Abstract
Purpose
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) shares common signal pathways and forms a heterodimer with EGFR. In this study, we investigated the clinical and pathologic implications of serum EGF levels in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
Methods
We analyzed serum EGF levels from baseline serum samples of consecutive patients with HER2-positive MBC who received first-line trastuzumab plus taxane chemotherapy and correlated them with treatment outcomes and pathologic features.
Results
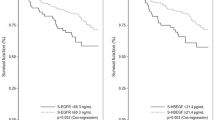
A total of 50 women were analyzed. The median age was 47 years (range 27–72 years). Patients with high serum EGF levels (≥10.0 pg/mL) had significantly longer overall survival (47.0 months (95 % confidence interval (CI) 28.3–65.7 months) vs. 23.3 months (95 % CI 13.5–33.1 months); p = 0.009) with a tendency toward longer progression-free survival (p = 0.123). Serum EGF levels were not associated with hematologic or cardiac adverse events. Progesterone receptor-positive patients had significantly higher serum EGF levels than progesterone receptor-negative patients (24.3 pg/mL (range 9.5–69.0 pg/mL) vs. 12.3 pg/mL (range 0.0–59.5 pg/mL); p = 0.006).
Conclusions
Our data suggest that high serum EGF levels may be associated with good prognosis in patients with HER2-positive MBC receiving trastuzumab plus taxane chemotherapy. In addition, serum EGF levels were associated with progesterone receptor positivity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235(4785):177–182
Ross JS, Fletcher JA (1998) The HER-2/neu oncogene in breast cancer: prognostic factor, predictive factor, and target for therapy. Oncologist 3(4):237–252
Noh JM, Choi DH, Huh SJ, Park W, Yang JH, Nam SJ, Im YH, Ahn JS (2011) Patterns of recurrence after breast-conserving treatment for early stage breast cancer by molecular subtype. J Breast Cancer 14(1):46–51. doi:10.4048/jbc.2011.14.1.46
Kong SY, do Lee H, Lee ES, Park S, Lee KS, Ro J (2006) Serum HER2 as a response indicator to various chemotherapeutic agents in tissue HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res Treatment 38(1):35–39. doi:10.4143/crt.2006.38.1.35
Lupu R, Dickson RB, Lippman ME (1992) The role of erbB-2 and its ligands in growth control of malignant breast epithelium. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 43(1–3):229–236. doi:0960-0760(92)90212-2
Mosesson Y, Yarden Y (2004) Oncogenic growth factor receptors: implications for signal transduction therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 14(4):262–270. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2004.04.005
Graus-Porta D, Beerli RR, Daly JM, Hynes NE (1997) ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J 16(7):1647–1655. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.7.1647
Revillion F, Lhotellier V, Hornez L, Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP (2008) ErbB/HER ligands in human breast cancer, and relationships with their receptors, the bio-pathological features and prognosis. Ann Oncol 19(1):73–80. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm431
Marty M, Cognetti F, Maraninchi D, Snyder R, Mauriac L, Tubiana-Hulin M, Chan S, Grimes D, Anton A, Lluch A, Kennedy J, O’Byrne K, Conte P, Green M, Ward C, Mayne K, Extra JM (2005) Randomized phase II trial of the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab combined with docetaxel in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer administered as first-line treatment: the M77001 study group. J Clin Oncol 23(19):4265–4274. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.173
Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, Gianni L, Baselga J, Bell R, Jackisch C, Cameron D, Dowsett M, Barrios CH, Steger G, Huang CS, Andersson M, Inbar M, Lichinitser M, Lang I, Nitz U, Iwata H, Thomssen C, Lohrisch C, Suter TM, Ruschoff J, Suto T, Greatorex V, Ward C, Straehle C, McFadden E, Dolci MS, Gelber RD (2005) Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353(16):1659–1672. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa052306
Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE Jr, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman PA, Swain SM, Pisansky TM, Fehrenbacher L, Kutteh LA, Vogel VG, Visscher DW, Yothers G, Jenkins RB, Brown AM, Dakhil SR, Mamounas EP, Lingle WL, Klein PM, Ingle JN, Wolmark N (2005) Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353(16):1673–1684. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa052122
Valabrega G, Montemurro F, Aglietta M (2007) Trastuzumab: mechanism of action, resistance and future perspectives in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Ann Oncol 18(6):977–984. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl475
Hudis CA (2007) Trastuzumab–mechanism of action and use in clinical practice. N Engl J Med 357(1):39–51. doi:10.1056/NEJMra043186
King CR, Borrello I, Bellot F, Comoglio P, Schlessinger J (1988) Egf binding to its receptor triggers a rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of the erbB-2 protein in the mammary tumor cell line SK-BR-3. EMBO J 7(6):1647–1651
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer A, McShane LM, Paik S, Pegram MD, Perez EA, Press MF, Rhodes A, Sturgeon C, Taube SE, Tubbs R, Vance GH, van de Vijver M, Wheeler TM, Hayes DF (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(1):118–145. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2775
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Han SW, Oh DY, Im SA, Park SR, Lee KW, Song HS, Lee NS, Lee KH, Choi IS, Lee MH, Kim MA, Kim WH, Bang YJ, Kim TY (2009) Phase II study and biomarker analysis of cetuximab combined with modified FOLFOX6 in advanced gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 100(2):298–304. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604861
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2003) Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol 21(14):2787–2799. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.01.504
Dotzlaw H, Miller T, Karvelas J, Murphy LC (1990) Epidermal growth factor gene expression in human breast cancer biopsy samples: relationship to estrogen and progesterone receptor gene expression. Cancer Res 50(14):4204–4208
Murphy LC, Murphy LJ, Dubik D, Bell GI, Shiu RP (1988) Epidermal growth factor gene expression in human breast cancer cells: regulation of expression by progestins. Cancer Res 48(16):4555–4560
DiAugustine RP, Petrusz P, Bell GI, Brown CF, Korach KS, McLachlan JA, Teng CT (1988) Influence of estrogens on mouse uterine epidermal growth factor precursor protein and messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology 122(6):2355–2363
Byyny RL, Orth DN, Cohen S, Doyne ES (1974) Epidermal growth factor: effects of androgens and adrenergic agents. Endocrinology 95(3):776–782
Wang J, Ohara N, Wang Z, Chen W, Morikawa A, Sasaki H, DeManno DA, Chwalisz K, Maruo T (2006) A novel selective progesterone receptor modulator asoprisnil (J867) down-regulates the expression of EGF, IGF-I, TGFbeta3 and their receptors in cultured uterine leiomyoma cells. Hum Reprod 21(7):1869–1877. doi:10.1093/humrep/del035
Reiner A, Neumeister B, Spona J, Reiner G, Schemper M, Jakesz R (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of estrogen and progesterone receptor and prognosis in human primary breast cancer. Cancer Res 50(21):7057–7061
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Seoul National University Hospital Research Fund (04-2009-0270); the Priority Research Centers Program (2009-0093820) and the Basic Science Research Program (2010-0022299) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology, Korea.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JW., Kim, J.H., Im, SA. et al. Serum epidermal growth factor is associated with prognosis and hormone receptor status in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer treated with first-line trastuzumab plus taxane chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72, 1023–1029 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2268-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2268-9