Abstract
Purpose
Paclitaxel (PTX) is a widely used chemotherapy agent and may cause cell death by apoptosis subsequent to microtubule (MT) disruption. In this paper, we have investigated whether cell cycle transit and or Cdc2 (Cdk1) activity is required for the apoptosis induced by PTX.
Methods
Cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry, Cdc2 was assayed bio chemically. Cdc2 activity was decreased by siRNA and dominant negative (dn) Cdc2 expression. Cells were arrested by chemical or biological inhibitors in a G1or S phase. Apoptosis was measured by DNA fragmentation and examination of nuclei by microscopy. JNK and AKT activations were assessed as well.
Results
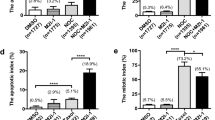
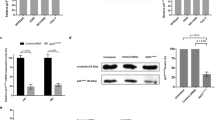
Cell cycle inhibition was highly effective in decreasing PTX induced apoptosis. MT morphology was not altered by these inhibitors. PTX induced JNK activity or AKT mediated BAD phosphorylation was unaffected by cell cycle inhibitors. Abrogation of Cdc 2 activity was without effect on PTX induced apoptosis.
Conclusions
While cell cycle transit is required for PTX induced apoptosis; Cdc2 activity is not required.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Dn:
-
Dominant negative
- MTs:
-
Microtubules
- MTAs:
-
MT disrupting agents
- m.o.i:
-
Multiplicity of infection
- PTX:
-
Paclitaxel
- p.f.u:
-
Plaque forming unit
Reference
Gilewski TA, Dang C, Surbone A, Norton L (2000) Principles of chemotherapy: cytokinetics. In: Holland JF, Frei E (eds) Cancer medicine, 5th edn. B.C. Decker, Canada, pp 511–538
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137
Mollinedo F, Gajate C (2003) Microtubules, microtubule-interfering agents and apoptosis. Apoptosis 8:413–450
Beck WT, Cass CE, Houghton PJ (2000) Microtublue-targetting anticancer drugs derived from plants and microbes. In: Holland JF, Frei E (eds) Cancer medicine, 5th edn. B.C. Decker Inc, Canada, pp 680–698
Jordan MA, Wilson L (2004) Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 4:253–265
DeAngelis LMPJB (2005) Neurologic complications. In: Blast RC Jr, et al (eds) B.C Decker inc, Canada
Jordan MA, Wendell K, Gardiner S, Derry WB, Copp H, Wilson L (1996) Mitotic block induced in HeLa cells by low concentrations of paclitaxel (Taxol) results in abnormal mitotic exit and apoptotic cell death. Cancer Res 56:816–825
Mamay CL, Mingo-Sion AM, Wolf DM, Molina MD, Van Den Berg CL (2003) An inhibitory function for JNK in the regulation of IGF-I signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene 22:602–614
Razandi M, Pedram A, Levin ER (2000) Plasma membrane estrogen receptors signal to antiapoptosis in breast cancer [In Process Citation]. Mol Endocrinol 14(9):1434–1447
Lin MT, Chang CC, Chen ST, Chang HL, Su JL, Chau YP, Kuo ML (2004) Cyr61 expression confers resistance to apoptosis in breast cancer MCF-7 cells by a mechanism of NF-kappaB-dependent XIAP up-regulation. J Biol Chem 279:24015–24023
Chadderton A, Villeneuve DJ, Gluck S, Kirwan-Rhude AF, Gannon BR, Blais DE, Parissenti AM (2000) Role of specific apoptotic pathways in the restoration of paclitaxel-induced apoptosis by valspodar in doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 59:231–244
Ling X, Bernacki RJ, Brattain MG, Li F (2004) Induction of survivin expression by taxol (paclitaxel) is an early event, which is independent of taxol-mediated G2/M arrest. J Biol Chem 279:15196–15203
Wang TH, Wang HS, Ichijo H, Giannakakou P, Foster JS, Fojo T, Wimalasena J (1998) Microtubule-interfering agents activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase through both Ras and apoptosis signal- regulating kinase pathways. J Biol Chem 273:4928–4936
Lee LF, Li G, Templeton DJ, Ting JP (1998) Paclitaxel (Taxol)-induced gene expression and cell death are both mediated by the activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK). J Biol Chem 273:28253–28260
Amato SF, Swart JM, Berg M, Wanebo HJ, Mehta SR, Chiles TC (1998) Transient stimulation of the c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase/activator protein 1 pathway and inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase are early effects in paclitaxel-mediated apoptosis in human B lymphoblasts. Cancer Res 58:241–247
Wang TH, Popp DM, Wang HS, Saitoh M, Mural JG, Henley DC, Ichijo H, Wimalasena J (1999) Microtubule dysfunction induced by paclitaxel initiates apoptosis through both c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent and -independent pathways in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 274:8208–8216
Harborth J, Elbashir SM, Bechert K, Tuschl T, Weber K (2001) Identification of essential genes in cultured mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. J Cell Sci 114:4557–4565
McConnell BB, Gregory FJ, Stott FJ, Hara E, Peters G (1999) Induced expression of p16(INK4a) inhibits both CDK4- and CDK2-associated kinase activity by reassortment of cyclin-CDK-inhibitor complexes. Mol Cell Biol 19:1981–1989
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M (1999) SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat Cell Biol 1:193–199
Tsai LH, Lees E, Faha B, Harlow E, Riabowol K (1993) The cdk2 kinase is required for the G1-to-S transition in mammalian cells. Oncogene 8:1593–1602
Craig C, Kim M, Ohri E, Wersto R, Katayose D, Li Z, Choi YH, Mudahar B, Srivastava S, Seth P, et al (1998) Effects of adenovirus-mediated p16INK4A expression on cell cycle arrest are determined by endogenous p16 and Rb status in human cancer cells. Oncogene 16:265–272
Leone G, DeGregori J, Sears R, Jakoi L, Nevins JR (1997) Myc and Ras collaborate in inducing accumulation of active cyclin E/Cdk2 and E2F [published erratum appears in Nature 387(6636):932]. Nature 387:422–426
Craig C, Wersto R, Kim M, Ohri E, Li Z, Katayose D, Lee SJ, Trepel J, Cowan K, Seth P (1997) A recombinant adenovirus expressing p27Kip1 induces cell cycle arrest and loss of cyclin-Cdk activity in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 14:2283–2289
Sears R, Leone G, DeGregori J, Nevins JR (1999) Ras enhances Myc protein stability. Mol Cell 3:169–179
Stein GS, Stein JL, Lian JB, Last TJ, McCabe L (1998) Synchronization of normal diploid and transformed mammalian cells. In: Julio E. Celis (ed) Cell biology, vol 1, 2nd edn. pp253–260
Foster JS, Henley DC, Bukovsky A, Seth P, Wimalasena J (2001) Multifaceted regulation of cell cycle progression by estrogen: regulation of Cdk inhibitors and Cdc25A independent of cyclin D1-Cdk4 function. Mol Cell Biol 21:794–810
Foster JS, Wimalasena J (1996) Estrogen regulates activity of cyclin-dependent kinases and retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 10:488–498
Ahamed S, Foster JS, Bukovsky A, Wimalasena J (2001) Signal transduction through the ras/Erk pathway is essential for the mycoestrogen zearalenone-induced cell-cycle progression in MCF-7 cells. Mol Carcinog 30:88–98
Foster JS, Henley DC, Ahamed S, Wimalasena J (2001) Estrogens and cell-cycle regulation in breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:320–327
Foster JS, Fernando RI, Ishida N, Nakayama KI, Wimalasena J (2003) Estrogens down-regulate p27Kip1 in breast cancer cells through SKP2,and through nuclear export mediated by the extracellular signal-regulatedkinase (Erk) pathway. J Biol Chem 278:41355–41366
Ahamed S, Foster JS, Bukovsky A, Diehl JA, Wimalasena J (2002) Removal of Cdk inhibitors through both sequestration and downregulation in zearalenone-treated MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog 34:45–58
Fernando RI, Wimalasena J (2004) Estradiol abrogates apoptosis in breast cancer cells through inactivation of BAD: ras-dependent nongenomic pathways requiring signaling through ERK and Akt. Mol Biol Cell 15:3266–3284
Resnitzky D, Reed SI (1995) Different roles for cyclins D1 and E in regulation of the G1-to-S transition. Mol Cell Biol 15:3463–3469
Jazirehi AR, Gan XH, De Vos S, Emmanouilides C, Bonavida B (2003) Rituximab (anti-CD20) selectively modifies Bcl-xL and apoptosis protease activating factor-1 (Apaf-1) expression and sensitizes human non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma B cell lines to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 2:1183–1193
Strobel T, Tai YT, Korsmeyer S, Cannistra SA (1998) BAD partly reverses paclitaxel resistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 17:2419–2427
Page C, Lin HJ, Jin Y, Castle VP, Nunez G, Huang M, Lin J (2000) Overexpression of Akt/AKT can modulate chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Anticancer Res 20:407–416
Blajeski AL, Phan VA, Kottke TJ, Kaufmann SH (2002) G(1) and G(2) cell-cycle arrest following microtubule depolymerization in human breast cancer cells. J Clin Invest 110:91–99
Torres K, Horwitz SB (1998) Mechanisms of Taxol-induced cell death are concentration dependent. Cancer Res 58:3620–3626
Jordan MA (2002) Mechanism of action of antitumor drugs that interact with microtubules and tubulin. Curr Med Chem Anti-Canc Agents 2:1–17
Wahl AF, Donaldson KL, Fairchild C, Lee FY, Foster SA, Demers GW, Galloway DA (1996) Loss of normal p53 function confers sensitization to Taxol by increasing G2/M arrest and apoptosis [see comments]. Nat Med 2:72–79
Blajeski AL, Kottke TJ, Kaufmann SH (2001) A multistep model for paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines. Exp Cell Res 270:277–288
Johnson KR, Young KK, Fan W (1999) Antagonistic interplay between antimitotic and G1-S arresting agents observed in experimental combination therapy. Clin Cancer Res 5:2559–2565
Castedo M, Perfettini JL, Roumier T, Kroemer G (2002) Cyclin-dependent kinase-1: linking apoptosis to cell cycle and mitotic catastrophe. Cell Death Differ 9:1287–1293
Harvey KJ, Lukovic D, Ucker DS (2000) Caspase-dependent Cdk activity is a requisite effector of apoptotic death events. J Cell Biol 148:59–72
Chadebech P, Truchet I, Brichese L, Valette A (2000) Up-regulation of cdc2 protein during paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Int J Cancer 87:779–786
Motwani M, Delohery TM, Schwartz GK (1999) Sequential dependent enhancement of caspase activation and apoptosis by flavopiridol on paclitaxel-treated human gastric and breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 5:1876–1883
Ling YH, Consoli U, Tornos C, Andreeff M, Perez-Soler R (1998) Accumulation of cyclin B1, activation of cyclin B1-dependent kinase and induction of programmed cell death in human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells treated with taxol. Int J Cancer 75:925–932
Harvey KJ, Blomquist JF, Ucker DS (1998) Commitment and effector phases of the physiological cell death pathway elucidated with respect to Bcl-2 caspase, and cyclin-dependent kinase activities. Mol Cell Biol 18:2912–2922
Shen SC, Huang TS, Jee SH, Kuo ML (1998) Taxol-induced p34cdc2 kinase activation and apoptosis inhibited by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in human breast MCF-7 carcinoma cells. Cell Growth Differ 9:23–29
Vantieghem A, Xu Y, Assefa Z, Piette J, Vandenheede JR, Merlevede W, De Witte PA, Agostinis P (2002) Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 in G2/M phase-arrested cells following photodynamic therapy with hypericin involves a CDK1-mediated signal and delays the onset of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277:37718–37731
Tan X, Wang JY (1998) The caspase-RB connection in cell death. Trends Cell Biol 8:116–120
Meikrantz W (1996) Suppression of apoptosis by dominant negative mutants of cyclin-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem 271:10205–10209
Ye K, Zhou J, Landen JW, Bradbury EM, Joshi HC (2001) Sustained activation of p34(cdc2) is required for noscapine-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276:46697–46700
Konishi Y, Lehtinen M, Donovan N, Bonni A (2002) Cdc2 phosphorylation of BAD links the cell cycle to the cell death machinery. Mol Cell 9:1005–1016
Yao SL (1996) Requirement of p34cdc2 kinase for apoptosis mediated by the Fas/APO-1 receptor and interleukin 1beta-converting enzyme-related proteases. Cancer Res 56:4551–4555
Yu C, Rahmani M, Dai Y, Conrad D, Krystal G, Dent P, Grant S (2003) The lethal effects of pharmacological cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in human leukemia cells proceed through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent process. Cancer Res 63:1822–1833
Ham YM, Choi KJ, Song SY, Jin YH, Chun MW, Lee SK (2003) Xylocydine, a novel inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases, prevents the TRAIL-induced apoptotic cell death of SK-HEP-1 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther
Shu CH, Yang WK, Shih YL, Kuo ML, Huang TS (1997) Cell cycle G2/M arrest and activation of cyclin-dependent kinases associated with low-dose paclitaxel-induced sub-G1 apoptosis. Apoptosis 2:463–470
Shi L, Nishioka WK, Th’ng J, Bradbury EM, Litchfield DW, Greenberg AH (1994) Premature p34cdc2 activation required for apoptosis. Science 263:1143–1145
Hiromura K, Pippin JW, Blonski MJ, Roberts JM, Shankland SJ (2002) The subcellular localization of cyclin dependent kinase 2 determines the fate of mesangial cells: role in apoptosis and proliferation. Oncogene 21:1750–1758
Ongkeko W, Ferguson DJ, Harris AL, Norbury C (1995) Inactivation of Cdc2 increases the level of apoptosis induced by DNA damage. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 8):2897–2904
Itzhaki JE, Gilbert CS, Porter AC (1997) Construction by gene targeting in human cells of a “conditional” CDC2 mutant that rereplicates its DNA. Nat Genet 15:258–265
Patel V, Senderowicz AM, Pinto DJ, Igishi T, Raffeld M, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ensley JF, Sausville EA, Gutkind JS (1998) Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, suppresses the growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by inducing apoptosis. J Clin Invest 102:1674–1681
Zhai S, Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA, Figg WD (2002) Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in clinical development. Ann Pharmacother 36:905–911
Tamm I, Schumacher A, Karawajew L, Ruppert V, Arnold W, Nussler AK, Neuhaus P, Dorken B, Wolff G (2002) Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of P16INK4/CDKN2 into bax-negative colon cancer cells induces apoptosis and tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 9:641–650
Samuelsson MK, Pazirandeh A, Okret S (2002) A pro-apoptotic effect of the CDK inhibitor p57(Kip2) on staurosporine-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296:702–709
Basile JR, Eichten A, Zacny V, Munger K (2003) NF-kappaB-mediated induction of p21(Cip1/Waf1) by tumor necrosis factor alpha induces growth arrest and cytoprotection in normal human keratinocytes. Mol Cancer Res 1:262–270
Carvalho A, Carmena M, Sambade C, Earnshaw WC, Wheatley SP (2003) Survivin is required for stable checkpoint activation in taxol-treated HeLa cells. J Cell Sci 116:2987–2998
O’Connor DS, Wall NR, Porter AC, Altieri DC (2002) A p34(cdc2) survival checkpoint in cancer. Cancer Cell 2:43–54
Mesri M, Wall NR, Li J, Kim RW, Altieri DC (2001) Cancer gene therapy using a survivin mutant adenovirus. J Clin Invest 108:981–990
Giodini A, Kallio MJ, Wall NR, Gorbsky GJ, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Symons M, Altieri DC (2002) Regulation of microtubule stability and mitotic progression by survivin. Cancer Res 62:2462–2467
Tanaka K, Iwamoto S, Gon G, Nohara T, Iwamoto M, Tanigawa N (2000) Expression of survivin and its relationship to loss of apoptosis in breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 6:127–134
Song Z, Yao X, Wu M (2003) Direct Interaction between Survivin and Smac/DIABLO is essential for the anti-apoptotic activity of Survivin during Taxol-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278:23130–23140
O’Connor DS, Grossman D, Plescia J, Li F, Zhang H, Villa A, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC (2000) Regulation of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13103–13107
Boldt S, Weidle UH, Kolch W (2002) The role of MAPK pathways in the action of chemotherapeutic drugs. Carcinogenesis 23:1831–1838
Shtil AA, Mandlekar S, Yu R, Walter RJ, Hagen K, Tan TH, Roninson IB, Kong AN (1999) Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by microtubule-binding agents in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 18:377–384
McDaid HM, Horwitz SB (2001) Selective potentiation of paclitaxel (taxol)-induced cell death by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition in human cancer cell lines. Mol Pharmacol 60:290–301
Stadheim TA, Xiao H, Eastman A (2001) Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) mediates cell cycle phase independent apoptosis in vinblastine-treated ML-1 cells. Cancer Res 61:1533–1540
Kolfschoten GM, Hulscher TM, Duyndam MC, Pinedo HM, Boven E (2002) Variation in the kinetics of caspase-3 activation, Bcl-2 phosphorylation and apoptotic morphology in unselected human ovarian cancer cell lines as a response to docetaxel. Biochem Pharmacol 63:733–743
Zhang H, Shi X, Zhang QJ, Hampong M, Paddon H, Wahyuningsih D, Pelech S (2002) Nocodazole-induced p53-dependent c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation reduces apoptosis in human colon carcinoma HCT116 cells. J Biol Chem 277:43648–43658
Denicourt C, Dowdy SF (2004) Cip/Kip proteins: more than just CDKs inhibitors. Genes Dev 18:851–855
Besson A, Gurian-West M, Schmidt A, Hall A, Roberts JM (2004) p27Kip1 modulates cell migration through the regulation of RhoA activation. Genes Dev 18:862–876
Kim GY, Mercer SE, Ewton DZ, Yan Z, Jin K, Friedman E (2002) The stress-activated protein kinases p38 alpha and JNK1 stabilize p21(Cip1) by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 277:29792–29802
Heliez C, Baricault L, Barboule N, Valette A (2003) Paclitaxel increases p21 synthesis and accumulation of its AKT-phosphorylated form in the cytoplasm of cancer cells. Oncogene 22:3260–3268
MacKeigan JP, Taxman DJ, Hunter D, Earp HS III, Graves LM, Ting JP (2002) Inactivation of the antiapoptotic phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt pathway by the combined treatment of taxol and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition. Clin Cancer Res 8:2091–2099
Hu L, Hofmann J, Lu Y, Mills GB, Jaffe RB (2002) Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase increases efficacy of paclitaxel in in vitro and in vivo ovarian cancer models. Cancer Res 62:1087–1092
Mitsuuchi Y, Johnson SW, Selvakumaran M, Williams SJ, Hamilton TC, Testa JR (2000) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signal transduction pathway plays a critical role in the expression of p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1 induced by cisplatin and paclitaxel. Cancer Res 60:5390–5394
Lin HL, Lui WY, Liu TY, Chi CW (2003) Reversal of Taxol resistance in hepatoma by cyclosporin a: involvement of the PI-3 kinase-AKT 1 pathway. Br J Cancer 88:973–980
Boudny V, Nakano S (2003) Src tyrosine kinase but not activated Ras augments sensitivity to taxanes through apoptosis in human adenocarcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 23:7–12
Beck WT, Cass CE, Houghton P (2000) In: Holland JF, Frei E (eds) Cancer medicine, 5th edn. B.C. Decker, Canada, pp 680–695
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Amber Bible for editorial support and Richard Andrews for flow cytometry analyses. The study was supported by NIH (CA 84048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henley, D., Isbill, M., Fernando, R. et al. Paclitaxel induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells requires cell cycle transit but not Cdc2 activity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59, 235–249 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-006-0262-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-006-0262-1