Abstract
Purpose
Comparative pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of the mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) in rats and mice.
Methods
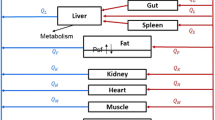
Blood cell partitioning, plasma protein binding and PK parameters of RAD001 in blood and tissues (including brain) of both mice and rats were determined. PK modeling predicted plasma/blood and tumor levels from a variety of regimens and these were compared with the known human PK profile. DCE-MRI was used to compare tumor vascularity between mice and rats. Estimation of IC50 values in vitro and ED50 values in vivo were used to provide an indication of anti-tumor activity.
Results
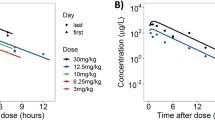
The PK properties of RAD001 differed between mice and rats, including erythrocyte partitioning, plasma protein binding, plasma/blood t 1/2, oral bioavailability, volume of distribution, tissue/tumor penetration and elimination. Modeling of tumor and blood/plasma PK suggested that in mice, multiple daily administrations result in a ~2-fold increase in tumor levels of RAD001 at steady state, whereas in rats, a ~7.9-fold increase would occur. Weekly high-dose regimens were predicted not to facilitate tumor accumulation in either species. Total tumor levels of RAD001 were four- to eight-fold greater in rats than in mice. Rat tumors had a >2-fold greater plasma content and permeability compared to mouse tumors, which could contribute to differences in tumor drug uptake. Maximal antitumor effects (T/C of 0.04–0.35) were observed in both species after daily administration with similar C max and AUC values of unbound (free) RAD001. These free levels of RAD001 are exceeded in serum from cancer patients receiving clinically beneficial daily regimens. In rodents, brain penetration of RAD001 was poor, but was dose-dependent and showed over-proportional uptake in rats with a longer t 1/2 compared to the systemic circulation.
Conclusions
The PK of RAD001 differed between mice and rats, with rats having a PK profile closer to that of humans. High intermittent doses of RAD001 may be more appropriate for treatment of brain tumors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulay A, Lane HA (2007) The mammalian target of rapamycin kinase and tumor growth inhibition. Recent Results Cancer Res 172:99–124
Albanell J, Dalmases A, Rovira A, Rojo F (2007) mTOR signalling in human cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 9:484–493
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM (2007) Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell 12:9–22
Abraham RT, Eng CH (2008) Mammalian target of rapamycin as a therapeutic target in oncology. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12:209–222
Jiang BH, Lui LZ (2008) Role of mTOR in anticancer drug resistance: perspectives for improved drug treatment. Drug Resist Updat 11:63–76
Lane HA, Wood JM, McSheehy PM, Allegrini PR, Boulay A, Brueggen J, Littlewood-Evans A, Maira SM, Martiny-Baron G, Schnell CR, Sini P, O’Reilly T (2009) Evaluation in vitro and in vivo of the anti-angiogenic/anti-vascular properties of the mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) has antiangiogenic/vascular properties distinct from a VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 15:1612–1622
Shinohara ET, Cao C, Niermann K, Mu Y, Zeng F, Hallahan DE, Lu B (2005) Enhanced radiation damage of tumor vasculature by mTOR inhibitors. Oncogene 24:5414–5422
Beuvink I, Boulay A, Fumagalli S, Zilbermann F, Ruetz S, O’Reilly T, Natt F, Hall J, Lane HA, Thomas G (2005) The mTOR inhibitor RAD001 sensitizes tumor cells to DNA-damaged induced apoptosis through inhibition of p21 translation. Cell 120:747–5938
Boulay A, Zumstein-Mecker S, Stephan C, Stephan C, Beuvink I, Zilbermann F, Haller R, Tobler S, Heusser C, O’Reilly T, Stolz B, Marti A, Thomas G, Lane HA (2004) Antitumor efficacy of intermittent treatment schedules with the rapamycin derivative RAD001 correlates with prolonged inactivation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cancer Res 64:252–261
Mabuchi S, Altomare DA, Cheung M, Zhang L, Poulikakos PI, Hensley HH, Schilder RJ, Ozols RF (2007) Testa JR (2007) RAD001 inhibits human ovarian cancer cell proliferation, enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis, and prolongs survival in an ovarian cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 13:4261–4270
Mabuchi S, Altomare DA, Connolly DC, Klein-Szanto A, Litwin S, Hoelzle MK, Hensley HH, Hamilton TC, Testa JR (2007) RAD001 (Everolimus) delays tumor onset and progression in a transgenic mouse model of ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 67:2408–2413
Awada A, Cardoso F, Fontaine C et al (2008) The oral mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (everolimus) in combination with letrozole in patients with advanced breast cancer: results of a phase I study with pharmacokinetics. Eur J Cancer 44:84–91
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Urbanowitz G, Berg WJ, Kay A, Lebwohl D, Ravaud A; RECORD-1 Study Group (2008) Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet 372(9637):449–456
O’Donnell A, Faivre S, Burris HA, Rea D, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Shand N, Lane HA, Hazell K, Zoellner U, Kovarik JM, Brock C, Jones S, Raymond E, Judson I (2008) I.Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 26:1588–1595
Tabernero J, Rojo F, Calvo E, Burris H, Judson I, Hazell K, Martinelli E, Ramon y Cajal S, Jones S, Vidal L, Shand N, Macarulla T, Ramos FJ, Dimitrijevic S, Zoellner U, Tang P, Stumm M, Lane HA, Lebwohl D, Baselga J (2008) Dose- and schedule-dependent inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway with everolimus: a phase I tumor pharmacodynamic study in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 26:1603–1610
Crowe A, Bruelisauer A, Duerr L, Guntz P, Lemaire M (1999) Absorption and intestinal metabolism of SDZ-RAD and rapamycin in rats. Drug Metab Dispos 27:627–632
Laplanche R, Meno-Tetang GML, Kawai R (2007) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of everolimus (RAD001) in rats involving non-linear tissue uptake. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodynam 34:373–400
Kirchner GI, Meier-Wiedenbach I, Manns MP (2004) Clinical pharmacokinetics of everolimus. Pharmacokinet 43:83–95
Kovarik JM, Beyer D, Bizot MN, Jiang Q, Allison MJ, Schmouder RL (2005) Pharmacokinetic interaction between verapamil and everolimus in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 60:434–437
Kovarik JM, Kaplan B, Tedesco Silva H, Kahan BD, Dantal J, Vitko S, Boger R, Rordorf C (2002) Exposure-response relationships for everolimus in de novo kidney transplantation: defining a therapeutic range. Transplantation 73:920–925
Fouladi M, Laningham F, Wu J, O’Shaughnessy MA, Molina K, Broniscer A, Spunt SL, Luckett I, Stewart CF, Houghton PJ, Gilbertson RJ, Furman WL (2007) Phase I study of everolimus in pediatric patients with refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 25:4806–4812
Tanaka C, O’Reilly T, Kovarik JM, Shand N, Hazell K, Judson I, Raymond E, Zumstein-Mecker S, Stephan C, Boulay A, Hattenberger M, Thomas G, Lane HA (2008) Identifying optimal biologic doses of everolimus (RAD001) in patients with cancer based on the modeling of preclinical and clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data. J Clin Oncol 26:1596–1602
Weidensteiner C, Rausch M, McSheehy PM, Allegrini PR (2006) Quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in tumor-bearing rats and mice with inversion recovery TrueFISP and two contrast agents at 4.7 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:646–656
Ebenhan T, Honer M, Amethamey S, Schubiger P, Becquet M, Ferretti S, Cannet C, Rausch M, McSheehy P (2009) Comparison of [18F]-tracers in various experimental tumour models by PET imaging and identification of an early response biomarker for the novel microtubule stabiliser patupilone. Mol Imaging Biol (published on-line, May 2009)
Ludden TM, Beal SL, Sheiner LB (1994) Comparison of the Akaike Information Criterion, the Schwarz Criterion and the F-test as guides to model selection. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 22:431–445
Boernsen KO, Egge-Jacobsen W, Inverardi B, Strom T, Streit F, Schiebel HM, Benet LZ, Christians U (2007) Assessment and validation of the MS/MS fragmentation patterns of the macrolide immunosuppressant everolimus. J Mass Spectrom 42:793–802
Blakeley J (2008) Drug delivery to brain tumors. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 8:235–241
de Vries NA, Beijnen JH, Boogerd W, van Tellingen O (2006) Blood-brain barrier and chemotherapeutic treatment of brain tumors. Expert Rev Neurother 6:1199–1209
Yang L, Clarke MJ, Carlson BL, Mladek AC, Schroeder MA, Decker P, Wu W, Kitange GJ, Grogan PT, Goble JM, Uhm J, Galanis E, Giannini C, Lane HA, James CD, Sarkaria JN (2008) PTEN loss does not predict for response to RAD001 (Everolimus) in a glioblastoma orthotopic xenograft test panel. Clin Cancer Res 14:3993–4001
Chu C, Abbara C, Noël-Hudson MS, Thomas-Bourgneuf L, Gonin P, Farinotti R, Bonhomme-Faivre L- (2009) Disposition of everolimua in mdr1a-/mdr1b mice and after a pre-treatment of lapatinib in Swiss mice. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1629–1634
Yokomasu A, Yano I, Sato E, Masuda S, Katsura T, Inui K (2008) Effect of intestinal and hepatic first-pass extraction on the pharmacokinetics of everolimus in rats. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 22:469–475
Harrer JU, Parker GJ, Haroon HA, Buckley DL, Embelton K, Roberts C, Balériaux D, Jackson A (2004) Comparative study of methods for determining vascular permeability and blood volume in human gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:748–757
Fisher MJ, Adamson PC (2002) Anti-angiogenic agents for the treatment of brain tumors. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 12:477–499
Folkerth RD (2000) Descriptive analysis and quantification of angiogenesis in human brain tumors. J Neurooncol 50:165–172
Acknowledgments
M. Lemaire, J. Figueiredo, G. Kraus and H. Kaufmann are thanked for their input in obtaining part of the data. Melanie Muller, Marc Hattenberger, Julianne Vaxelaire, and Stephane Ferretti provided excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Reilly, T., McSheehy, P.M.J., Kawai, R. et al. Comparative pharmacokinetics of RAD001 (everolimus) in normal and tumor-bearing rodents. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 65, 625–639 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-009-1068-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-009-1068-8