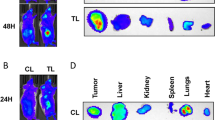
Abstract
Purpose
SF1126 is a vascular-targeted pan-PI-3K inhibitor prodrug with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity and has completed phase I clinical trial in solid tumors and B-cell malignancies. In this study, we investigated the effect of SF1126 on hypoxic HIF-1α/HIF-2α stability as well as on antitumor and/or antiangiogenic activity in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) models in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
The effect of SF1126 on hypoxic HIF-1α/HIF-2α protein stability, antitumor and antiangiogenic activity was studied on VHL-null (786-0) and VHL-WT (Caki) RCC cells.
Results
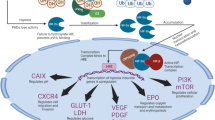
Our data demonstrate that SF1126 treatment abrogates the stabilization of HIF-2α in 786-0 (VHL-mutated) RCC cell line under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Similarly, hypoxic stabilization of HIF-1α and its activity were also suppressed following SF1126 treatment in Caki cell line (VHL-WT). Herein, we provide mechanistic evidence that HIF-2α can be degraded in cytoplasm under hypoxic conditions via the 26S proteasome and that MDM2 is the E3 ligase which induces the hypoxic degradation of HIF-2α in PI-3K-dependent manner in VHL-deficient RCC cells. Moreover, SF1126 administered to RCC-xenografted mice at 25 mg/kg/dose subcutaneously three times per week for 3 weeks results in marked inhibition of tumor growth (>90 % inhibition) (P < 0.05). Consistent with SF1126 treatment’s effects on HIF-1α/HIF-2α, microvessel density analysis of Caki and 786-0 tumor tissues demonstrated that SF1126 has potent antiangiogenic activity in vivo. Finally, SF1126 caused a profound inhibition of integrin-mediated migration and blocked the integrin-induced conversion of GDP-Rac1 to its GTP-bound active state.
Conclusions
These results validate the in vivo efficacy of SF1126 as a clinically viable antiangiogenic, pan-PI-3K inhibitor prodrug for phase II clinical trials in the treatment of RCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL, Fraumeni JF Jr (1999) Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States. JAMA 281(17):1628–1631
Hock LM, Lynch J, Balaji KC (2002) Increasing incidence of all stages of kidney cancer in the last 2 decades in the United States: an analysis of surveillance, epidemiology and end results program data. J Urol 167(1):57–60
Maranchie JK, Zhan Y (2005) Nox4 is critical for hypoxia-inducible factor 2-alpha transcriptional activity in von Hippel–Lindau-deficient renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 65(20):9190–9193. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2105
Brauch H, Weirich G, Brieger J, Glavac D, Rodl H, Eichinger M, Feurer M, Weidt E, Puranakanitstha C, Neuhaus C, Pomer S, Brenner W, Schirmacher P, Storkel S, Rotter M, Masera A, Gugeler N, Decker HJ (2000) VHL alterations in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma: association with advanced tumor stage and a novel hot spot mutation. Cancer Res 60(7):1942–1948
Krieg M, Haas R, Brauch H, Acker T, Flamme I, Plate KH (2000) Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha under normoxic conditions in renal carcinoma cells by von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor gene loss of function. Oncogene 19(48):5435–5443. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203938
Lidgren A, Hedberg Y, Grankvist K, Rasmuson T, Vasko J, Ljungberg B (2005) The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is a favorable independent prognostic factor in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 11(3):1129–1135
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, von Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel–Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292(5516):468–472. doi:10.1126/science.1059796
Kaelin WG Jr (2002) Molecular basis of the VHL hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat Rev Cancer 2(9):673–682. doi:10.1038/nrc885
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399(6733):271–275. doi:10.1038/20459
Ohh M, Park CW, Ivan M, Hoffman MA, Kim TY, Huang LE, Pavletich N, Chau V, Kaelin WG (2000) Ubiquitination of hypoxia-inducible factor requires direct binding to the beta-domain of the von Hippel–Lindau protein. Nat Cell Biol 2(7):423–427. doi:10.1038/35017054
Smaldone MC, Maranchie JK (2009) Clinical implications of hypoxia inducible factor in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol 27(3):238–245. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2007.12.001
Sufan RI, Jewett MA, Ohh M (2004) The role of von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor protein and hypoxia in renal clear cell carcinoma. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287(1):F1–F6. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00424.2003
Raval RR, Lau KW, Tran MG, Sowter HM, Mandriota SJ, Li JL, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Harris AL, Ratcliffe PJ (2005) Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel–Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Biol 25(13):5675–5686. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.13.5675-5686.2005
Maranchie JK, Vasselli JR, Riss J, Bonifacino JS, Linehan WM, Klausner RD (2002) The contribution of VHL substrate binding and HIF1-alpha to the phenotype of VHL loss in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 1(3):247–255
Kondo K, Klco J, Nakamura E, Lechpammer M, Kaelin WG Jr (2002) Inhibition of HIF is necessary for tumor suppression by the von Hippel–Lindau protein. Cancer Cell 1(3):237–246
Shen C, Beroukhim R, Schumacher SE, Zhou J, Chang M, Signoretti S, Kaelin WG Jr (2011) Genetic and functional studies implicate HIF1alpha as a 14q kidney cancer suppressor gene. Cancer Discov 1(3):222–235. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0098
Brenner W, Farber G, Herget T, Lehr HA, Hengstler JG, Thuroff JW (2002) Loss of tumor suppressor protein PTEN during renal carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer 99(1):53–57. doi:10.1002/ijc.10303
Horiguchi A, Oya M, Uchida A, Marumo K, Murai M (2003) Elevated Akt activation and its impact on clinicopathological features of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 169(2):710–713. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000038952.59355.b2
Alimov A, Li C, Gizatullin R, Fredriksson V, Sundelin B, Klein G, Zabarovsky E, Bergerheim U (1999) Somatic mutation and homozygous deletion of PTEN/MMAC1 gene of 10q23 in renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 19(5B):3841–3846
Kondo K, Yao M, Kobayashi K, Ota S, Yoshida M, Kaneko S, Baba M, Sakai N, Kishida T, Kawakami S, Uemura H, Nagashima Y, Nakatani Y, Hosaka M (2001) PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 mutations in human primary renal-cell carcinomas and renal carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 91(2):219–224. doi:10.1002/1097-0215(20010115)91:2<219:AID-IJC1034>3.0.CO;2-3
Hara S, Oya M, Mizuno R, Horiguchi A, Marumo K, Murai M (2005) Akt activation in renal cell carcinoma: contribution of a decreased PTEN expression and the induction of apoptosis by an Akt inhibitor. Ann Oncol 16(6):928–933. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi182
Frew IJ, Thoma CR, Georgiev S, Minola A, Hitz M, Montani M, Moch H, Krek W (2008) pVHL and PTEN tumour suppressor proteins cooperatively suppress kidney cyst formation. EMBO J 27(12):1747–1757. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.96
Hager M, Haufe H, Kemmerling R, Hitzl W, Mikuz G, Moser PL, Kolbitsch C (2009) Increased activated Akt expression in renal cell carcinomas and prognosis. J Cell Mol Med 13(8B):2181–2188. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00488.x
Steck PA, Pershouse MA, Jasser SA, Yung WK, Lin H, Ligon AH, Langford LA, Baumgard ML, Hattier T, Davis T, Frye C, Hu R, Swedlund B, Teng DH, Tavtigian SV (1997) Identification of a candidate tumour suppressor gene, MMAC1, at chromosome 10q23.3 that is mutated in multiple advanced cancers. Nat Genet 15(4):356–362. doi:10.1038/ng0497-356
Ikediobi ON, Davies H, Bignell G, Edkins S, Stevens C, O’Meara S, Santarius T, Avis T, Barthorpe S, Brackenbury L, Buck G, Butler A, Clements J, Cole J, Dicks E, Forbes S, Gray K, Halliday K, Harrison R, Hills K, Hinton J, Hunter C, Jenkinson A, Jones D, Kosmidou V, Lugg R, Menzies A, Mironenko T, Parker A, Perry J, Raine K, Richardson D, Shepherd R, Small A, Smith R, Solomon H, Stephens P, Teague J, Tofts C, Varian J, Webb T, West S, Widaa S, Yates A, Reinhold W, Weinstein JN, Stratton MR, Futreal PA, Wooster R (2006) Mutation analysis of 24 known cancer genes in the NCI-60 cell line set. Mol Cancer Ther 5(11):2606–2612. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0433
Velickovic M, Delahunt B, McIver B, Grebe SK (2002) Intragenic PTEN/MMAC1 loss of heterozygosity in conventional (clear-cell) renal cell carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. Mod Pathol 15(5):479–485. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880551
Shin Lee J, Seok Kim H, Bok Kim Y, Cheol Lee M, Soo Park C (2003) Expression of PTEN in renal cell carcinoma and its relation to tumor behavior and growth. J Surg Oncol 84(3):166–172. doi:10.1002/jso.10302
Sourbier C, Lindner V, Lang H, Agouni A, Schordan E, Danilin S, Rothhut S, Jacqmin D, Helwig JJ, Massfelder T (2006) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway: a new target in human renal cell carcinoma therapy. Cancer Res 66(10):5130–5142. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1469
Blancher C, Moore JW, Robertson N, Harris AL (2001) Effects of ras and von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) gene mutations on hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression and their regulation by the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Cancer Res 61(19):7349–7355
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E, Hanrahan C, Georgescu MM, Simons JW, Semenza GL (2000) Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res 60(6):1541–1545
Jiang BH, Jiang G, Zheng JZ, Lu Z, Hunter T, Vogt PK (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell Growth Differ 12(7):363–369
Muh CR, Joshi S, Singh AR, Kesari S, Durden DL, Makale MT (2014) PTEN status mediates 2ME2 anti-tumor efficacy in preclinical glioblastoma models: role of HIF1alpha suppression. J Neurooncol 116(1):89–97. doi:10.1007/s11060-013-1283-3
Joshi S, Singh AR, Durden DL (2014) MDM2 regulates hypoxic hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha stability in an E3 ligase, proteasome, and PTEN-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 289(33):22785–22797. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.587493
Joshi S, Singh AR, Zulcic M, Durden DL (2014) A macrophage dominant PI-3K isoform controls hypoxia induced HIF1alpha & HIF2alpha stability and tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Mol Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0682
Toschi A, Lee E, Gadir N, Ohh M, Foster DA (2008) Differential dependence of hypoxia-inducible factors 1 alpha and 2 alpha on mTORC1 and mTORC2. J Biol Chem 283(50):34495–34499. doi:10.1074/jbc.C800170200
Garlich JR, De P, Dey N, Su JD, Peng X, Miller A, Murali R, Lu Y, Mills GB, Kundra V, Shu HK, Peng Q, Durden DL (2008) A vascular targeted pan phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor prodrug, SF1126, with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res 68(1):206–215. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0669
Mahadevan D, Chiorean EG, Harris WB, Von Hoff DD, Stejskal-Barnett A, Qi W, Anthony SP, Younger AE, Rensvold DM, Cordova F, Shelton CF, Becker MD, Garlich JR, Durden DL, Ramanathan RK (2012) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the pan-PI3K/mTORC vascular-targeted prodrug SF1126 in patients with advanced solid tumours and B-cell malignancies. Eur J Cancer 48(18):3319–3327. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.06.027
Joshi S, Singh AR, Kumar A, Misra PC, Siddiqi MI, Saxena JK (2008) Molecular cloning and characterization of Plasmodium falciparum transketolase. Mol Biochem Parasitol 160(1):32–41. doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.03.005
Singh AR, Joshi S, Arya R, Kayastha AM, Srivastava KK, Tripathi LM, Saxena JK (2008) Molecular cloning and characterization of Brugia malayi hexokinase. Parasitol Int 57(3):354–361. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2008.03.004
Hartman LL, Crawford JR, Makale MT, Milburn M, Joshi S, Salazar AM, Hasenauer B, VandenBerg SR, MacDonald TJ, Durden DL (2014) Pediatric phase II trials of poly-ICLC in the management of newly diagnosed and recurrent brain tumors. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 36(6):451–457. doi:10.1097/MPH.0000000000000047
Joshi S, Singh AR, Zulcic M, Bao L, Messer K, Ideker T, Dutkowski J, Durden DL (2014) Rac2 controls tumor growth, metastasis and M1–M2 macrophage differentiation in vivo. PLoS ONE 9(4):e95893. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095893
Emmenegger BA, Hwang EI, Moore C, Markant SL, Brun SN, Dutton JW, Read TA, Fogarty MP, Singh AR, Durden DL, Yang C, McKeehan WL, Wechsler-Reya RJ (2013) Distinct roles for fibroblast growth factor signaling in cerebellar development and medulloblastoma. Oncogene 32(35):4181–4188. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.440
Dey N, De PK, Wang M, Zhang H, Dobrota EA, Robertson KA, Durden DL (2007) CSK controls retinoic acid receptor (RAR) signaling: a RAR-c-SRC signaling axis is required for neuritogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 27(11):4179–4197. doi:10.1128/MCB.01352-06
Joshi S, Singh AR, Zulcic M, Durden DL (2014) A PKC-SHP1 signaling axis desensitizes Fcgamma receptor signaling by reducing the tyrosine phosphorylation of CBL and regulates FcgammaR mediated phagocytosis. BMC Immunol 15:18. doi:10.1186/1471-2172-15-18
Hu L, Zaloudek C, Mills GB, Gray J, Jaffe RB (2000) In vivo and in vitro ovarian carcinoma growth inhibition by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor (LY294002). Clin Cancer Res 6(3):880–886
Su JD, Mayo LD, Donner DB, Durden DL (2003) PTEN and phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase inhibitors up-regulate p53 and block tumor-induced angiogenesis: evidence for an effect on the tumor and endothelial compartment. Cancer Res 63(13):3585–3592
Nutley BP, Raynaud F, Hayes A, Goddard P, Jarman M, Workman P (2001) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the phospatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 in the mouse. In: Proceedings of the American Association of Cancer Research 92nd annual meeting 2001, p 380
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF (1994) A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 269(7):5241–5248
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M, Tafuri A, Stivala F, Libra M, Basecke J, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM, Franklin RA (2007) Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773(8):1263–1284. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001
Hoeflich KP, O’Brien C, Boyd Z, Cavet G, Guerrero S, Jung K, Januario T, Savage H, Punnoose E, Truong T, Zhou W, Berry L, Murray L, Amler L, Belvin M, Friedman LS, Lackner MR (2009) In vivo antitumor activity of MEK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors in basal-like breast cancer models. Clin Cancer Res 15(14):4649–4664. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0317
Mirzoeva OK, Das D, Heiser LM, Bhattacharya S, Siwak D, Gendelman R, Bayani N, Wang NJ, Neve RM, Guan Y, Hu Z, Knight Z, Feiler HS, Gascard P, Parvin B, Spellman PT, Shokat KM, Wyrobek AJ, Bissell MJ, McCormick F, Kuo WL, Mills GB, Gray JW, Korn WM (2009) Basal subtype and MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK)-phosphoinositide 3-kinase feedback signaling determine susceptibility of breast cancer cells to MEK inhibition. Cancer Res 69(2):565–572. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3389
Shinojima T, Oya M, Takayanagi A, Mizuno R, Shimizu N, Murai M (2007) Renal cancer cells lacking hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha expression maintain vascular endothelial growth factor expression through HIF-2alpha. Carcinogenesis 28(3):529–536. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl143
Post DE, Van Meir EG (2001) Generation of bidirectional hypoxia/HIF-responsive expression vectors to target gene expression to hypoxic cells. Gene Ther 8(23):1801–1807. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3301605
Mayo LD, Donner DB (2001) A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes translocation of Mdm2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(20):11598–11603. doi:10.1073/pnas.181181198
Gu L, Zhu N, Zhang H, Durden DL, Feng Y, Zhou M (2009) Regulation of XIAP translation and induction by MDM2 following irradiation. Cancer Cell 15(5):363–375. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.002
Nobes CD, Hall A (1995) Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81(1):53–62
Keely PJ, Westwick JK, Whitehead IP, Der CJ, Parise LV (1997) Cdc42 and Rac1 induce integrin-mediated cell motility and invasiveness through PI(3)K. Nature 390(6660):632–636. doi:10.1038/37656
Tan BL, Yazicioglu MN, Ingram D, McCarthy J, Borneo J, Williams DA, Kapur R (2003) Genetic evidence for convergence of c-Kit- and alpha4 integrin-mediated signals on class IA PI-3kinase and the Rac pathway in regulating integrin-directed migration in mast cells. Blood 101(12):4725–4732. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-08-2521
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359(4):378–390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM, Figlin RA (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356(2):115–124. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa065044
Escudier B, Szczylik C, Hutson TE, Demkow T, Staehler M, Rolland F, Negrier S, Laferriere N, Scheuring UJ, Cella D, Shah S, Bukowski RM (2009) Randomized phase II trial of first-line treatment with sorafenib versus interferon Alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27(8):1280–1289. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.19.3342
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Staehler M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Anderson S, Hofilena G, Shan M, Pena C, Lathia C, Bukowski RM (2009) Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: final efficacy and safety results of the phase III treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial. J Clin Oncol 27(20):3312–3318. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.19.5511
Singh AR, Peirce SK, Joshi S, Durden DL (2014) PTEN and PI-3 kinase inhibitors control LPS signaling and the lymphoproliferative response in the CD19+ B cell compartment. Exp Cell Res 327(1):78–90. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.05.016
Manser E, Leung T, Salihuddin H, Zhao ZS, Lim L (1994) A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature 367(6458):40–46. doi:10.1038/367040a0
King AJ, Sun H, Diaz B, Barnard D, Miao W, Bagrodia S, Marshall MS (1998) The protein kinase Pak3 positively regulates Raf-1 activity through phosphorylation of serine 338. Nature 396(6707):180–183. doi:10.1038/24184
Wee S, Jagani Z, Xiang KX, Loo A, Dorsch M, Yao YM, Sellers WR, Lengauer C, Stegmeier F (2009) PI3K pathway activation mediates resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant cancers. Cancer Res 69(10):4286–4293. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4765
Belozerov VE, Van Meir EG (2005) Hypoxia inducible factor-1: a novel target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16(9):901–909
Powis G, Kirkpatrick L (2004) Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha as a cancer drug target. Mol Cancer Ther 3(5):647–654
Giaccia AJ, Simon MC, Johnson R (2004) The biology of hypoxia: the role of oxygen sensing in development, normal function, and disease. Genes Dev 18(18):2183–2194. doi:10.1101/gad.1243304
Kondo K, Kim WY, Lechpammer M, Kaelin WG Jr (2003) Inhibition of HIF2alpha is sufficient to suppress pVHL-defective tumor growth. PLoS Biol 1(3):E83. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0000083
Semenza GL (2000) HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 88(4):1474–1480
Wenger RH (2000) Mammalian oxygen sensing, signalling and gene regulation. J Exp Biol 203(Pt 8):1253–1263
Saxena NK, Sharma D, Ding X, Lin S, Marra F, Merlin D, Anania FA (2007) Concomitant activation of the JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and ERK signaling is involved in leptin-mediated promotion of invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 67(6):2497–2507. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3075
Welch HC, Coadwell WJ, Stephens LR, Hawkins PT (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent activation of Rac. FEBS Lett 546(1):93–97
Han J, Luby-Phelps K, Das B, Shu X, Xia Y, Mosteller RD, Krishna UM, Falck JR, White MA, Broek D (1998) Role of substrates and products of PI 3-kinase in regulating activation of Rac-related guanosine triphosphatases by Vav. Science 279(5350):558–560
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all of the dedicated people at SignalRx and the Durden laboratory for the commitment to bringing the first pan-PI-3K inhibitor into patient care. Funding for this work were from grants CA94233 and Georgia Cancer Coalition to DLD. This work was supported by the Aflac Cancer Center, St Balderick’s Foundation, Alex Lemonade Stand Foundation and Cricket Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, S., Singh, A.R. & Durden, D.L. Pan-PI-3 kinase inhibitor SF1126 shows antitumor and antiangiogenic activity in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75, 595–608 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2639-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2639-x