Abstract
Purpose
Optimal chemotherapy for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with interstitial lung disease (ILD) is established for paclitaxel and carboplatin, but is otherwise controversial. Therefore, we assessed the efficacy and safety of paclitaxel and carboplatin with or without bevacizumab for treating these patients.
Methods
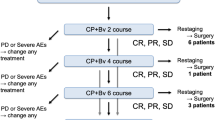
We analyzed the outcomes of 21 patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC with ILD who received paclitaxel and carboplatin without (paclitaxel–carboplatin group; n = 11) or with bevacizumab (paclitaxel–carboplatin–bevacizumab group; n = 10) between April 2008 and October 2013.
Results
The median progression-free survival time of the paclitaxel–carboplatin–bevacizumab group was 5.3 months (95 % CI 0.4–11.6 months) compared with 4.4 months (95 % CI 0.9–6.3 months) for the paclitaxel–carboplatin group (p = 0.060). Their respective median overall survival times were 16.1 months (range 0.4–34.8 months) and 9.7 months (range 2.6–37.0 months) (p = 0.772) with corresponding overall response rates of 40 and 27 % (p = 0.659), respectively. One patient in the paclitaxel–carboplatin–bevacizumab group experienced chemotherapy-related exacerbation of ILD (0/11 vs. 1/10; p = 0.476).
Conclusions
The addition of bevacizumab to paclitaxel and carboplatin may provide an effective and safe treatment option for patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC with ILD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramalingam SS, Owonikoko TK, Khuri FR (2011) Lung cancer: new biological insights and recent therapeutic advances. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):91–112. doi:10.3322/caac.20102
Azzoli CG, Baker S Jr, Temin S, Pao W, Aliff T, Brahmer J, Johnson DH, Laskin JL, Masters G, Milton D, Nordquist L, Pfister DG, Piantadosi S, Schiller JH, Smith R, Smith TJ, Strawn JR, Trent D, Giaccone G, American Society of Clinical O (2009) American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update on chemotherapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(36):6251–6266. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.23.5622
Hubbard R, Venn A, Lewis S, Britton J (2000) Lung cancer and cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. A population-based cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161(1):5–8. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.161.1.9906062
Bouros D, Hatzakis K, Labrakis H, Zeibecoglou K (2002) Association of malignancy with diseases causing interstitial pulmonary changes. Chest 121(4):1278–1289
Jin GY, Lynch D, Chawla A, Garg K, Tammemagi MC, Sahin H, Misumi S, Kwon KS (2013) Interstitial lung abnormalities in a CT lung cancer screening population: prevalence and progression rate. Radiology 268(2):563–571. doi:10.1148/radiol.13120816
Sverzellati N, Guerci L, Randi G, Calabro E, La Vecchia C, Marchiano A, Pesci A, Zompatori M, Pastorino U (2011) Interstitial lung diseases in a lung cancer screening trial. Eur Respir J 38(2):392–400. doi:10.1183/09031936.00201809
Ozawa Y, Suda T, Naito T, Enomoto N, Hashimoto D, Fujisawa T, Nakamura Y, Inui N, Nakamura H, Chida K (2009) Cumulative incidence of and predictive factors for lung cancer in IPF. Respirology 14(5):723–728. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2009.01547.x
Isobe K, Hata Y, Sakamoto S, Takai Y, Shibuya K, Homma S (2010) Clinical characteristics of acute respiratory deterioration in pulmonary fibrosis associated with lung cancer following anti-cancer therapy. Respirology 15(1):88–92. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2009.01666.x
Minegishi Y, Takenaka K, Mizutani H, Sudoh J, Noro R, Okano T, Azuma A, Yoshimura A, Ando M, Tsuboi E, Kudoh S, Gemma A (2009) Exacerbation of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias associated with lung cancer therapy. Intern Med 48(9):665–672
Pavlakis N, Bell DR, Millward MJ, Levi JA (1997) Fatal pulmonary toxicity resulting from treatment with gemcitabine. Cancer 80(2):286–291
Read WL, Mortimer JE, Picus J (2002) Severe interstitial pneumonitis associated with docetaxel administration. Cancer 94(3):847–853
Shukuya T, Ishiwata T, Hara M, Muraki K, Shibayama R, Koyama R, Takahashi K (2010) Carboplatin plus weekly paclitaxel treatment in non-small cell lung cancer patients with interstitial lung disease. Anticancer Res 30(10):4357–4361
Minegishi Y, Sudoh J, Kuribayasi H, Mizutani H, Seike M, Azuma A, Yoshimura A, Kudoh S, Gemma A (2011) The safety and efficacy of weekly paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Lung Cancer 71(1):70–74. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2010.04.014
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R, Johnson DH (2006) Paclitaxel–carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 355(24):2542–2550. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061884
Hanumegowda C, Farkas L, Kolb M (2012) Angiogenesis in pulmonary fibrosis: too much or not enough? Chest 142(1):200–207. doi:10.1378/chest.11-1962
Richeldi L, Costabel U, Selman M, Kim DS, Hansell DM, Nicholson AG, Brown KK, Flaherty KR, Noble PW, Raghu G, Brun M, Gupta A, Juhel N, Kluglich M, du Bois RM (2011) Efficacy of a tyrosine kinase inhibitor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 365(12):1079–1087. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1103690
Socinski MA, Langer CJ, Huang JE, Kolb MM, Compton P, Wang L, Akerley W (2009) Safety of bevacizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 27(31):5255–5261. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.22.0616
American Thoracic S, European Respiratory S (2002) American thoracic society/European respiratory society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165(2):277–304. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01
Lynch DA, Godwin JD, Safrin S, Starko KM, Hormel P, Brown KK, Raghu G, King TE Jr, Bradford WZ, Schwartz DA, Richard Webb W, Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Study G (2005) High-resolution computed tomography in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and prognosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172(4):488–493. doi:10.1164/rccm.200412-1756OC
Collard HR, Moore BB, Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Kaner RJ, King TE Jr, Lasky JA, Loyd JE, Noth I, Olman MA, Raghu G, Roman J, Ryu JH, Zisman DA, Hunninghake GW, Colby TV, Egan JJ, Hansell DM, Johkoh T, Kaminski N, Kim DS, Kondoh Y, Lynch DA, Muller-Quernheim J, Myers JL, Nicholson AG, Selman M, Toews GB, Wells AU, Martinez FJ, Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical ResearchNetwork I (2007) Acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176(7):636–643. doi:10.1164/rccm.200703-463PP
Fisseler-Eckhoff A (2009) New TNM classification of malignant lung tumors 2009 from a pathology perspective. Der Pathologe 30(Suppl 2):193–199. doi:10.1007/s00292-009-1195-3
Johnson DH, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny WF, Herbst RS, Nemunaitis JJ, Jablons DM, Langer CJ, DeVore RF 3rd, Gaudreault J, Damico LA, Holmgren E, Kabbinavar F (2004) Randomized phase II trial comparing bevacizumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel with carboplatin and paclitaxel alone in previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(11):2184–2191. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.11.022
Niho S, Kunitoh H, Nokihara H, Horai T, Ichinose Y, Hida T, Yamamoto N, Kawahara M, Shinkai T, Nakagawa K, Matsui K, Negoro S, Yokoyama A, Kudoh S, Kiura K, Mori K, Okamoto H, Sakai H, Takeda K, Yokota S, Saijo N, Fukuoka M, Group JOS (2012) Randomized phase II study of first-line carboplatin-paclitaxel with or without bevacizumab in Japanese patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 76(3):362–367. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.12.005
Kenmotsu H, Naito T, Kimura M, Ono A, Shukuya T, Nakamura Y, Tsuya A, Kaira K, Murakami H, Takahashi T, Endo M, Yamamoto N (2011) The risk of cytotoxic chemotherapy-related exacerbation of interstitial lung disease with lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6(7):1242–1246. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318216ee6b
Mancuso MR, Davis R, Norberg SM, O’Brien S, Sennino B, Nakahara T, Yao VJ, Inai T, Brooks P, Freimark B, Shalinsky DR, Hu-Lowe DD, McDonald DM (2006) Rapid vascular regrowth in tumors after reversal of VEGF inhibition. J Clin Investig 116(10):2610–2621. doi:10.1172/JCI24612
Nathan N, Thouvenin G, Fauroux B, Corvol H, Clement A (2011) Interstitial lung disease: physiopathology in the context of lung growth. Paediatr Respir Rev 12(4):216–222. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2011.04.003
Strieter RM, Gomperts BN, Keane MP (2007) The role of CXC chemokines in pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Investig 117(3):549–556. doi:10.1172/JCI30562
Ebina M, Shimizukawa M, Shibata N, Kimura Y, Suzuki T, Endo M, Sasano H, Kondo T, Nukiwa T (2004) Heterogeneous increase in CD34-positive alveolar capillaries in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169(11):1203–1208. doi:10.1164/rccm.200308-1111OC
Cosgrove GP, Brown KK, Schiemann WP, Serls AE, Parr JE, Geraci MW, Schwarz MI, Cool CD, Worthen GS (2004) Pigment epithelium-derived factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a role in aberrant angiogenesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170(3):242–251. doi:10.1164/rccm.200308-1151OC
Soria JC, Mauguen A, Reck M, Sandler AB, Saijo N, Johnson DH, Burcoveanu D, Fukuoka M, Besse B, Pignon JP, meta-analysis of bevacizumab in advanced Ncg (2013) Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised, phase II/III trials adding bevacizumab to platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 24(1):20–30. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds590
Kim DS, Park JH, Park BK, Lee JS, Nicholson AG, Colby T (2006) Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: frequency and clinical features. Eur Respir J 27(1):143–150. doi:10.1183/09031936.06.00114004
Azuma A, Nukiwa T, Tsuboi E, Suga M, Abe S, Nakata K, Taguchi Y, Nagai S, Itoh H, Ohi M, Sato A, Kudoh S (2005) Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171(9):1040–1047. doi:10.1164/rccm.200404-571OC
Sato T, Teramukai S, Kondo H, Watanabe A, Ebina M, Kishi K, Fujii Y, Mitsudomi T, Yoshimura M, Maniwa T, Suzuki K, Kataoka K, Sugiyama Y, Kondo T, Date H, for the Japanese Association for Chest S (2013) Impact and predictors of acute exacerbation of interstitial lung diseases after pulmonary resection for lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.09.050
Yamamoto H, Toyooka S, Mitsudomi T (2009) Impact of EGFR mutation analysis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 63(3):315–321. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.06.021
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, Ou SH, Dezube BJ, Janne PA, Costa DB, Varella-Garcia M, Kim WH, Lynch TJ, Fidias P, Stubbs H, Engelman JA, Sequist LV, Tan W, Gandhi L, Mino-Kenudson M, Wei GC, Shreeve SM, Ratain MJ, Settleman J, Christensen JG, Haber DA, Wilner K, Salgia R, Shapiro GI, Clark JW, Iafrate AJ (2010) Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 363(18):1693–1703. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1006448
Fujimoto D, Tomii K, Otoshi T, Kawamura T, Tamai K, Takeshita J, Tanaka K, Matsumoto T, Monden K, Nagata K, Otsuka K, Nakagawa A, Hata A, Tachikawa R, Otsuka K, Hamakawa H, Katakami N, Takahashi Y, Imai Y (2013) Preexisting interstitial lung disease is inversely correlated to tumor epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 80(2):159–164. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.01.017
Kudoh S, Kato H, Nishiwaki Y, Fukuoka M, Nakata K, Ichinose Y, Tsuboi M, Yokota S, Nakagawa K, Suga M, Japan Thoracic Radiology G, Jiang H, Itoh Y, Armour A, Watkins C, Higenbottam T, Nyberg F (2008) Interstitial lung disease in Japanese patients with lung cancer: a cohort and nested case-control study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177(12):1348–1357. doi:10.1164/rccm.200710-1501OC
Watanabe N, Nakahara Y, Taniguchi H, Kimura T, Kondoh Y, Kataoka K, Sakamoto K (2014) Crizotinib-induced acute interstitial lung disease in a patient with EML4-ALK positive non-small cell lung cancer and chronic interstitial pneumonia. Acta Oncol 53(1):158–160. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2013.802838
Sakakibara T, Inoue A, Sugawara S, Maemondo M, Ishida T, Usui K, Abe T, Kanbe M, Watanabe H, Saijo Y, Nukiwa T (2010) Randomized phase II trial of weekly paclitaxel combined with carboplatin versus standard paclitaxel combined with carboplatin for elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 21(4):795–799. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp401
Belani CP, Ramalingam S, Perry MC, LaRocca RV, Rinaldi D, Gable PS, Tester WJ (2008) Randomized, phase III study of weekly paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin versus standard every-3-weeks administration of carboplatin and paclitaxel for patients with previously untreated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(3):468–473. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.13.1912
Hata A, Katakami N, Tanaka K, Takeshita J, Matsumoto T, Monden K, Nagata K, Masago K, Kaji R, Fujita S, Tachikawa R, Otsuka K, Otsuka K, Tomii K (2014) Bevacizumab plus weekly paclitaxel with or without carboplatin for previously-treated non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 34(1):275–281
Cushley M, Davison A, du Bois R et al (1999) The diagnosis, assessment and treatment of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in adults. Introduction. Thorax 54(Suppl 1):S1–S14
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, Lynch DA, Ryu JH, Swigris JJ, Wells AU, Ancochea J, Bouros D, Carvalho C, Costabel U, Ebina M, Hansell DM, Johkoh T, Kim DS, King TE Jr, Kondoh Y, Myers J, Muller NL, Nicholson AG, Richeldi L, Selman M, Dudden RF, Griss BS, Protzko SL, Schunemann HJ, Fibrosis AEJACoIP (2011) An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183(6):788–824. doi:10.1164/rccm.2009-040GL
Flaherty KR, King TE Jr, Raghu G, Lynch JP 3rd, Colby TV, Travis WD, Gross BH, Kazerooni EA, Toews GB, Long Q, Murray S, Lama VN, Gay SE, Martinez FJ (2004) Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: What is the effect of a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170(8):904–910. doi:10.1164/rccm.200402-147OC
Johkoh T, Muller NL, Cartier Y, Kavanagh PV, Hartman TE, Akira M, Ichikado K, Ando M, Nakamura H (1999) Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: diagnostic accuracy of thin-section CT in 129 patients. Radiology 211(2):555–560. doi:10.1148/radiology.211.2.r99ma01555
Acknowledgments
We thank Keiko Sakuragawa for administrative assistance. This study was supported by internal funding and the Ethics Committee of Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, R., Fujimoto, D., Kato, R. et al. The safety and efficacy of paclitaxel and carboplatin with or without bevacizumab for treating patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer with interstitial lung disease. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74, 1159–1166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2590-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2590-x