Abstract
Background
Nivolumab is a monoclonal antibody directed against programmed death-1 that has been shown to improve survival in patients with metastatic melanoma. However, the efficacy of nivolumab and other agents in melanoma remains limited. The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of retreatment with nivolumab in metastatic melanoma patients who previously progressed on nivolumab.
Patients and methods
A retrospective review was performed on eight consecutive metastatic melanoma patients retreated with nivolumab who progressed on previous nivolumab. These patients received nivolumab 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks. Best responses to each treatment were assessed using RECIST 1.1.
Results
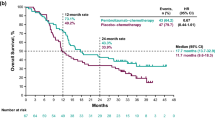
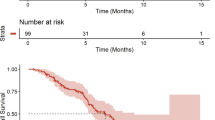
Of eight metastatic melanoma patients, three patients received chemotherapy before first nivolumab. The median first nivolumab treatment period was 4.1 months. During first nivolumab, 3 (37.5%) patients achieved a partial response and 3 (37.5%) patients achieved stable disease as their best response. First nivolumab was discontinued due to disease progression in seven patients and grade 3 colitis in 1 patient. Patients were subsequently treated with ipilimumab (n = 6), vemurafenib (n = 1), or no other medical treatment (n = 1). The median treatment period between first and second nivolumab was 3.0 months. Four patients received radiation therapy between first and second nivolumab. The median second nivolumab treatment period was 4.3 months. Among the eight patients who received second nivolumab, 2 (25%) patients achieved a partial response and 3 (37.5%) patients achieved stable disease as their best response. Second nivolumab was discontinued due to disease progression in seven patients. One patient continues to receive second nivolumab. Among the four patients treated with ipilimumab and radiotherapy between first and second nivolumab, the response rate was 50% and the disease control rate was 75%.
Conclusions
This study showed that retreatment with nivolumab is an option for select metastatic melanoma patients after previous nivolumab treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB,et al (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723
Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, Hodi FS, Gutzmer R, Neyns B et al (2015) Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 16:375–384
Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, Dutriaux C, Maio M, Mortier L et al (2015) Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med 372:320–330
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Cowey CL, Lao CD et al (2015) Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med 373:23–34
Weber JS, Gibney G, Sullivan RJ, Sosman JA, Slingluff CL Jr, Lawrence DP et al (2016) Sequential administration of nivolumab and ipilimumab with a planned switch in patients with advanced melanoma (CheckMate 064): an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 17:943–955
Lebbé C, Weber JS, Maio M, Neyns B, Harmankaya K, Hamid O et al (2014) Survival follow-up and ipilimumab retreatment of patients with advanced melanoma who received ipilimumab in prior phase II studies. Ann Oncol 25:2277–2284
Chiarion-Sileni V, Pigozzo J, Ascierto PA, Simeone E, Maio M, Calabrò L et al (2014) Ipilimumab retreatment in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma: the expanded access programme in Italy. Br J Cancer 110:1721–1726
Robert C, Schadendorf D, Messina M, Hodi FS, O’Day S,et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of retreatment with ipilimumab in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma who progressed after initially achieving disease control. Clin Cancer Res 19:2232–2239
Amann VC, Hoffmann D, Mangana J, Dummer R, Goldinger SM (2017) Successful retreatment with combined BRAF/MEK inhibition in metastatic BRAFV600-mutated melanoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. doi:10.1111/jdv.14268
Blasig H, Bender C, Hassel JC, Eigentler TK, Sachse MM, Hiernickel J et al (2017) Reinduction of PD1-inhibitor therapy: first experience in eight patients with metastatic melanoma. Melanoma Res 27:321–325
Reits EA, Hodge JW, Herberts CA, Groothuis TA, Chakraborty M, Wansley EK et al (2006) Radiation modulates the peptide repertoire, enhances MHC class I expression, and induces successful antitumor immunotherapy. J Exp Med 203:1259–1271
Burnette BC, Liang H, Lee Y, Chlewicki L, Khodarev NN, Weichselbaum RR et al (2011) The efficacy of radiotherapy relies upon induction of type i interferon-dependent innate and adaptive immunity. Cancer Res 71:2488–2496
Lugade AA, Moran JP, Gerber SA, Rose RC, Frelinger JG, Lord EM (2005) Local radiation therapy of B16 melanoma tumors increases the generation of tumor antigen-specific effector cells that traffic to the tumor. J Immunol 174:7516–7523
Deng L, Liang H, Burnette B, Beckett M, Darga T, Weichselbaum RR et al (2014) Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J Clin Invest 124:687–695
Qin R, Olson A, Singh B et al (2016) Safety and efficacy of radiation therapy in advanced melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96:72–77
Koller KM, Mackley HB, Liu J et al (2017) Improved survival and complete response rates in patients with advanced melanoma treated with concurrent ipilimumab and radiotherapy versus ipilimumab alone. Cancer Biol Ther 18:36–42
Zak KM, Grudnik P, Magiera K et al (2017) Structural biology of the immune checkpoint receptor PD-1 and its ligands PD-L1/PD-L2. Structure 25:1163–1174
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375:1823–1833
Gettinger S, Rizvi NA, Chow LQ et al (2016) Nivolumab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 34:2980–2987
D’Angelo SP, Larkin J, Sosman JA, Lebbé C, Brady B, Neyns B et al (2017) Efficacy and safety of nivolumab alone or in combination with ipilimumab in patients with mucosal melanoma: a pooled analysis. J Clin Oncol 35:226–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
None of the authors have financial disclosures or funding support.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have conflicts of interest to declare.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nomura, M., Otsuka, A., Kondo, T. et al. Efficacy and safety of retreatment with nivolumab in metastatic melanoma patients previously treated with nivolumab. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80, 999–1004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3444-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3444-0