Abstract
Glucocorticoids (GC) are lipophilic hormones commonly used as therapeutics in acute and chronic inflammatory disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease due to their attributed anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive actions. Although the adrenal glands are the major source of endogenous GC, there is increasing evidence for the production of extra-adrenal GC in the brain, thymus, skin, vasculature, and the intestine. However, the physiological relevance of extra-adrenal-produced GC remains still ambiguous. Therefore, this review attracts attention to discuss possible biological benefits of extra-adrenal-synthesized GC, especially focusing on the impact of locally synthesized GC in the regulation of intestinal immune responses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahashi I, Kiyono H (1999) Gut as the largest immunologic tissue. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 23:S7–S12. doi:10.1177/014860719902300107
Boirivant M, Amendola A, Butera A (2008) Intestinal microflora and immunoregulation. Mucosal Immunol 1(Suppl 1):S47–S49. doi:10.1038/mi.2008.52
McGuckin MA, Eri R, Simms LA, Florin TH, Radford-Smith G (2009) Intestinal barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:100–113. doi:10.1002/ibd.20539
Lee J, Gonzales-Navajas JM, Raz E (2008) The “polarizing-tolerizing” mechanism of intestinal epithelium: its relevance to colonic homeostasis. Semin Immunopathol 30:3–9. doi:10.1007/s00281-007-0099-7
Coombes JL, Powrie F (2008) Dendritic cells in intestinal immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol 8:435–446. doi:10.1038/nri2335
Magalhaes JG, Tattoli I, Girardin SE (2007) The intestinal epithelial barrier: how to distinguish between the microbial flora and pathogens. Semin Immunol 19:106–115. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2006.12.006
Macpherson AJ (2006) IgA adaptation to the presence of commensal bacteria in the intestine. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 308:117–136. doi:10.1007/3-540-30657-9_5
Artis D (2008) Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol 8:411–420. doi:10.1038/nri2316
Kelly D, Conway S, Aminov R (2005) Commensal gut bacteria: mechanisms of immune modulation. Trends Immunol 26:326–333. doi:10.1016/j.it.2005.04.008
Round JL, Mazmanian SK (2009) The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9(5):313–23
Salzman NH, Underwood MA, Bevins CL (2007) Paneth cells, defensins, and the commensal microbiota: a hypothesis on intimate interplay at the intestinal mucosa. Semin Immunol 19:70–83. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2007.04.002
Izcue A, Coombes JL, Powrie F (2006) Regulatory T cells suppress systemic and mucosal immune activation to control intestinal inflammation. Immunol Rev 212:256–271. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00423.x
Becker C, Fantini MC, Neurath MF (2006) TGF-beta as a T cell regulator in colitis and colon cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:97–106. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.09.004
Powrie F, Correa-Oliveira R, Mauze S, Coffman RL (1994) Regulatory interactions between CD45RBhigh and CD45RBlow CD4+ T cells are important for the balance between protective and pathogenic cell-mediated immunity. J Exp Med 179:589–600. doi:10.1084/jem.179.2.589
Powrie F, Leach MW (1995) Genetic and spontaneous models of inflammatory bowel disease in rodents: evidence for abnormalities in mucosal immune regulation. Ther Immunol 2:115–123
Cima I, Corazza N, Dick B, Fuhrer A, Herren S, Jakob S, Ayuni E, Mueller C, Brunner T (2004) Intestinal epithelial cells synthesize glucocorticoids and regulate T cell activation. J Exp Med 200:1635–1646. doi:10.1084/jem.20031958
Cancedda C, Filaci G, Puppo F, Ghio M, Contini P, Indiveri F (2002) Immune homeostasis requires several biologic factors including glucocorticoid hormones. Ann N Y Acad Sci 966:49–63
Wajchenberg BL, Prestes Cesar F, Okada H, Torres de Toledo e Souza I, Lerario AC, Borghi VC, Malerbi DA, Giurna Filho A, Liberman B, Gianella D (1984) Glucocorticoids, glucose metabolism and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. Adv Exp Med Biol 171:25–44
Berglund M, Thomas JA, Hornquist EH, Hultgren OH (2008) Toll-like receptor cross-hyporesponsiveness is functional in interleukin-1-receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1)-deficient macrophages: differential role played by IRAK-1 in regulation of tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-10 production. Scand J Immunol 67:473–479. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02096.x
Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G (1995) Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell 83:851–857. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90201-5
Kunicka JE, Talle MA, Denhardt GH, Brown M, Prince LA, Goldstein G (1993) Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of production of multiple lymphokines by in vivo administration of dexamethasone. Cell Immunol 149:39–49. doi:10.1006/cimm.1993.1134
Almawi WY, Beyhum HN, Rahme AA, Rieder MJ (1996) Regulation of cytokine and cytokine receptor expression by glucocorticoids. J Leukoc Biol 60:563–572
Unlap T, Jope RS (1995) Inhibition of NFkB DNA binding activity by glucocorticoids in rat brain. Neurosci Lett 198:41–44. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(95)11963-W
Schaaf MJ, Cidlowski JA (2002) Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action and resistance. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 83:37–48. doi:10.1016/S0960-0760(02)00263-7
De Bosscher K, Vanden Berghe W, Haegeman G (2000) Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory action and of immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: negative interference of activated glucocorticoid receptor with transcription factors. J Neuroimmunol 109:16–22. doi:10.1016/S0165-5728(00)00297-6
Scheinman RI, Gualberto A, Jewell CM, Cidlowski JA, Baldwin AS Jr (1995) Characterization of mechanisms involved in transrepression of NF-kappa B by activated glucocorticoid receptors. Mol Cell Biol 15:943–953
Karin M (1998) New twists in gene regulation by glucocorticoid receptor: is DNA binding dispensable? Cell 93:487–490. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81177-0
Amsterdam A, Tajima K, Sasson R (2002) Cell-specific regulation of apoptosis by glucocorticoids: implication to their anti-inflammatory action. Biochem Pharmacol 64:843–850. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(02)01147-4
Amsterdam A, Sasson R (2002) The anti-inflammatory action of glucocorticoids is mediated by cell type specific regulation of apoptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 189:1–9. doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(01)00722-5
Iglesias-Serret D, de Frias M, Santidrian AF, Coll-Mulet L, Cosialls AM, Barragan M, Domingo A, Gil J, Pons G (2007) Regulation of the proapoptotic BH3-only protein BIM by glucocorticoids, survival signals and proteasome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 21:281–287. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404483
Erlacher M, Michalak EM, Kelly PN, Labi V, Niederegger H, Coultas L, Adams JM, Strasser A, Villunger A (2005) BH3-only proteins Puma and Bim are rate-limiting for gamma-radiation- and glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of lymphoid cells in vivo. Blood 106:4131–4138. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-04-1595
Wang Z, Malone MH, He H, McColl KS, Distelhorst CW (2003) Microarray analysis uncovers the induction of the proapoptotic BH3-only protein Bim in multiple models of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278:23861–23867. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301843200
Cupps TR, Fauci AS (1982) Corticosteroid-mediated immunoregulation in man. Immunol Rev 65:133–155. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.1982.tb00431.x
Perretti M, D'Acquisto F (2009) Annexin A1 and glucocorticoids as effectors of the resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 9:62–70. doi:10.1038/nri2470
Kaufman DB, Shapiro R, Lucey MR, Cherikh WS, Bustami RT, Dyke DB (2004) Immunosuppression: practice and trends. Am J Transplant 4(Suppl 9):38–53. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6135.2004.00397.x
Di Munno O, Delle Sedie A (2008) Effects of glucocorticoid treatment on focal and systemic bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. J Endocrinol Invest 31:43–47
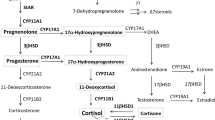
Simpson ER (1979) Cholesterol side-chain cleavage, cytochrome P450, and the control of steroidogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 13:213–227. doi:10.1016/0303-7207(79)90082-0
Bornstein SR, Ehrhart-Bornstein M (2000) Basic and clinical aspects of intraadrenal regulation of steroidogenesis. Z Rheumatol 59 Suppl 2: II:12–17
Wang W, Zhang C, Marimuthu A, Krupka HI, Tabrizizad M, Shelloe R, Mehra U, Eng K, Nguyen H, Settachatgul C, Powell B, Milburn MV, West BL (2005) The crystal structures of human steroidogenic factor-1 and liver receptor homologue-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:7505–7510. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409482102
Arlt W, Stewart PM (2005) Adrenal corticosteroid biosynthesis, metabolism, and action. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 34:293–313. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2005.01.002 viii
Buckingham JC (2006) Glucocorticoids: exemplars of multi-tasking. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S258–S268. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp. 0706456
Meeking S (2007) Treatment of acute adrenal insufficiency. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract 22:36–39. doi:10.1053/j.ctsap. 2007.02.006
Gonzalo JA, Gonzalez-Garcia A, Martinez C, Kroemer G (1993) Glucocorticoid-mediated control of the activation and clonal deletion of peripheral T cells in vivo. J Exp Med 177:1239–1246. doi:10.1084/jem.177.5.1239
Payne AH, Hales DB (2004) Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones. Endocr Rev 25:947–970. doi:10.1210/er.2003-0030
Annane D (2005) Glucocorticoids in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin Crit Care 11:449–453. doi:10.1097/01.ccx.0000176691.95562.43
Vacchio MS, Ashwell JD (1997) Thymus-derived glucocorticoids regulate antigen-specific positive selection. J Exp Med 185:2033–2038. doi:10.1084/jem.185.11.2033
Vacchio MS, Lee JY, Ashwell JD (1999) Thymus-derived glucocorticoids set the thresholds for thymocyte selection by inhibiting TCR-mediated thymocyte activation. J Immunol 163:1327–1333
Lechner O, Wiegers GJ, Oliveira-Dos-Santos AJ, Dietrich H, Recheis H, Waterman M, Boyd R, Wick G (2000) Glucocorticoid production in the murine thymus. Eur J Immunol 30:337–346. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200002)30:2<337::AID-IMMU337>3.0.CO;2-L
Pazirandeh A, Xue Y, Rafter I, Sjovall J, Jondal M, Okret S (1999) Paracrine glucocorticoid activity produced by mouse thymic epithelial cells. FASEB J 13:893–901
Davies E, MacKenzie SM (2003) Extra-adrenal production of corticosteroids. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:437–445. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1681.2003.03867.x
Keeney DS, Jenkins CM, Waterman MR (1995) Developmentally regulated expression of adrenal 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P450 in the mouse embryo. Endocrinology 136:4872–4879. doi:10.1210/en.136.11.4872
Brunner T, Arnold D, Wasem C, Herren S, Frutschi C (2001) Regulation of cell death and survival in intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ 8:706–714. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400854
Atanasov AG, Leiser D, Roesselet C, Noti M, Corazza N, Schoonjans K, Brunner T (2008) Cell cycle-dependent regulation of extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in murine intestinal epithelial cells. FASEB J 22:4117–4125. doi:10.1096/fj.08-114157
Mueller M, Cima I, Noti M, Fuhrer A, Jakob S, Dubuquoy L, Schoonjans K, Brunner T (2006) The nuclear receptor LRH-1 critically regulates extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in the intestine. J Exp Med 203:2057–2062. doi:10.1084/jem.20060357
Mueller M, Atanasov A, Cima I, Corazza N, Schoonjans K, Brunner T (2007) Differential regulation of glucocorticoid synthesis in murine intestinal epithelial versus adrenocortical cell lines. Endocrinology 148:1445–1453. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0591
Val P, Lefrancois-Martinez AM, Veyssiere G, Martinez A (2003) SF-1 a key player in the development and differentiation of steroidogenic tissues. Nucl Recept 1:8. doi:10.1186/1478-1336-1-8
Bland ML, Jamieson CA, Akana SF, Bornstein SR, Eisenhofer G, Dallman MF, Ingraham HA (2000) Haploinsufficiency of steroidogenic factor-1 in mice disrupts adrenal development leading to an impaired stress response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:14488–14493. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.26.14488
Fayard E, Auwerx J, Schoonjans K (2004) LRH-1: an orphan nuclear receptor involved in development, metabolism and steroidogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 14:250–260. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2004.03.008
Saxena D, Escamilla-Hernandez R, Little-Ihrig L, Zeleznik AJ (2007) Liver receptor homolog-1 and steroidogenic factor-1 have similar actions on rat granulosa cell steroidogenesis. Endocrinology 148:726–734. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0108
Labelle-Dumais C, Jacob-Wagner M, Pare JF, Belanger L, Dufort D (2006) Nuclear receptor NR5A2 is required for proper primitive streak morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 235:3359–3369. doi:10.1002/dvdy.20996
Coste A, Dubuquoy L, Barnouin R, Annicotte JS, Magnier B, Notti M, Corazza N, Antal MC, Metzger D, Desreumaux P, Brunner T, Auwerx J, Schoonjans K (2007) LRH-1-mediated glucocorticoid synthesis in enterocytes protects against inflammatory bowel disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13098–13103. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702440104
Boivin MA, Ye D, Kennedy JC, Al-Sadi R, Shepela C, Ma TY (2007) Mechanism of glucocorticoid regulation of the intestinal tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292:G590–G598. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00252.2006
Harke N, Leers J, Kietz S, Drenckhahn D, Forster C (2008) Glucocorticoids regulate the human occludin gene through a single imperfect palindromic glucocorticoid response element. Mol Cell Endocrinol 295:39–47. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2008.08.011
Kimura T (1986) Transduction of ACTH signal from plasma membrane to mitochondria in adrenocortical steroidogenesis. Effects of peptide, phospholipid, and calcium. J Steroid Biochem 25:711–716. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(86)90299-2
Watanabe N, Inoue H, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1994) Regulatory mechanisms of cAMP-dependent and cell-specific expression of human steroidogenic cytochrome P450scc (CYP11A1) gene. Eur J Biochem 222:825–834. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18929.x
Rosenberg D, Groussin L, Bertagna X, Bertherat J (2002) cAMP pathway alterations from the cell surface to the nucleus in adrenocortical tumors. Endocr Res 28:765–775. doi:10.1081/ERC-120017071
Burendahl S, Treuter E, Nilsson L (2008) Molecular dynamics simulations of human LRH-1: the impact of ligand binding in a constitutively active nuclear receptor. Biochemistry 47:5205–5215. doi:10.1021/bi7025084
Kim YS, Ryu JH, Han SJ, Choi KH, Nam KB, Jang IH, Lemaitre B, Brey PT, Lee WJ (2000) Gram-negative bacteria-binding protein, a pattern recognition receptor for lipopolysaccharide and beta-1, 3-glucan that mediates the signaling for the induction of innate immune genes in Drosophila melanogaster cells. J Biol Chem 275:32721–32727. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003934200
Lee YK, Choi YH, Chua S, Park YJ, Moore DD (2006) Phosphorylation of the hinge domain of the nuclear hormone receptor LRH-1 stimulates transactivation. J Biol Chem 281:7850–7855. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509115200
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby C, Brennan T, Wendling O, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Thomas W, Auwerx J, Schoonjans K (2004) Synergy between LRH-1 and beta-catenin induces G1 cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell 15:499–509. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.07.009
Schoonjans K, Dubuquoy L, Mebis J, Fayard E, Wendling O, Haby C, Geboes K, Auwerx J (2005) Liver receptor homolog 1 contributes to intestinal tumor formation through effects on cell cycle and inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:2058–2062. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409756102
Rutgeerts P (1998) Medical therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion 59:453–469. doi:10.1159/000007523
Cerny A, Chisari FV (1999) Pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis C: immunological features of hepatic injury and viral persistence. Hepatology 30:595–601. doi:10.1002/hep. 510300312
Van Assche G, Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P (2008) Optimizing treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases with biologic agents. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 10:591–596. doi:10.1007/s11894-008-0107-7
Neurath MF, Fuss I, Pasparakis M, Alexopoulou L, Haralambous S, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Strober W, Kollias G (1997) Predominant pathogenic role of tumor necrosis factor in experimental colitis in mice. Eur J Immunol 27:1743–1750. doi:10.1002/eji.1830270722
Naito Y, Takagi T, Handa O, Ishikawa T, Nakagawa S, Yamaguchi T, Yoshida N, Minami M, Kita M, Imanishi J, Yoshikawa T (2003) Enhanced intestinal inflammation induced by dextran sulfate sodium in tumor necrosis factor-alpha deficient mice. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:560–569. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.03034.x
Ebach DR, Newberry R, Stenson WF (2005) Differential role of tumor necrosis factor receptors in TNBS colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11:533–540. doi:10.1097/01.MIB.0000163698.34592.30
Rutgeerts P, Vermeire S, Van Assche G (2009) Biological therapies for inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 136:1182–1197. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.02.001
Kassiotis G, Kollias G (2001) Uncoupling the proinflammatory from the immunosuppressive properties of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) at the p55 TNF receptor level: implications for pathogenesis and therapy of autoimmune demyelination. J Exp Med 193:427–434. doi:10.1084/jem.193.4.427
Zheng L, Fisher G, Miller RE, Peschon J, Lynch DH, Lenardo MJ (1995) Induction of apoptosis in mature T cells by tumour necrosis factor. Nature 377:348–351. doi:10.1038/377348a0
Zhou T, Edwards CK III, Yang P, Wang Z, Bluethmann H, Mountz JD (1996) Greatly accelerated lymphadenopathy and autoimmune disease in lpr mice lacking tumor necrosis factor receptor I. J Immunol 156:2661–2665
Matthys P, Billiau A (1997) Cytokines and cachexia. Nutrition 13:763–770. doi:10.1016/S0899-9007(97)00185-8
Clayburgh DR, Barrett TA, Tang Y, Meddings JB, Van Eldik LJ, Watterson DM, Clarke LL, Mrsny RJ, Turner JR (2005) Epithelial myosin light chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. J Clin Invest 115:2702–2715. doi:10.1172/JCI24970
Rubin EM, Raptopoulos VD (2005) Images in clinical medicine. The virtual apple core of a colonic carcinoma. N Engl J Med 352:2733. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm040235
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation, the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America, and Oncosuisse. D.S. is recipient of a fellowship from the Swiss National Science Foundation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noti, M., Sidler, D. & Brunner, T. Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in the intestinal epithelium: more than a drop in the ocean?. Semin Immunopathol 31, 237–248 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-009-0159-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-009-0159-2