciulionyte D, Hermann R, Soltesz G, Fuchtenbusch M, Ziegler AG, Kondrashova A, Romanov A, Kaplan B, Laron Z, Koskela P, Vesikari T, Huhtala H, Knip M, Hyoty H (2005) Relationship between the incidence of type 1 diabetes and maternal enterovirus antibodies: time trends and geographical variation. Diabetologia 48:1280–1287
Viskari HR, Koskela P, Lonnrot M, Luonuansuu S, Reunanen A, Baer M, Hyoty H (2000) Can enterovirus infections explain the increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes? Diabetes Care 23:414–416
Viskari HR, Roivainen M, Reunanen A, Pitkaniemi J, Sadeharju K, Koskela P, Hovi T, Leinikki P, Vilja P, Tuomilehto J, Hyoty H (2002) Maternal first-trimester enterovirus infection and future risk of type 1 diabetes in the exposed fetus. Diabetes 51:2568–2571
von Herrath M (2009) Diabetes: a virus-gene collaboration. Nature 459:518–519
Woodruff JF (1980) Viral myocarditis. A review. Am J Pathol 101:425–484
Yin H, Berg AK, Tuvemo T, Frisk G (2002) Enterovirus RNA is found in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in a majority of type 1 diabetic children at onset. Diabetes 51:1964–1971
Yin H, Berg AK, Westman J, Hellerstrom C, Frisk G (2002) Complete nucleotide sequence of a Coxsackievirus B-4 strain capable of establishing persistent infection in human pancreatic islet cells: effects on insulin release, proinsulin synthesis, and cell morphology. J Med Virol 68:544–557
Ylipaasto P, Klingel K, Lindberg AM, Otonkoski T, Kandolf R, Hovi T, Roivainen M (2004) Enterovirus infection in human pancreatic islet cells, islet tropism in vivo and receptor involvement in cultured islet beta cells. Diabetologia 47:225–239
Yoon JW, Austin M, Onodera T, Notkins AL (1979) Isolation of a virus from the pancreas of a child with diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med 300:1173–1179
Yoon JW, Notkins AL (1983) Virus-induced diabetes in mice. Metabolism 32:37–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published as part of the Special Issue on Immunopathology of the pancreas in type 1 diabetes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tauriainen, S., Oikarinen, S., Oikarinen, M. et al. Enteroviruses in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Semin Immunopathol 33, 45–55 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-010-0207-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-010-0207-y