Abstract
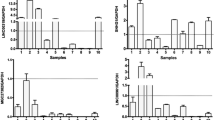
Lung cancer, with the highest morbidity and second highest death rates, is one of the most common cancers in both males and females worldwide. Lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) is the main lung cancer class. KCNQ1 Opposite Strand/Antisense Transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) gene is an lncRNA which had been reported high-expression in colorectal cancer. In this study, the expression of KCNQ1OT1 was confirmed to be highly expressed in LAD tissues and cells contrast to control tissues and cells, and high KCNQ1OT1 expression correlated to malignant behaviors of LAD, including big tumor size, poor differentiation, positive lymphatic metastasis and high TNM stages. The transfection of si-KCNQ1OT1 could effectually knockdown the expression of KCNQ1OT1 in A549 and A549/PA cells. The KCNQ1OT1 knockdown depressed the proliferation and invasion of A549 cells, and advanced cellular apoptosis of A549 cells. The expression of KCNQ1OT1 in LAD patients insensitive to paclitaxel was much higher than that in LAD patients sensitive to paclitaxel; the KCNQ1OT1 expression in A549/PA cells was also much higher than that in control A549 cells. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of paclitaxel in A549/PA cells was depressed by KCNQ1OT1 knockdown, chemoresistance of A549/PA cells was inhibited significantly. KCNQ1OT1 knockdown also depressed the expression of multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1) protein in A549/PA cells. In summary, lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 was highly expressed in LAD and functioned as a potential oncogene to inhibit malignancy and chemoresistance of LAD cells, which might be a novel potential therapeutic target for LAD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 5(2):87–108
Morgensztern D, Ng SH, Gao F, Govindan R (2010) Trends in stage distribution for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a National Cancer Database Survey. J Thorac Oncol 5(1):29–33
Carrizosa DR, Gold KA (2015) New strategies in immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 4(5):553–559
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (2009) Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet 10(3):155–159
Lian Y, Cai Z, Gong H, Xue S, Wu D, Wang K (2016) HOTTIP: a critical oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers. Mol BioSyst 12(11):3247–3253
Ma C, Shi X, Zhu Q, Li Q, Liu Y, Yao Y, Song Y (2016) The growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5): a pivotal tumor suppressor long noncoding RNA in human cancers. Tumour Biol 37(2):1437–1444
Wu L, Jin L, Zhang W, Zhang L (2016) Roles of long non-coding RNA CCAT2 in cervical cancer cell growth and apoptosis. Med Sci Monit 22:875–879
Pawar K, Hanisch C, Palma Vera SE, Einspanier R, Sharbati S (2016) Down regulated lncRNA MEG3 eliminates mycobacteria in macrophages via autophagy. Sci Rep 6:19416
Shang C, Guo Y, Hong Y, Xue YX (2016) Long non-coding RNA TUSC7, a target of miR-23b, plays tumor-suppressing roles in human gliomas. Front Cell Neurosci 10:235
Sunamura N, Ohira T, Kataoka M, Inaoka D, Tanabe H, Nakayama Y, Oshimura M, Kugoh H (2016) Regulation of functional KCNQ1OT1 lncRNA by β-catenin. Sci Rep 6:20690
Gong W, Zheng J, Liu X, Liu Y, Guo J, Gao Y, Tao W, Chen J, Li Z, Ma J, Xue Y (2017) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 restrained glioma cells’ malignancy by activating miR-370/CCNE2 axis. Front Cell Neurosci 22(11):84. doi:10.3389/fncel.2017.00084
Yan J, Dang Y, Liu S, Zhang Y, Zhang G (2016) LncRNA HOTAIR promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by targeting miR-126 to activate the PI3 K/AKT/MRP1 genes. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-016-5448-5
Shang C, Guo Y, Zhang J, Huang B (2016) Silence of long noncoding RNA UCA1 inhibits malignant proliferation and chemotherapy resistance to adriamycin in gastric cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 7(5):1061–1067
Liu G, Xiang T, Wu QF, Wang WX (2016) Long Noncoding RNA H19-Derived miR-675 Enhances Proliferation and Invasion via RUNX1 in Gastric Cancer Cells. Oncol Res 23(3):99–107
Liu J, Wan L, Lu K, Sun M, Pan X, Zhang P, Lu B, Liu G, Wang Z (2015) The long noncoding RNA MEG3 contributes to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One 10(5):e0114586
Mitsuya K, Meguro M, Lee MP, Katoh M, Schulz TC, Kugoh H, Yoshida MA, Niikawa N, Feinberg AP, Oshimura M (1999) LIT1, an imprinted antisense RNA in the human KvLQT1 locus identified by screening for differentially expressed transcripts using monochromosomal hybrids. Hum Mol Genet 8(7):1209–1217
Deng H, Zhang J, Shi J, Guo Z, He C, Ding L, Tang JH, Hou Y (2016) Role of long non-coding RNA in tumor drug resistance. Tumour Biol 37(9):11623–11631
Wang Q, Cheng N, Li X, Pan H, Li C, Ren S, Su C, Cai W, Zhao C, Zhang L, Zhou C (2016) Correlation of long non-coding RNA H19 expression with cisplatin-resistance and clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.13708 (Epub ahead of print)
Shang C, Guo Y, Zhang H, Xue YX (2016) Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is a prognostic biomarker and inhibits chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 77(3):507–513
Liu Z, Sun M, Lu K, Liu J, Zhang M, Wu W, De W, Wang Z, Wang R (2013) The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via downregulation of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. PLoS One 8(10):e77293
Mei Y, Si J, Wang Y, Huang Z, Zhu H, Feng S, Wu X, Wu L (2017) Long noncoding RNA GAS5 suppresses tumorigenesis by inhibiting miR-23a 5 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Res. doi:10.3727/096504016X14822800040451 (Epub ahead of print)
Silva R, Vilas-Boas V, Carmo H, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Carvalho F, de Lourdes Bastos M, Remião F (2015) Modulation of P-glycoprotein efflux pump: induction and activation as a therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol Ther 149:1–123
Munoz JL, Walker ND, Scotto KW, Rameshwar P (2015) Temozolomide competes for P-glycoprotein and contributes to chemoresistance in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett 367(1):69–75
Tsang WP, Kwok TT (2007) Riboregulator H19 induction of MDR1-associated drug resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene 26(33):4877–4881
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Doctoral Research Initiation Foundation of Liaoning Province (201601121).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with Ethics Committees of Dalian Medical University and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, K., Xu, R., Huang, J. et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 depressed chemoresistance to paclitaxel in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80, 243–250 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3356-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3356-z