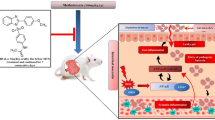
Abstract
Purpose
One of the major toxic side effects of methotrexate (MTX) is enterocolitis. To date, there is no efficient standard treatment for this side effect. Nitrosative stress is reported to play a critical role in MTX-induced mucositis. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether pretreatment with melatonin, an inhibitor of nitro-oxidative stress, prevents MTX-induced mucositis in rats.
Methods
Rats were pretreated with melatonin (20 and 40 mg/kg body weight) i.p. daily 1 h before MTX (7 mg/kg body weight) administration for three consecutive days. After the final dose of MTX, the rats were killed and the small intestines were used for analysis.
Results
The small intestines of MTX-treated rats showed moderate to severe injury. The villi were distorted, blunted, and atrophied and focally absent in various segments of the small intestines. Crypt abscesses were also found, suggesting an inflammatory response. Pretreatment with melatonin had a dose-dependent protective effect on MTX-induced mucositis. Morphology was saved to a moderate extent with 20 mg melatonin pretreatment, and near-normal morphology was achieved with 40 mg melatonin pretreatment. Damage to the villi and crypt abscess was reduced. The villi/crypt ratio was almost restored. Melatonin pretreatment protected the small intestines from MTX-induced damage by attenuating nitrosative stress, protein tyrosine nitration and PARP expression.
Conclusion
Because of its versatility in protecting against nitro-oxidative stress and reducing inflammation, we suggest that melatonin could be beneficial in ameliorating MTX-induced enteritis in humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardeland R, Coto-Montes A, Poeggeler B (2003) Circadian rhythms, oxidative stress and antioxidative defense mechanisms. Chronobiol Int 20:921–962
Burger D, Travis S (2011) Conventional medical management of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 140:1827–1837
Saibeni S, Bollani S, Losco A, Michielan A, Sostegni R, Devani M, Lupinacci G, Pirola L, Cucino C, Meucci G, Basilisco G, D’Incà R, Bruno S (2012) The use of methotrexate for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in clinical practice. Dig Liver Dis 44:123–127
Muscaritoli M, Grieco G, Capria S, Iori AP, Rossi Fanelli F (2002) Nutritional and metabolic support in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Am J Clin Nutr 75:183–190
Keefe DM, Gibson RJ, Hauer-Jensen M (2004) Gastrointestinal mucositis. Semin Oncol Nurs 20:38–47
Nagakubo J, Tomimatsu T, Kitajima M, Takayama H, Aimi N, Horie T (2001) Characteristics of transport of fluoresceinated methotrexate in rat small intestine. Life Sci 69:739–747
Keefe DM, Cummins AG, Dale BM, Kotasek D, Robb TA, Sage RE (1997) Effect of high-dose chemotherapy on intestinal permeability in humans. Clin Sci (Lond) 92:385–389
Pico JL, Avila-Garavito A, Naccache P (1998) Mucositis: its occurrence, consequences, and treatment in the oncology setting. Oncologist 3:446–451
Ballabeni V, Ghizzardi P, Cattaruzza F, Bertoni S, Lagrasta CA, Impicciatore M (2006) The selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase prevents intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Nitric Oxide 14:212–218
Dong W, Mei Q, Yu J, Xu J-M, Xiang L, Xu Y (2003) Effect of melatonin on the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in rat models of colitis. World J Gastroenterol 9:1307–1311
Hosoi T, Goto H, Arisawa T (2001) Role of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in experimental colitis induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28:9–12
Bian K, Harari Y, Zhong M, Lai M, Castro G, Weisbrodt N, Murad F (2001) Down-regulation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase (NOS-2) during parasite-induced gut inflammation: a path to identify a selective NOS-2 inhibitor. Mol Pharmacol 59:939–947
Kolli VK, Abraham P, Rabi S (2008) Methotrexate-induced nitrosative stress may play a critical role in small intestinal damage in the rat. Arch Toxicol 82:763–770
Leitão RF, Brito GA, Oriá RB, Braga-Neto MB, Bellaguarda EA, Silva JV, Gomes AS, Lima-Júnior RC, Siqueira FJ, Freire RS, Vale ML, Ribeiro RA (2011) Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway on methotrexate-induced intestinal mucositis in rodents. BMC Gastroenterol 11:90–111
El-Boghdady NA (2011) Protective effect of ellagic acid and pumpkin seed oil against methotrexate-induced small intestine damage in rats. Indian J Biochem Biophys 48:380–387
Sewerynek E, Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D (1996) Oxidative damage in the liver induced by ischemia reperfusion: protection by melatonin. Hepatogastroenterology 43:898–905
Chang HM, Ling EA, Chen CF, Lue H, Wen CY, Shieh JY (2002) Melatonin attenuates the neuronal NADPH-d/NOS expression in the no dose ganglion of acute hypoxic rats. J Pineal Res 32:65–73
Ersoz N, Guven A, Cayci T, Uysal B, Turk E, Oztas E, Akgul EO, Korkmaz A, Cetiner S (2009) Comparison of the efficacy of melatonin and 1,400 W on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: a role for inhibiting iNOS. Ren Fail 31:704–710
Kelly RW, Amato F, Seamark RF (1984) N-Acetyl-5-methoxy kynurenamine, a brain metabolite of melatonin, is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 121:372–379
Szabó C (2006) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase activation by reactive nitrogen species—relevance for the pathogenesis of inflammation. Nitric Oxide 14:169–179
Razzouk BI, Rose SR, Hongeng S, Wallace D, Smeltzer MP, Zacher M, Pui CH, Hudson MM (2007) Obesity in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:1183–1189
Kehoe JE, Harvey LP, Daly JM (1986) Alteration of chemotherapy toxicity using a chemically defined liquid diet in rats. Cancer Res 46:4047–4052
Warden RA, Noltorp RS, Lynn Francis J, Dunkley PR, O’Loughlin EV (1997) Vitamin A deficiency exacerbates methotrexate-induced jejunal injury in rats. J Nutr 127:770–776
Ucar M, Korkmaz A, Reiter RJ (2007) Melatonin alleviates lung damage induced by the chemical warfare agent nitrogen mustard. Toxicol Lett 173:124–131
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ, Gurd FN (1970) Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. I. A morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg 101:478–483
Cuzzocrea S, Zingarelli B, Costantino G (1997) Beneficial effects of 3-aminobenzamide, an inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase in a rat model of splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion. Br J Pharmacol 121:1065–1074
Sastry KV, Moudgal RP, Mohan J, Tyagi JS, Rao GS (2002) Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper–cadmium alloy. Anal Biochem 306:79–82
Kupper JH, van Gool L, Muller M (1996) Detection of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase and its reaction product by immunohistochemistry. Histochem J 28:391–395
Bubenik GA, Pang SF, Cockshut JR (2000) Circadian variation of portal, arterial and venous blood levels of melatonin in pigs and its relationship to food intake and sleep. J Pineal Res 28:9–15
Stefulj J, Hörtner M, Ghosh M (2001) Gene expression of the key enzymes of melatonin synthesis in extrapineal tissues of the rat. J Pineal Res 30:243–247
Bubenik GA, Brown GM (1997) Pinealectomy reduces melatonin levels in the serum but not in the gastrointestinal tract of rats. Biol Signals 6:40–44
Kvetnoy IM, Ingel IE, Kvetnaia TV, Malinovskaya NK, Rapoport SI, Raikhlin NT, Trofimov AV, Yuzhakov VV (2002) Gastrointestinal melatonin: cellular identification and biological role. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 23:121–132
Lee PPN, Pang SF (1993) Melatonin and its receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. Biol Signals 2:181–193
Pandi-Perumal SR, Srinivasan V, Maestroni GJM, Cardinali DP, Poeggeler B, Hardeland R (2006) Melatonin nature is most versatile biological signal? FEBS J 273:2813–2838
Seabra ML, Bignotto M, Pinto LR Jr, Tufik S (2000) Randomized, double-blind clinical trial, controlled with placebo, of the toxicology of chronic melatonin treatment. J Pineal Res 29:193–200
Weishaupt JH, Bartels C, Pölking E, Dietrich J, Rohde G, Poeggeler B, Mertens N, Sperling S, Bohn M, Hüther G, Schneider A, Bach A, Sirén AL, Hardeland R, Bähr M, Nave KA, Ehrenreich H (2006) Reduced oxidative damage in ALS by high-dose enteral melatonin treatment. J Pineal Res 41:313–323
Nordlund JJ, Lerner AB (1977) The effects of oral melatonin on skin color and on the release of pituitary hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 45:768–774
Lusardi P, Piazza E, Fogari R (2000) Cardiovascular effects of melatonin in hypertensive patients well controlled by nifedipine: a 24-hour study. Br J Clin Pharmacol 49:423–427
Lewy AJ, Ahmed S, Sack RL (1996) Phase shifting the human circadian clock using melatonin. Behav Brain Res 73:131–134
Brzezinski A (1997) Melatonin in humans. N Engl J Med 336:186–195
Bejarano I, Espino J, Barriga C, Reiter RJ, Pariente JA, Rodríguez AB (2011) Pro-oxidant effect of melatonin in tumour leucocytes: relation with its cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic effects. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 108:14–20
Kadoma Y, Fujisawa S (2011) Radical-scavenging activity of melatonin, either alone or in combination with vitamin E, ascorbate or 2-mercaptoethanol as co-antioxidants, using the induction period method. In vivo 25:49–53
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank CSIR, New Delhi, for the financial support. Mr. Viswa Kalyan Kolli is a senior research fellow on the project.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolli, V.K., Kanakasabapathy, I., Faith, M. et al. A preclinical study on the protective effect of melatonin against methotrexate-induced small intestinal damage: effect mediated by attenuation of nitrosative stress, protein tyrosine nitration, and PARP activation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71, 1209–1218 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2115-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2115-z