Abstract
Purpose
RG7112, the first selective small-molecule MDM2 antagonist in clinical testing, is a non-genotoxic oral p53 activator. To optimize its dose and schedule, a number of clinical pharmacology characteristics were explored in this multicenter trial in patients with advanced solid tumors.
Method
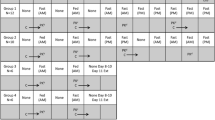
In part 1, the impact of high-energy/high-fat meal and formulations (crystalline and amorphous) on relative bioavailability was examined in single-dose crossover designs. In part 2, schedule optimization (4 schedules of drug administration under fasting condition and 2 cohorts with liquid supplementation) was investigated in parallel, dose escalation designs. Clinical endpoints were pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD) including MIC-1 elevation and platelet reduction, and safety/tolerability.
Results
With a single-dose treatment, a high-fat/high-energy meal and a new formulation under fasting condition, respectively, enhanced overall bioavailability of RG7112 slightly over twofold. Following multiple-dose administrations, all four schedules yielded the comparable per-cycle (28-d) exposure (AUC), as designed; liquid supplements also enhanced bioavailability. High-dose treatments of consecutive daily dosing for 5 and 3 days resulted in higher on-treatment-day exposure to RG7112 than both weekly and low-dose/long-duration (20-day) daily schedules. Serum MIC-1 and blood platelet profiles showed similar patterns to those of PK when the clinical pharmacology conditions were varied, suggesting the relative importance of treatment-day exposure than overall per-cycle AUC.
Conclusion
Food (both high-fat and low-fat meals) and new formulation enhanced bioavailability. High-dose consecutive daily treatment for 3–5 days is superior to weekly and low-dose/long-duration (20-day) daily schedules in yielding the sufficiently high drug exposure and PD effects potentially required for cancer treatment efficacy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chene P (2003) Inhibiting the p53-MDM2 interaction: an important target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:102–109
Vu B, Wovkulich P, Pizzolato G, Lovey A, Ding Q, Jiang N, Liu J-J, Zhao C, Glenn K, Wen Y, Tovar C, Packman K, Vassilev L, Graves B (2013) Discovery of RG7112: a small-molecule MDM2 inhibitor in clinical development. ACS Med Chem Lett 4:466–469
Tovar C, Graves B, Packman K, Filipovic Z, Higgins B, Xia M et al (2013) MDM2 small-molecule antagonist RG7112 activates p53 signaling and regresses human tumors in preclinical cancer models. Cancer Res 73:2587–2597
Higgins B, Glenn K, Walz A, Tovar C, Filipovic Z, Hussain S, Lee E, Kolinsky K, Tannu S, Adames V, Garrido R, Linn M, Meille C, Heimbrook D, Vassilev L, Packman K (2014) Preclinical optimization of MDM2 antagonist scheduling for cancer treatment by using a model-based approach. Clin Cancer Res 20:3742–3752
Kurzrock R, Blay J-Y, Bui BN, Wagner AJ, Maki RG, Schwartz GK, Patnaik A, Gore L, Wu L, Vassilev LT, Ding M, Geho D, Zhi J, Middleton S, Nichols GL (2012) A phase I study of MDM2 antagonist RG7112 in patients with relapsed/refractory solid tumors. ASCO 2012 Abstract
Ray-Coquard IL, Blay J-Y, Italiano A, Le Cesne A, Penel N, Zhi J, Heil F, Rueger R, Graves B, Ding M, Geho D, Middleton SA, Vassilev L, Nichols GL, Bui BN (2012) Effect of the MDM2 antagonist RG7112 on the p53 pathway in patients with MDM2-amplified well-differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma: an exploratory proof-of mechanism study. Lancet Oncol 13(11):1133–1140
Iancu-Rubin C, Mosoyan G, Glenn K, Gordon RE, Nichols GL, Hoffman R (2014) Activation of p53 by the MDM2 inhibitor RG7112 impairs thrombopoiesis. Exp Hematol 42(2):137–145
Revised 24 Jul 2009, Source www torsades org
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge key contributions from Roche colleagues, investigational site staff, and patient volunteers.
Financial support
The study was sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche. The funding sources had no role in the design, analysis, and interpretation of the results, and thus, the authors were independent from the funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
GN, SM, AB, NS, RP, and JZ are employees of Hoffmann-La Roche. All other authors report no potential conflict of interest for the work under consideration.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patnaik, A., Tolcher, A., Beeram, M. et al. Clinical pharmacology characterization of RG7112, an MDM2 antagonist, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76, 587–595 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2830-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2830-8