Abstract
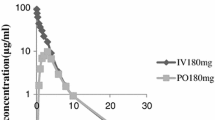
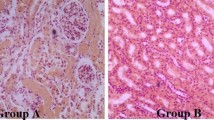
Plasma lonidamine concentration and toxicity were investigated in dogs receiving 100, 200, 400, 800, 1200 mg/m2 orally twice daily for 30 days and in dogs receiving single intravenous doses of 200, 400, 800, 1200 mg/m2. Physical or laboratory signs of toxicity were not observed in dogs receiving oral lonidamine, but severe vomiting and signs of acute hepatic and pancreatic toxicity were observed in dogs receiving intravenous doses that exceeded 400 mg/m2. The area under the lonidamine concentration versus time curve (AUC) in dogs receiving 200, 400, and 800 mg/m2 of lonidamine intravenously was a 1.8-, 3.3-, and 8.7-fold higher than in dogs receiving oral lonidamine. This suggests that the bioavailability of oral lonidamine may be limited. However, centrilobular hepatocellular swelling and vacuolation were observed in dogs receiving oral lonidamine. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity was increased in dogs receiving intra-venous lonidamine. These findings suggest that lonidamine is hepatotoxic in dogs. However, serum ALT was increased in only 1/4 dogs receiving 400 mg/m2 of lonidamine intravenously and plasma concentration were within the range capable of sensitizing hyperthermia and chemotherapy. Therefore, this dose and route appears to be a viable and controllable method for prospective quantification of lonidamine interaction with systemic chemotherapy and/or hyperthermia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 October 1993 /Accepted: 9 October 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Price, G., Page, R., Riviere, J. et al. Pharmacokinetics and toxicity of oral and intravenous lonidamine in dogs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 38, 129–135 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050460
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050460