Abstract
Purpose
This study characterized the multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of vemurafenib 240–960 mg twice daily (bid) in BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic melanoma patients, using the commercial formulation (240-mg microprecipitated bulk powder film-coated tablets).
Methods
Melanoma patients (N = 52) were randomly allocated to four vemurafenib dose cohorts (240, 480, 720, or 960 mg bid for 14 days). After the day 15 morning dose, doses were interrupted until day 22, at which point patients were restarted on vemurafenib. Serial pharmacokinetic samples were collected after the morning dose on days 1, 9, and 15; trough pharmacokinetic samples were collected on day 2.
Results
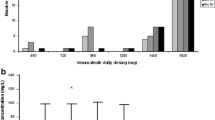
Vemurafenib concentration increased with multiple doses to steady state at day 15; C max, AUC0–8h, and AUC0–168h increased between 3.3- and 3.8-fold across the fourfold dose range tested. Statistical analysis indicated dose proportionality across the dose range of 240–960 mg bid. Day 15 mean accumulation ratios (ratio of AUC0–8h on day 15/AUC0–8h on day 1) ranged from ~19 to 25 across cohorts. At steady state, the peak-to-trough ratio for vemurafenib exhibited a relatively flat concentration–time profile throughout the bid dosing interval. During dose interruption (days 15–22), mean vemurafenib trough concentrations decreased to minimal levels; vemurafenib exhibited a mean terminal phase half-life of 31.5–38.4 h.
Conclusions
Vemurafenib plasma concentration accumulates with multiple bid doses of 240 mg. Vemurafenib exposure (AUC and C max) is dose proportional over the 240- to 960-mg bid dose range and exhibits constant drug levels over the bid dosing interval.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J, Ibrahim PN, Cho H, Spevak W, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Habets G, Burton EA, Wong B, Tsang G, West BL, Powell B, Shellooe R, Marimuthu A, Nguyen H, Zhang KY, Artis DR, Schlessinger J, Su F, Higgins B, Iyer R, D’Andrea K, Koehler A, Stumm M, Lin PS, Lee RJ, Grippo J, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, Chapman PB, Flaherty KT, Xu X, Nathanson KL, Nolop K (2010) Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature 467:596–599
Søndergaard JN, Nazarian R, Wang Q, Guo D, Hsueh T, Mok S, Sazegar H, MacConaill LE, Barretina JG, Kehoe SM, Attar N, von Euw E, Zuckerman JE, Chmielowski B, Comin-Anduix B, Koya RC, Mischel PS, Lo RS, Ribas A (2010) Differential sensitivity of melanoma cell lines with BRAFV600E mutation to the specific Raf inhibitor PLX4032. J Transl Med 8:39
Tsai J, Lee JT, Wang W, Zhang J, Cho H, Mamo S, Bremer R, Gillette S, Kong J, Haass NK, Sproesser K, Li L, Smalley KS, Fong D, Zhu YL, Marimuthu A, Nguyen H, Lam B, Liu J, Cheung I, Rice J, Suzuki Y, Luu C, Settachatgul C, Shellooe R, Cantwell J, Kim SH, Schlessinger J, Zhang KY, West BL, Powell B, Habets G, Zhang C, Ibrahim PN, Hirth P, Artis DR, Herlyn M, Bollag G (2008) Discovery of a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent antimelanoma activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:3041–3046
Thomas RK, Baker AC, Debiasi RM, Winckler W, Laframboise T, Lin WM, Wang M, Feng W, Zander T, MacConaill L, Lee JC, Nicoletti R, Hatton C, Goyette M, Girard L, Majmudar K, Ziaugra L, Wong KK, Gabriel S, Beroukhim R, Peyton M, Barretina J, Dutt A, Emery C, Greulich H, Shah K, Sasaki H, Gazdar A, Minna J, Armstrong SA, Mellinghoff IK, Hodi FS, Dranoff G, Mischel PS, Cloughesy TF, Nelson SF, Liau LM, Mertz K, Rubin MA, Moch H, Loda M, Catalona W, Fletcher J, Signoretti S, Kaye F, Anderson KC, Demetri GD, Dummer R, Wagner S, Herlyn M, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Garraway LA (2007) High-throughput oncogene mutation profiling in human cancer. Nat Genet 39:347–351
Shull AY, Latham-Schwark A, Ramasamy P, Leskoske K, Oroian D, Birtwistle MR, Buckhaults PJ (2012) Novel somatic mutations to PI3K pathway genes in metastatic melanoma. PLoS ONE 7:e43369
Gray-Schopfer V, Wellbrock C, Marais R (2007) Melanoma biology and new targeted therapy. Nature 445:851–857
Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC database): http://www.sanger.ac.uk/perl/genetics/CGP/cosmic; Release 51, Jan 2011
Wellbrock C, Karasarides M, Marais R (2004) The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:875–885
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, O’Dwyer PJ, Lee RJ, Grippo JF, Nolop K, Chapman PB (2010) Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:809–819
Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, Gonzalez R, Pavlick AC, Weber JS, McArthur GA, Hutson TE, Moschos SJ, Flaherty KT, Hersey P, Kefford R, Lawrence D, Puzanov I, Lewis KD, Amaravadi RK, Chmielowski B, Lawrence HJ, Shyr Y, Ye F, Li J, Nolop KB, Lee RJ, Joe AK, Ribas A (2012) Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with vemurafenib. N Engl J Med 366:707–714
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, Hogg D, Lorigan P, Lebbe C, Jouary T, Schadendorf D, Ribas A, O’Day SJ, Sosman JA, Kirkwood JM, Eggermont AM, Dreno B, Nolop K, Li J, Nelson B, Hou J, Lee RJ, Flaherty KT, McArthur GA, BRIM-3 Study Group (2011) Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 364:2507–2516
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Larkin J, Haanen JB, Ribas A, Hogg D, Hamid O, Ascierto P, Testori A, Lorigan P, Dummer R, Sosman JA, Garbe C, Maio M, Nolop K, Nelson BJ, Joe AK, Flaherty KT, McArthur GA (2012) Updated overall survival results for BRIM-3, a phase III randomized, open-label, multicenter trial comparing BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib with dacarbazine in previously untreated patients with BRAFV600E-mutated melanoma [abstract]. J Clin Oncol 30(suppl):8502. Available at: http://www.asco.org/ASCOv2/MultiMedia/Virtual+Meeting?&vmview=vm_session_presentations_view&confID=114&sessionID=4825
Shah N, Iyer RM, Mair H-J, Choi DS, Tian H, Diodone R, Fähnrich K, Pabst-Ravot A, Tang K, Scheubel E, Grippo JF, Moreira SA, Go Z, Mouskountakis J, Louie T, Ibrahim PN, Sandhu H, Rubia L, Chokshi H, Singhal D, Malick W (2013) Improved human bioavailability of vemurafenib, a practically insoluble drug, using an amorphous polymer stabilized solid dispersion prepared by a solvent controlled co-precipitation process. J Pharm Sci 102:967–981
Zelboraf® (vemurafenib) [prescribing information]. South San Francisco: Genentech, Inc.; 2012. Available at: http://www.gene.com/download/pdf/zelboraf_prescribing.pdf. Last Assessed 8 Apr 2013
Roberts MS, Magnusson BM, Burczynski FJ, Weiss M (2002) Enterohepatic circulation: physiological, pharmacokinetic and clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet 41:751–790
Shou M, Lu W, Kari PH, Xiang C, Lu P, Cui D, Emary WB, Michel KB, Adelsberger JK, Brunner JE, Rodrigues AD (2005) Population pharmacokinetic modeling for enterohepatic recirculation in Rhesus monkey. Eur J Pharm Sci 26:151–161
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Drs. Daniels, Hallmeyer, and Gajewski for their participation in the study. Support for third-party editing assistance for this manuscript was provided by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The study was sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Conflict of interest
Joseph Grippo is an employee of Hoffmann-La Roche, received financial support for this research, and is a shareholder of Hoffmann-La Roche. Weijing Zhang is an employee of Hoffmann-La Roche and received financial support for this research. Dominik Heinzmann is an employee of Hoffmann-La Roche, received financial support for this research, and is a shareholder of Hoffmann-La Roche. Kuo-Hsiung Yang was a previous employee of Hoffmann-La Roche but has no current conflicts of interest. Jenny Wong is an employee of Hoffmann-La Roche and a shareholder of Hoffmann-La Roche. Andrew Joe was a previous employee of Hoffmann-La Roche but has no current conflicts of interest. Pamela Munster has received financial support for research projects from Merck. Nenand Sarapa is an employee of Hoffmann-La Roche, received financial support for this research, and is a shareholder of Hoffmann-La Roche. Adil Daud has served as a consultant to Merck and Amgen. Dr. Daud has also received financial support for research projects from Genentech/Roche, GSK, Merck, OncoSec, Novartis, and Pfizer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grippo, J.F., Zhang, W., Heinzmann, D. et al. A phase I, randomized, open-label study of the multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of vemurafenib in patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic melanoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 103–111 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2324-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2324-5