Abstract
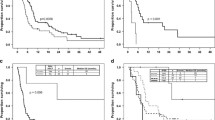
Expression and functional activity of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) were measured in 182 acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) patients: 136 patients were treated with the AML-6 protocol (EORTC), containing daunorubicin, vincristine, and conventional-dose cytarabine (ara-C), and 21 patients received idarubicin, vepeside, and conventional-dose ara-C (ICE-AML-10 protocol/EORTC). An additional 25 patients were treated with a dose of idarubicin and ara-C, modified as compared with the ICE protocol, but with the same dose of etopside (ICE-I protocol). P-gp was determined using monoclonal antibody 4E3.16 and functional activity using the rhodamine 123 accumulation test. P-gp positivity was defined as a Kolmogorov Smirnov (KS) D value ≥0.15, P-gp negativity as a KS D value <0.15. P-gp activity was defined as a ratio of mean rhodamine 123 accumulation with/without verapamil. In AML patients at primary diagnosis and early relapse/refractoriness a significant (p<0.05) difference between P-gp-positive and P-gp-negative patients was ascertained using the AML-6 protocol; the difference corresponded to the complete remission rate. For ICE- and ICE-I-treated AML patients at primary diagnosis this significance was not shown. Compared with AML patients at primary diagnosis and patients at early relapse or refractoriness, a significantly (p<0.05) increased incidence of non-pumping P-gp and a trend (p=0.054) to a higher percentage of non-P-gp-related mechanisms in AML patients at late relapse was determined. When the AML-6 protocol is used, age, activated P-gp, and CD34 expression are independent prognostic factors in AML patients. A test system which determines a functional P-gp overexpression is a major tool for identifying a group of AML patients with a poor prognosis. In order to effectively use so-called P-gp modulator substances, the degree of P-gp expression, the activated or nonactivated P-gp condition, and detection of non-P-gp-related resistance mechanisms are of utmost interest for optimal design and analysis of P-gp modulator trials and for understanding the complexity of chemotherapy-related resistance mechanisms in patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 March 1997/Accepted: 10 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nuessler, V., Gullis, E., Pelka-Fleischer, R. et al. Expression and functional activity of P-glycoprotein in adult acute myelogenous leukemia patients. Ann Hematol 75, 17–26 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770050307
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770050307