Abstract
Background
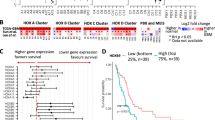
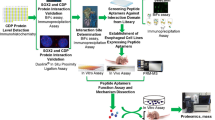
Meningiomas are the most common type of intracranial tumor, accounting for between 24 and 30 % of primary intracranial tumors. Thus far, no biomarkers exist to reliably predict the clinical outcome of meningiomas. A previous genome-wide methylation analysis revealed that HOXA9 is one of the most functionally relevant biomarkers. In this study, we have examined whether HOXA9 is a potential therapeutic target in meningiomas, using HXR9, a peptide inhibitor of the interaction between HOXA9 and its cofactor PBX.
Methods
We determined the expression level of HOXA9 in human meningiomas, meningioma cell lines, and normal brain tissue. Meningioma in culture and in subcutaneous tumors was treated with HXR9. We also examined the disruption of HOXA9/PBX dimers.
Results
We first confirmed that HOXA9 is highly expressed in meningiomas, but not in normal brain tissue. The HXR9 peptide blocks the binding of HOXA9 to PBX, leading to an alteration of DNA binding, and subsequent regulation of their target genes. HXR9 markedly inhibited the growth of meningioma cells and subcutaneous meningeal tumors.
Conclusion
There is no effective chemotherapy for meningiomas at present, and targeting the HOXA9/PBX interaction may represent a novel treatment option for this disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Hamada J, Takahashi O, Takahashi Y, Tada M, Miyamoto M, Morikawa T, Kondo S, Moriuchi T (2006) Disordered expression of HOX genes in human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep 15:797–802
Aghi MK, Carter BS, Cosgrove GR, Ojemann RG, Amin-Hanjani S, Martuza RL, Curry WT Jr, Barker FG (2009) Long-term recurrence rates of atypical meningiomas after gross total resection with or without postoperative adjuvant radiation. Neurosurgery 64:56–60
Andrae N, Kirches E, Hartig R, Haase D, Keilhoff G, Kalinski T, Mawrin C (2012) Sunitinib targets PDGF-receptor and Flt3 and reduces survival and migration of human meningioma cells. Euro J Cancer 48:1831–1841
Backer-Grøndahl T, Moen BH, Torp SH (2012) The histopathological spectrum of human meningiomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 5:231
Cantile M, Procino A, D’Armiento M, Cindolo L, Cillo C (2003) HOX gene network is involved in the transcriptional regulation of in vivo human adipogenesis. J Cell Physiol 194:225–236
Costa BM, Smith JS, Chen Y, Chen J, Phillips HS, Aldape KD, Zardo G, Nigro J, James CD, Fridlyand J, Reis RM, Costello JF (2010) Reversing HOXA9 oncogene activation by PI3 K inhibition: epigenetic mechanism and prognostic significance in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 70:453–462
Daniels TR, Neacato II, Rodriguez JA, Pandha HS, Morgan R, Penichet ML (2010) Disruption of HOX activity leads to cell death that can be enhanced by the interference of iron uptake in malignant B cells. Leuk Off J Leuk Soc Am Leuk Res Fund U.K 24:1555–1565
Durston AJ (2011) Hox homeotic selector genes: key regulators of embryogenesis. WebmedCentral EMBRYOLOGY 2:WMC002573
Eichhorst ST, Muller M, Li-Weber M, Schulze-Bergkamen H, Angel P, Krammer PH (2000) A novel AP-1 element in the CD95 ligand promoter is required for induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells upon treatment with anticancer drugs. Mol Cell Biol 20:7826–7837
Eklund EA (2007) The role of HOX genes in malignant myeloid disease. Cur Opin Hematol 14:85–89
Grier D, Thompson A, Kwasniewska A, McGonigle G, Halliday H, Lappin T (2005) The pathophysiology of HOX genes and their role in cancer. J Pathol 205:154–171
Hoegg S, Meyer A (2005) Hox clusters as models for vertebrate genome evolution. Trends Genet 21:421–424
Huang Y, Sitwala K, Bronstein J, Sanders D, Dandekar M, Collins C, Robertson G, MacDonald J, Cezard T, Bilenky M, Thiessen N, Zhao Y, Zeng T, Hirst M, Hero A, Jones S, Hess JL (2012) Identification and characterization of Hoxa9 binding sites in hematopoietic cells. Blood 119:388–398
Iimura T, Pourquié O (2007) Hox genes in time and space during vertebrate body formation. Dev Growth Differ 49:265–275
Kasibhatla S, Brunner T, Genestier L, Echeverri F, Mahboubi A, Green DR (1998) DNA damaging agents induce expression of Fas ligand and subsequent apoptosis in T lymphocytes via the activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1. Mol Cell 1:543–551
Kishida Y, Natsume A, Kondo Y, Takeuchi I, An B, Okamoto Y, Shinjo K, Saito K, Ando H, Ohka F (2012) Epigenetic subclassification of meningiomas based on genome-wide DNA methylation analyses. Carcinogenesis 33:436–441
Ko SY, Barengo N, Ladanyi A, Lee JS, Marini F, Lengyel E, Naora H (2012) HOXA9 promotes ovarian cancer growth by stimulating cancer-associated fibroblasts. J Clin Investig 122:3603–3617
Laurent A, Bihan R, Omilli F, Deschamps S, Pellerin I (2008) PBX proteins: much more than Hox cofactors. Int J Dev Biol 52:9
Maier H, Öfner D, Hittmair A, Kitz K, Budka H (1992) Classic, atypical, and anaplastic meningioma: three histopathological subtypes of clinical relevance. J Neurosurg 77:616–623
McIntyre DC, Rakshit S, Yallowitz AR, Loken L, Jeannotte L, Capecchi MR, Wellik DM (2007) Hox patterning of the vertebrate rib cage. Development 134:2981–2989
Miller GJ, Miller HL, van Bokhoven A, Lambert JR, Werahera PN, Schirripa O, Lucia MS, Nordeen SK (2003) Aberrant HOXC expression accompanies the malignant phenotype in human prostate. Cancer Res 63:5879–5888
Moens CB, Selleri L (2006) Hox cofactors in vertebrate development. Dev Biol 291:193–206
Morgan R, Boxall A, Harrington KJ, Simpson GR, Gillett C, Michael A, Pandha HS (2012) Targeting the HOX/PBX dimer in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136:389–398
Morgan R, Pirard PM, Shears L, Sohal J, Pettengell R, Pandha HS (2007) Antagonism of HOX/PBX dimer formation blocks the in vivo proliferation of melanoma. Cancer Res 67:5806
Morgan R, Plowright L, Harrington KJ, Michael A, Pandha HS (2010) Targeting HOX and PBX transcription factors in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 10:89
Plowright L, Harrington K, Pandha H, Morgan R (2009) HOX transcription factors are potential therapeutic targets in non-small-cell lung cancer (targeting HOX genes in lung cancer). Br J Cancer 100:470–475
Rich KA, Zhan Y, Blanks JC (1997) Aberrant expression of c-Fos accompanies photoreceptor cell death in the rd mouse. J Neurobiol 32:593–612
Shears L, Plowright L, Harrington K, Pandha HS, Morgan R (2008) Disrupting the interaction between HOX and PBX causes necrotic and apoptotic cell death in the renal cancer lines CaKi-2 and 769-P. J Urol 180:2196–2201
Shears L, Plowright L, Harrington K, Pandha HS, Morgan R (2008) Disrupting the interaction between HOX and PBX causes necrotic and apoptotic cell death in the renal cancer lines CaKi-2 and 769-P. J Urol 180:2196–2201
Waltregny D, Alami Y, Clausse N, de Leval J, Castronovo V (2002) Overexpression of the homeobox gene HOXC8 in human prostate cancer correlates with loss of tumor differentiation. Prostate 50:162–169
Watanabe R, Nakasu Y, Tashiro H, Mitsuya K, Ito I, Nakasu S, Nakajima T (2011) O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase expression in tumor cells predicts outcome of radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide therapy in patients with primary glioblastoma. Brain Tumor Pathol 28:127–135
Yaskiv O, Rubin BP, He H, Falzarano S, Magi-Galluzzi C, Zhou M (2012) ERG protein expression in human tumors detected with a rabbit monoclonal antibody. Am J Clin Pathol 138:803–810
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid (B) for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (AN).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ando, H., Natsume, A., Senga, T. et al. Peptide-based inhibition of the HOXA9/PBX interaction retards the growth of human meningioma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 53–60 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2316-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2316-5