Abstract
Purpose
Anti-angiogenic agents combined with histone deacetylase inhibitors act synergistically in vitro and in vivo. We conducted a phase I study of the combination of the anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody bevacizumab and histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid in patients with advanced cancers.
Methods
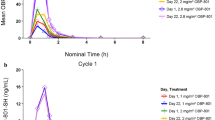
Bevacizumab was administered at escalating dosages of 2.5–11 mg/kg on days 1 and 15, and oral valproic acid at dosages of 5.3–10 mg/kg on days 1–28 every 28 days to determine the maximum tolerated dose. Pharmacodynamic parameters were assessed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (histone H3 acetylation) and serum (valproic acid levels).
Results
Fifty-seven patients were enrolled. Dose-limiting toxicities were grade 3 altered mental status (n = 2), related to valproic acid. Bevacizumab 11 mg/kg given on days 1 and 15 and valproic acid 5.3 mg/kg daily were the recommended phase II dosages. Stable disease (SD) ≥6 months was reported in 4/57 (7 %) of patients, including two patients with colorectal cancer who had progressed previously on bevacizumab. Of the 39 patients evaluated for histone acetylation, 2 of 3 (67 %) patients with SD ≥6 months showed histone acetylation, while 8 of 36 (22 %) without SD ≥6 months demonstrated histone acetylation (p = 0.16). Patients with any grade of hypertension, compared to others, had a prolonged median survival (11.1 vs. 5.8 months; p = 0.012).
Conclusions
The combination of bevacizumab 11 mg/kg and valproic acid 5.3 mg/kg is safe in patients with advanced malignancies, with activity in colorectal, gastroesophageal junction, and prostate cancer. Patients with hypertension had improved overall survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (2006) Angiogenesis. Annu Rev Med 57:1–18. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.57.121304.131306
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J 13(1):9–22
Miller KD, Chap LI, Holmes FA, Cobleigh MA, Marcom PK, Fehrenbacher L, Dickler M, Overmoyer BA, Reimann JD, Sing AP, Langmuir V, Rugo HS (2005) Randomized phase III trial of capecitabine compared with bevacizumab plus capecitabine in patients with previously treated metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(4):792–799. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.05.098
Hurwitz H (2004) Integrating the anti-VEGF-A humanized monoclonal antibody bevacizumab with chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 4(Suppl 2):S62–S68
Sandler A (2007) Bevacizumab in non small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(15 Pt 2):s4613–s4616. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0647
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27(28):4733–4740. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.19.8721
Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C, Chevreau C, Filipek M, Melichar B, Bajetta E, Gorbunova V, Bay JO, Bodrogi I, Jagiello-Gruszfeld A, Moore N (2007) Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet 370(9605):2103–2111. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61904-7
Marks PA, Richon VM, Miller T, Kelly WK (2004) Histone deacetylase inhibitors. Adv Cancer Res 91:137–168. doi:10.1016/S0065-230X(04)91004-4
Marks P, Rifkind RA, Richon VM, Breslow R, Miller T, Kelly WK (2001) Histone deacetylases and cancer: causes and therapies. Nat Rev Cancer 1(3):194–202. doi:10.1038/35106079
Johannessen CU, Johannessen SI (2003) Valproate: past, present, and future. CNS Drug Rev 9(2):199–216
Deroanne CF, Bonjean K, Servotte S, Devy L, Colige A, Clausse N, Blacher S, Verdin E, Foidart JM, Nusgens BV, Castronovo V (2002) Histone deacetylases inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents altering vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. Oncogene 21(3):427–436. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205108
Kim MS, Kwon HJ, Lee YM, Baek JH, Jang JE, Lee SW, Moon EJ, Kim HS, Lee SK, Chung HY, Kim CW, Kim KW (2001) Histone deacetylases induce angiogenesis by negative regulation of tumor suppressor genes. Nat Med 7(4):437–443. doi:10.1038/86507
Qian DZ, Wang X, Kachhap SK, Kato Y, Wei Y, Zhang L, Atadja P, Pili R (2004) The histone deacetylase inhibitor NVP-LAQ824 inhibits angiogenesis and has a greater antitumor effect in combination with the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584. Cancer Res 64(18):6626–6634. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0540
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, Carbone PP (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5(6):649–655
Criteria Committee of the New York Heart Association (1994) Nomenclature and criteria for diagnosis of diseases of the heart and great vessels. 9th edn. Little Brown & Co, Boston
Braiteh F, Soriano AO, Garcia-Manero G, Hong D, Johnson MM, Silva Lde P, Yang H, Alexander S, Wolff J, Kurzrock R (2008) Phase I study of epigenetic modulation with 5-azacytidine and valproic acid in patients with advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res 14(19):6296–6301. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1247
Phiel CJ, Zhang F, Huang EY, Guenther MG, Lazar MA, Klein PS (2001) Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and teratogen. J Biol Chem 276(39):36734–36741. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101287200
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Mantel N (1966) Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep 50(3):163–170
Horstmann E, McCabe MS, Grochow L, Yamamoto S, Rubinstein L, Budd T, Shoemaker D, Emanuel EJ, Grady C (2005) Risks and benefits of phase 1 oncology trials, 1991 through 2002. N Engl J Med 352(9):895–904. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa042220
Maitland ML, Bakris GL, Black HR, Chen HX, Durand JB, Elliott WJ, Ivy SP, Leier CV, Lindenfeld J, Liu G, Remick SC, Steingart R, Tang WH (2010) Initial assessment, surveillance, and management of blood pressure in patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibitors. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(9):596–604. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq091
Zhu X, Wu S, Dahut WL, Parikh CR (2007) Risks of proteinuria and hypertension with bevacizumab, an antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 49(2):186–193. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.11.039
Schneider BP, Wang M, Radovich M, Sledge GW, Badve S, Thor A, Flockhart DA, Hancock B, Davidson N, Gralow J, Dickler M, Perez EA, Cobleigh M, Shenkier T, Edgerton S, Miller KD (2008) Association of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 genetic polymorphisms with outcome in a trial of paclitaxel compared with paclitaxel plus bevacizumab in advanced breast cancer: ECOG 2100. J Clin Oncol 26(28):4672–4678. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.1612
Dahlberg SE, Sandler AB, Brahmer JR, Schiller JH, Johnson DH (2010) Clinical course of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients experiencing hypertension during treatment with bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel on ECOG 4599. J Clin Oncol 28(6):949–954. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.4482
Scartozzi M, Galizia E, Chiorrini S, Giampieri R, Berardi R, Pierantoni C, Cascinu S (2009) Arterial hypertension correlates with clinical outcome in colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line bevacizumab. Ann Oncol 20(2):227–230. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn637
Bono P, Elfving H, Utriainen T, Osterlund P, Saarto T, Alanko T, Joensuu H (2009) Hypertension and clinical benefit of bevacizumab in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 20(2):393–394. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn729
Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian HM, Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Yang H, Rosner G, Verstovsek S, Rytting M, Wierda WG, Ravandi F, Koller C, Xiao L, Faderl S, Estrov Z, Cortes J, O’Brien S, Estey E, Bueso-Ramos C, Fiorentino J, Jabbour E, Issa JP (2006) Phase 1/2 study of the combination of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine with valproic acid in patients with leukemia. Blood 108(10):3271–3279. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-03-009142
Soriano AO, Yang H, Faderl S, Estrov Z, Giles F, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Wierda WG, Ouzounian S, Quezada A, Pierce S, Estey EH, Issa JP, Kantarjian HM, Garcia-Manero G (2007) Safety and clinical activity of the combination of 5-azacytidine, valproic acid, and all-trans retinoic acid in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 110(7):2302–2308. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-03-078576
Garcia-Manero G, Assouline S, Cortes J, Estrov Z, Kantarjian H, Yang H, Newsome WM, Miller WH Jr, Rousseau C, Kalita A, Bonfils C, Dubay M, Patterson TA, Li Z, Besterman JM, Reid G, Laille E, Martell RE, Minden M (2008) Phase 1 study of the oral isotype specific histone deacetylase inhibitor MGCD0103 in leukemia. Blood 112(4):981–989. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-10-115873
Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferrajoli A, Cortes J, Wierda WG, Faderl S, Koller C, Morris G, Rosner G, Loboda A, Fantin VR, Randolph SS, Hardwick JS, Reilly JF, Chen C, Ricker JL, Secrist JP, Richon VM, Frankel SR, Kantarjian HM (2008) Phase 1 study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat [suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA)] in patients with advanced leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 111(3):1060–1066. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-06-098061
Kelly WK, O’Connor OA, Krug LM, Chiao JH, Heaney M, Curley T, MacGregore-Cortelli B, Tong W, Secrist JP, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Chu E, Olgac S, Marks PA, Scher H, Richon VM (2005) Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(17):3923–3931. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.14.167
Ryan QC, Headlee D, Acharya M, Sparreboom A, Trepel JB, Ye J, Figg WD, Hwang K, Chung EJ, Murgo A, Melillo G, Elsayed Y, Monga M, Kalnitskiy M, Zwiebel J, Sausville EA (2005) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of MS-275, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in patients with advanced and refractory solid tumors or lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23(17):3912–3922. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.02.188
Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, Hoshino K, Quintas-Cardama A, Richon VM, Garcia-Manero G (2006) Antileukemia activity of the combination of an anthracycline with a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Blood 108(4):1174–1182. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-09-008086
Kadia TM, Yang H, Ferrajoli A, Maddipotti S, Schroeder C, Madden TL, Holleran JL, Egorin MJ, Ravandi F, Thomas DA, Newsome W, Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Zwiebel JA, Espinoza-Delgado I, Kantarjian HM, Garcia-Manero G (2010) A phase I study of vorinostat in combination with idarubicin in relapsed or refractory leukaemia. Br J Haematol 150(1):72–82. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08211.x
Acknowledgements
Supported by Grant Number RR024148 from the National Center for Research Resources, a component of the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research. (http://nihroadmap.nih.gov/clinicalresearch/overview-translational.asp).
Conflict of interest
FJ has served as a consultant/advisor for Trovagene and has funding from Novartis, Roche, Biocartis, Trovagene and Transgenomi. All authors have not conflicts to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jennifer J. Wheler and Filip Janku have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wheler, J.J., Janku, F., Falchook, G.S. et al. Phase I study of anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody bevacizumab and histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid in patients with advanced cancers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 495–501 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2384-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2384-1