Abstract
Background
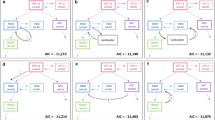
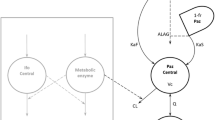
Enterohepatic recirculation of irinotecan and one of its metabolites, SN-38, has been observed in pharmacokinetic data sets from previous studies. A mathematical model that can incorporate this phenomenon was developed to describe the pharmacokinetics of irinotecan and its metabolites.
Patients and methods
A total of 32 patients with recurrent malignant glioma were treated with weekly intravenous administration of irinotecan at a dose of 125 mg/m2. Plasma concentrations of irinotecan and its three major metabolites were determined. Pharmacokinetic models were developed and tested for simultaneous fit of parent drug and metabolites, including a recirculation component.
Results
Rebound in the plasma concentration suggestive of enterohepatic recirculation at approximately 0.5–1 h post-infusion was observed in most irinotecan plasma concentration profiles, and in some plasma profiles of the SN-38 metabolite. A multi-compartment model containing a recirculation chain was developed to describe this process. The recirculation model was optimal in 22 of the 32 patients compared to the traditional model without the recirculation component.
Conclusion
A recirculation chain incorporated in a multi-compartment pharmacokinetic model of irinotecan and its metabolites appears to improve characterization of this drug’s disposition in patients with glioma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clamp AR, Maenpaa J, Cruickshank D, Ledermann J, Wilkinson PM, Welch R, Chan S, Vasey P, Sorbe B, Hindley A, Jayson GC (2006) SCOTROC 2B: feasibility of carboplatin followed by docetaxel or docetaxel-irinotecan as first-line therapy for ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 94(1):55–61
Matsumoto K, Katsumata N, Yamanaka Y, Yonemori K, Kohno T, Shimizu C, Andoh M, Fujiwara Y (2006) The safety and efficacy of the weekly dosing of irinotecan for platinum- and taxanes-resistant epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 100(2):412–416
Pitot HC, Wender DB, O’Connell MJ, Schroeder G, Goldberg RM, Rubin J, Mailliard JA, Knost JA, Ghosh C, Kirschling RJ, Levitt R, Windschitl HE (1997) Phase II trial of irinotecan in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 15(8):2910–2919
Conti JA, Kemeny NE, Saltz LB, Huang Y, Tong WP, Chou TC, Sun M, Pulliam S, Gonzalez C (1996) Irinotecan is an active agent in untreated patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 14(3):709–715
Stupp R, Hegi ME, van den Bent MJ, Mason WP, Weller M, Mirimanoff RO, Cairncross JG (2006) Changing paradigms—an update on the multidisciplinary management of malignant glioma. Oncologist 11(2):165–180
Slatter JG, Su P, Sams JP, Schaaf LJ, Wienkers LC (1997) Bioactivation of the anticancer agent CPT-11 to SN-38 by human hepatic microsomal carboxylesterases and the in vitro assessment of potential drug interactions. Drug Metab Dispos 25(10):1157–1164
Humerickhouse R, Lohrbach K, Li L, Bosron WF, Dolan ME (2000) Characterization of CPT-11 hydrolysis by human liver carboxylesterase isoforms hCE-1 and hCE-2. Cancer Res 60(5):1189–1192
Iyer L, King CD, Whitington PF, Green MD, Roy SK, Tephly TR, Coffman BL, Ratain MJ (1998) Genetic predisposition to the metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11). Role of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase isoform 1A1 in the glucuronidation of its active metabolite (SN-38) in human liver microsomes. J Clin Invest 101(4):847–854
Rivory LP, Robert J (1995) Identification and kinetics of a beta-glucuronide metabolite of SN-38 in human plasma after administration of the camptothecin derivative irinotecan. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 36(2):176–179
Catimel G, Chabot GG, Guastalla JP, Dumortier A, Cote C, Engel C, Gouyette A, Mathieu-Boue A, Mahjoubi M, Clavel M (1995) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan (CPT-11) administered daily for three consecutive days every three weeks in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann Oncol 6(2):133–140
Canal P, Gay C, Dezeuze A, Douillard JY, Bugat R, Brunet R, Adenis A, Herait P, Lokiec F, Mathieu-Boue A (1996) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of irinotecan during a phase II clinical trial in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 14(10):2688–2695
Santos A, Zanetta S, Cresteil T, Deroussent A, Pein F, Raymond E, Vernillet L, Risse ML, Boige V, Gouyette A, Vassal G (2000) Metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11) by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in humans. Clin Cancer Res 6(5):2012–2020
Chabot GG (1997) Clinical pharmacokinetics of irinotecan. Clin Pharmacokinet 33(4):245–259
Friedman HS, Petros WP, Friedman AH, Schaaf LJ, Kerby T, Lawyer J, Parry M, Houghton PJ, Lovell S, Rasheed K, Cloughsey T, Stewart ES, Colvin OM, Provenzale JM, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Cokgor I, Haglund M, Rich J, Ashley D, Malczyn J, Elfring GL, Miller LL (1999) Irinotecan therapy in adults with recurrent or progressive malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 17(5):1516–1525
Chabot GG, Abigerges D, Catimel G, Culine S, de Forni M, Extra JM, Mahjoubi M, Herait P, Armand JP, Bugat R, Clave M, Marty ME (1995) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of irinotecan (CPT-11) and active metabolite SN-38 during phase I trials. Ann Oncol 6(2):141–151
D’Argenio Schumitzky (1997) ADAPT II user’s guide: pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic systems analysis software. Biomedical Simulations Resource, Los Angeles
Yamaoka K, Nakagawa T, Uno T (1978) Application of Akaike’s information criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 6(2):165–175
Azrak RG, Yu J, Pendyala L, Smith PF, Cao S, Li X, Shannon WD, Durrani FA, McLeod HL, Rustum YM (2005) Irinotecan pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenomic alterations induced by methylselenocysteine in human head and neck xenograft tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 4(5):843–854
Prados MD, Yung WK, Jaeckle KA, Robins HI, Mehta MP, Fine HA, Wen PY, Cloughesy TF, Chang SM, Nicholas MK, Schiff D, Greenberg HS, Junck L, Fink KL, Hess KR, Kuhn J (2004) Phase 1 trial of irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma: a North American Brain Tumor Consortium study. Neuro Oncol 6(1):44–54
Venook AP, Enders KC, Fleming G, Hollis D, Leichman CG, Hohl R, Byrd J, Budman D, Villalona M, Marshall J, Rosner GL, Ramirez J, Kastrissios H, Ratain MJ (2003) A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction or with prior pelvic radiation: CALGB 9863. Ann Oncol 14(12):1783–1790
Xie R, Mathijssen RH, Sparreboom A, Verweij J, Karlsson MO (2002) Clinical pharmacokinetics of irinotecan and its metabolites in relation with diarrhea. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72(3):265–275
Poujol S, Bressolle F, Duffour J, Abderrahim AG, Astre C, Ychou M, Pinguet F (2006) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of irinotecan and its metabolites from plasma and saliva data in patients with metastatic digestive cancer receiving Folfiri regimen. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 58(3):292–305
Ma MK, Zamboni WC, Radomski KM, Furman WL, Santana VM, Houghton PJ, Hanna SK, Smith AK, Stewart CF (2000) Pharmacokinetics of irinotecan and its metabolites SN-38 and APC in children with recurrent solid tumors after protracted low-dose irinotecan. Clin Cancer Res 6(3):813–819
Kawato Y, Aonuma M, Hirota Y, Kuga H, Sato K (1991) Intracellular roles of SN-38, a metabolite of the camptothecin derivative CPT-11, in the antitumor effect of CPT-11. Cancer Res 51(16):4187–4191
Hertzberg RP, Caranfa MJ, Holden KG, Jakas DR, Gallagher G, Mattern MR, Mong SM, Bartus JO, Johnson RK, Kingsbury WD (1989) Modification of the hydroxy lactone ring of camptothecin: inhibition of mammalian topoisomerase I and biological activity. J Med Chem 32(3):715–720
Fassberg J, Stella VJ (1992) A kinetic and mechanistic study of the hydrolysis of camptothecin and some analogues. J Pharm Sci 81(7):676–684
Ouellet DM, Pollack GM (1995) Biliary excretion and enterohepatic recirculation of morphine-3-glucuronide in rats. Drug Metab Dispos 23(4):478–484
Davis TM, Daly F, Walsh JP, Ilett KF, Beilby JP, Dusci LJ, Barrett PH (2000) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of gliclazide in Caucasians and Australian Aborigines with type 2 diabetes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 49(3):223–230
Ezzet F, Krishna G, Wexler DB, Statkevich P, Kosoglou T, Batra VK (2001) A population pharmacokinetic model that describes multiple peaks due to enterohepatic recirculation of ezetimibe. Clin Ther 23(6):871–885
Moon YJ, Sagawa K, Frederick K, Zhang S, Morris ME (2006) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the isoflavone biochanin A in rats. AAPS J 8(3):E433–E442
Acknowledgments
This paper is supported in part by the Mylan Chair of Pharmacology at West Virginia University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Younis, I.R., Malone, S., Friedman, H.S. et al. Enterohepatic recirculation model of irinotecan (CPT-11) and metabolite pharmacokinetics in patients with glioma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63, 517–524 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0769-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0769-8