Abstract
Purpose
In this study, the antitumoral potential of a novel lectin (CvL) purified from the marine sponge Cliona varians was studied in different cancer cell lines.
Methods
CvL cytotoxicity was evaluated in mammalian tumor cells and in normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes by the MTT assay using the same range of concentrations (1–150 µg ml−1). The mechanisms involved in K562 cell death were investigated by confocal fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry and immunoblot.
Results
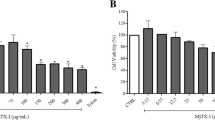
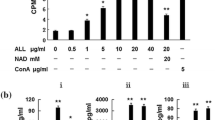
CvL inhibited the growth of human leukemia cells, with IC50 values of 70 and 100 µg ml−1 for K562 and JURKAT cells, respectively, but it was ineffective on blood lymphocytes and solid tumor cell lines. K562 cell death occurred 72 h after exposure to the lectin and with signs of apoptosis, as analyzed by DAPI and annexin V/PI staining. Investigation of the possible mediators of this process showed that cell death occurred via a caspase-independent pathway. Confocal fluorescence microscopy indicated a pivotal role for the lysosomal protease cathepsin B in mediating cell death. Accordingly, pre-incubation of K562 cells with the cathepsin inhibitor l-trans-epoxysuccinyl-l-leucylamido-(4-guanidino)butane (E-64) abolished CvL cytotoxic effect. Furthermore, we found upregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) and down-modulation of p65 subunit of nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) expression in CvL-treated cells. These effects were accompanied by increased levels of p21 and reduced expression of pRb, suggesting that CvL can induce cell cycle arrest.
Conclusions
Collectively, these findings indicate an antileukemic effect for CvL and suggest that cathepsin B acts as a death mediator in CvL-induced cytotoxicity possibly in an uncharacterized connection with the membrane death receptor pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broker LE, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G (2005) Cell death independent of caspases: a review. Clin Cancer Res 11:3155–3162
Fehrenbacher N, Jaattela M (2005) Lysosomes as targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Res 65:2993–2995
Guicciardi ME, Leist M, Gores GJ (2004) Lysosomes in cell death. Oncogene 23:2881–2890
Sharon N (1984) Carbohydrates as recognition determinants in phagocytosis and in lectin-mediated killing of target cells. Biol Cell 51(2):239–245
Abdullaev FI, de Mejia EG (1997) Antitumor effect of plant lectins. Nat Toxins 5:157–163
Atta AM, Barralnetto M, Peixinho S, Sousaatta MLB (1989) Isolation and functional-characterization of a mitogenic lectin from the marine sponge Cinachyrella alloclada. Braz J Med Biol Res 22:379–385
Hajto T, Hostanska K, Berki T, Palinkas L, Boldizsar F, Nemeth P (2005) Oncopharmacological perspectives of a plant lectin (Viscum album agglutinin-I): overview of recent results from in vitro experiments and in vivo animal models, and their possible relevance for clinical applications. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2:59–67
Wang H, Ng TB, Ooi VE, Liu WK (2000) Effects of lectins with different carbohydrate-binding specificities on hepatoma, choriocarcinoma, melanoma and osteosarcoma cell lines. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32:365–372
Arenas MI, Romo E, de Gaspar I, de Bethencourt FR, Sanchez-Chapado M, Fraile B, Paniagua R (1999) A lectin histochemistry comparative study in human normal prostate, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and prostatic carcinoma. Glycoconj J 16:375–382
Gorelik E, Galili U, Raz A (2001) On the role of cell surface carbohydrates and their binding proteins (lectins) in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 20:245–277
Opric MM, Poznanovic S, Kljajic Z, Sladic D, Pupic G, Perunovic B, Gasic MJ (1996) Labelling of breast carcinoma, thyroid carcinoma and melanoma with manno- and galacto-specific lectins from marine invertebrates. Eur J Histochem 40:211–218
Bantel H, Engels IH, Voelter W, Schulze-Osthoff K, Wesselborg S (1999) Mistletoe lectin activates caspase-8/FLICE independently of death receptor signaling and enhances anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 59:2083–2090
Miyoshi N, Koyama Y, Katsuno Y, Hayakawa S, Mita T, Ohta T, Kaji K, Isemura M (2001) Apoptosis induction associated with cell cycle dysregulation by rice bran agglutinin. J Biochem (Tokyo) 130:799–805
Ohba H, Moriwaki S, Bakalova R, Yasuda S, Yamasaki N (2004) Plant-derived abrin-a induces apoptosis in cultured leukemic cell lines by different mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 195:182–193
Park R, Kim MS, So HS, Jung BH, Moon SR, Chung SY, Ko CB, Kim BR, Chung HT (2000) Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in mistletoe lectin II-induced apoptosis of human myeloleukemic U937 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1685–1691
Yoon TJ, Yoo YC, Kang TB, Shimazaki K, Song SK, Lee KH, Kim SH, Park CH, Azuma I, Kim JB (1999) Lectins isolated from Korean mistletoe (Viscum album coloratum) induce apoptosis in tumor cells. Cancer Lett 136:33–40
Inamori K, Saito T, Iwaki D, Nagira T, Iwanaga S, Arisaka F, Kawabata S (1999) A newly identified horseshoe crab lectin with specificity for blood group A antigen recognizes specific O-antigens of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Biol Chem 274:3272–3278
Okino N, Kawabata S, Saito T, Hirata M, Takagi T, Iwanaga S (1995) Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of a 27-kDa lectin (L10) from horseshoe crab hemocytes. J Biol Chem 270:31008–31015
Pajic I, Kljajic Z, Dogovic N, Sladic D, Juranic Z, Gasic MJ (2002) A novel lectin from the sponge Haliclona cratera: isolation, characterization and biological activity. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 132:213–221
Schroder HC, Kljajic Z, Wegner R, Reuter P, Gasic M, Uhlenbruck G, Kurelac B, Muller WEG (1990) The galactose-specific lectin from the sponge Chondrilla nucula displays anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity in vitro via stimulation of the (2′-5′) oligoadenylate metabolism. Antivir Chem Chemother 1(2):99–105
Fukuda Y, Sugahara T, Ueno M, Fukuta Y, Ochi Y, Akiyama K, Miyazaki T, Masuda S, Kawakubo A, Kato K (2006) The anti-tumor effect of Euchema serra agglutinin on colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Drugs 17:943–947
Moura RM, Queiroz AF, Fook JM, Dias AS, Monteiro NK, Ribeiro JK, Moura GE, Macedo LL, Santos EA, Sales MP (2006) CvL, a lectin from the marine sponge Cliona varians: isolation, characterization and its effects on pathogenic bacteria and Leishmania promastigotes. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 145:517–523
Debray H, Decout D, Strecker G, Spik G, Montreuil J (1981) Specificity of 12 Lectins towards oligosaccharides and glycopeptides related to N-glycosylproteins. Eur J Biochem 117:41–55
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–683
Bromberg N, Justo GZ, Haun M, Duran N, Ferreira CV (2005) Violacein cytotoxicity on human blood lymphocytes and effect on phosphatases. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 20:449–454
de Carvalho DD, Costa FT, Duran N, Haun M (2006) Cytotoxic activity of violacein in human colon cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro 20:1514–1521
Guicciardi ME, Deussing J, Miyoshi H, Bronk SF, Svingen PA, Peters C, Kaufmann SH, Gores GJ (2000) Cathepsin B contributes to TNF-alpha-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis by promoting mitochondrial release of cytochrome c. J Clin Invest 106:1127–1137
Hartree EF (1972) Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem 48:422–427
Foghsgaard L, Wissing D, Mauch D, Lademann U, Bastholm L, Boes M, Elling F, Leist M, Jaattela M (2001) Cathepsin B acts as a dominant execution protease in tumor cell apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor. J Cell Biol 153:999–1010
Mathiasen IS, Hansen CM, Foghsgaard L, Jaattela M (2001) Sensitization to TNF-induced apoptosis by 1, 25-dihydroxy vitamin D(3) involves up-regulation of the TNF receptor 1 and cathepsin B. Int J Cancer 93:224–231
Turk B, Stoka V (2007) Protease signalling in cell death: caspases versus cysteine cathepsins. FEBS Lett 581:2761–2767
Nakanishi C, Toi M (2005) Nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitors as sensitizers to anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 5:297–309
Kirchner D, Duyster J, Ottmann O, Schmid RM, Bergmann L, Munzert G (2003) Mechanisms of Bcr-Abl-mediated NF-kappaB/Rel activation. Exp Hematol 31:504–511
Reuther JY, Reuther GW, Cortez D, Pendergast AM, Baldwin AS Jr (1998) A requirement for NF-kappaB activation in Bcr-Abl-mediated transformation. Genes Dev 12:968–981
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Sanchez-Garcia I, Grutz G (1995) Tumorigenic activity of the BCR-ABL oncogenes is mediated by BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5287–5291
Desrivieres S, Volarevic S, Mercep L, Ferrari S (1997) Evidence for different mechanisms of growth inhibition of T-cell lymphoma by phorbol esters and concanavalin A. J Biol Chem 272:2470–2476
Kulkarni GV, McCulloch CA (1995) Concanavalin A induced apoptosis in fibroblasts: the role of cell surface carbohydrates in lectin mediated cytotoxicity. J Cell Physiol 165:119–133
Cragg GM, Newman DJ, Yang SS (2006) Natural product extracts of plant and marine origin having antileukemia potential. The NCI experience. J Nat Prod 69:488–498
McGahon A, Bissonnette R, Schmitt M, Cotter KM, Green DR, Cotter TG (1994) BCR-ABL maintains resistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to apoptotic cell death. Blood 83:1179–1187
Vancompernolle K, Van Herreweghe F, Pynaert G, Van de Craen M, De Vos K, Totty N, Sterling A, Fiers W, Vandenabeele P, Grooten J (1998) Atractyloside-induced release of cathepsin B, a protease with caspase-processing activity. FEBS Lett 438:150–158
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Corey SJ, Dent P, Grant S (2004) A Bcr/Abl-independent, Lyn-dependent form of imatinib mesylate (STI-571) resistance is associated with altered expression of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem 279:34227–34239
Cortez D, Reuther G, Pendergast AM (1997) The Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase activates mitogenic signaling pathways and stimulates G1-to-S phase transition in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 15:2333–2342
Joyce D, Albanese C, Steer J, Fu M, Bouzahzah B, Pestell RG (2001) NF-kappaB and cell-cycle regulation: the cyclin connection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 12:73–90
Niculescu AB 3rd, Chen X, Smeets M, Hengst L, Prives C, Reed SI (1998) Effects of p21(Cip1/Waf1) at both the G1/S and the G2/M cell cycle transitions: pRb is a critical determinant in blocking DNA replication and in preventing endoreduplication. Mol Cell Biol 18:629–643
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (FINEP) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). The authors thank the Hemonorte, Natal, RN, Brazil, for the generous blood bag donation. R.A.S. was supported by a PhD fellowship from FAPESP (proc. 06/07315-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
A. F. S. Queiroz and R. A. Silva contributed equally to this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Queiroz, A.F.S., Silva, R.A., Moura, R.M. et al. Growth inhibitory activity of a novel lectin from Cliona varians against K562 human erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63, 1023–1033 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0825-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0825-4