Abstract
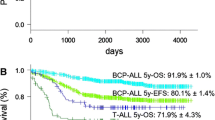
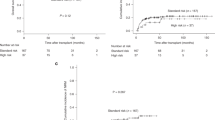
The prognostic impacts of BCR-ABL1 fusion gene mutations in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph + ALL) remain unknown. Using data from a nationwide Japanese registry, we have evaluated the prognostic impact of BCR-ABL1 mutations prior to the first allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). The cohort included 289 patients with a median of 48 years of age (range: 16–70). Point mutations were detected in 110 patients. Of these, 90 (82%) harbored T315I mutations, while 20 had other mutations. With a median follow-up period of 29 months (range: 1–125), outcomes after 2 years were worse with mutations than without (overall survival [OS]: 34% vs 68%, p < 0.001; relapse rate [RR]: 48% vs 18%, p < 0.001), particularly with the presence of the T315I mutation (OS: 29% vs 68%, p < 0.001; RR: 54% vs 18%, p < 0.001). OS was significantly worse in the T315I group even among the cohort with hematological (p < 0.001) or molecular complete remission (p = 0.025) as compared to the no mutation group. Multivariate analysis determined the prognostic impact of the T315I mutation (OS: hazard ratio [HR] = 2.19, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.5–3.3, p < 0.001; RR: HR = 2.51, 95% CI: 1.5–4.2, p < 0.001). This study is the first to report on the prognostic significance of BCR-ABL1 mutations in Ph + ALL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeuchi J, Kyo T, Naito K, Sao H, Takahashi M, Miyawaki S, Kuriyama K, Ohtake S, Yagasaki F, Murakami H, Asou N, Ino T, Okamoto T, Usui N, Nishimura M, Shinagawa K, Fukushima T, Taguchi H, Morii T, Mizuta S, Akiyama H, Nakamura Y, Ohshima T, Ohno R (2002) Induction therapy by frequent administration of doxorubicin with four other drugs, followed by intensive consolidation and maintenance therapy for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the JALSG-ALL93 study. Leukemia 16:1259–1266
Gleißner B, Gokbuget N, Bartram CR et al (2002) Leading prognostic relevance of the BCR-ABL translocation in adult acute B-lineage lymphoblastic leukemia: a prospective study of the German Multicenter Trial Group and confirmed polymerase chain reaction analysis. Blood 99:1536–1543
Dombret H, Gabert J, Boiron J-M, Rigal-Huguet F, Blaise D, Thomas X, Delannoy A, Buzyn A, Bilhou-Nabera C, Cayuela JM, Fenaux P, Bourhis JH, Fegueux N, Charrin C, Boucheix C, Lhéritier V, Espérou H, MacIntyre E, Vernant JP, Fière D, Groupe d'Etude et de Traitement de la Leucémie Aiguë Lymphoblastique de l'Adulte (GET-LALA Group) (2002) Outcome of treatment in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia—results of the prospective multicenter LALA-94 trial. Blood 100:2357–2366
Pullarkat V, Slovak ML, Kopecky KJ, Forman SJ, Appelbaum FR (2008) Impact of cytogenetics on the outcome of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of Southwest Oncology Group 9400 study. Blood 111:2563–2572
Fielding AK, Rowe JM, Richards SM, Buck G, Moorman AV, Durrant IJ, Marks DI, McMillan A, Litzow MR, Lazarus HM, Foroni L, Dewald G, Franklin IM, Luger SM, Paietta E, Wiernik PH, Tallman MS, Goldstone AH (2009) Prospective outcome data on 267 unselected adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome–positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia confirms superiority of allogeneic transplantation over chemotherapy in the pre-imatinib era: results from the International ALL Trial MRC UKALLXII/ECOG2993. Blood 113:4489–4496
Yanada M, Takeuchi J, Sugiura I, Akiyama H, Usui N, Yagasaki F, Kobayashi T, Ueda Y, Takeuchi M, Miyawaki S, Maruta A, Emi N, Miyazaki Y, Ohtake S, Jinnai I, Matsuo K, Naoe T, Ohno R, Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group (2006) High complete remission rate and promising outcome by combination of imatinib and chemotherapy for newly diagnosed BCR-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a phase II study by the Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group. J Clin Oncol 24:460–466
Mizuta S, Matsuo K, Yagasaki F, Yujiri T, Hatta Y, Kimura Y, Ueda Y, Kanamori H, Usui N, Akiyama H, Miyazaki Y, Ohtake S, Atsuta Y, Sakamaki H, Kawa K, Morishima Y, Ohnishi K, Naoe T, Ohno R (2011) Pre-transplant imatinib-based therapy improves the outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for BCR–ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 25:41–47
Thomas DA, Faderl S, Cortes J, O'Brien S, Giles FJ, Kornblau SM, Garcia-Manero G, Keating MJ, Andreeff M, Jeha S, Beran M, Verstovsek S, Pierce S, Letvak L, Salvado A, Champlin R, Talpaz M, Kantarjian H (2004) Treatment of Philadelphia chromosome–positive acute lymphocytic leukemia with hyper-CVAD and imatinib mesylate. Blood 103:4396–4407
Wassmann B, Pfeifer H, Goekbuget N, Beelen DW, Beck J, Stelljes M, Bornhäuser M, Reichle A, Perz J, Haas R, Ganser A, Schmid M, Kanz L, Lenz G, Kaufmann M, Binckebanck A, Brück P, Reutzel R, Gschaidmeier H, Schwartz S, Hoelzer D, Ottmann OG (2006) Alternating versus concurrent schedules of imatinib and chemotherapy as front-line therapy for Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL). Blood 108:1469–1477
de Labarthe A, Rousselot P, Huguet-Rigal F et al (2007) Imatinib combined with induction or consolidation chemotherapy in patients with de novo Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of the GRAAPH-2003 study. Blood 109:1408–1413
Ottmann OG, Wassmann B, Pfeifer H, Giagounidis A, Stelljes M, Dührsen U, Schmalzing M, Wunderle L, Binckebanck A, Hoelzer D, for the GMALL Study Group (2007) Imatinib compared with chemotherapy as front-line treatment of elderly patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ALL). Cancer 109:2068–2076
Vignetti M, Fazi P, Cimino G, Martinelli G, di Raimondo F, Ferrara F, Meloni G, Ambrosetti A, Quarta G, Pagano L, Rege-Cambrin G, Elia L, Bertieri R, Annino L, Foà R, Baccarani M, Mandelli F (2007) Imatinib plus steroids induces complete remissions and prolonged survival in elderly Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients without additional chemotherapy: results of the GIMEMA LAL0201-B protocol. Blood 109:3676–3678
Foà R, Vitale A, Vignetti M, Meloni G, Guarini A, de Propris MS, Elia L, Paoloni F, Fazi P, Cimino G, Nobile F, Ferrara F, Castagnola C, Sica S, Leoni P, Zuffa E, Fozza C, Luppi M, Candoni A, Iacobucci I, Soverini S, Mandelli F, Martinelli G, Baccarani M, on behalf of the GIMEMA Acute Leukemia Working Party (2011) Dasatinib as first-line treatment for adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome–positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 118:6521–6528
Rousselot P, Coudé MM, Gokbuget N, Gambacorti Passerini C, Hayette S, Cayuela JM, Huguet F, Leguay T, Chevallier P, Salanoubat C, Bonmati C, Alexis M, Hunault M, Glaisner S, Agape P, Berthou C, Jourdan E, Fernandes J, Sutton L, Banos A, Reman O, Lioure B, Thomas X, Ifrah N, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Bornand A, Morisset L, Robin V, Pfeifer H, Delannoy A, Ribera J, Bassan R, Delord M, Hoelzer D, Dombret H, Ottmann OG, European Working Group on Adult ALL (EWALL) group (2016) Dasatinib and low-intensity chemotherapy in elderly patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. Blood 128:774–782
Ravandi F, O'Brien S, Thomas D, Faderl S, Jones D, Garris R, Dara S, Jorgensen J, Kebriaei P, Champlin R, Borthakur G, Burger J, Ferrajoli A, Garcia-Manero G, Wierda W, Cortes J, Kantarjian H (2010) First report of phase 2 study of dasatinib with hyper-CVAD for the frontline treatment of patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 116:2070–2077
Yoon JH, Yhim HY, Kwak et al (2016) Minimal residual disease-based effect and long-term outcome of first-line dasatinib combined with chemotherapy for adult Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann Oncol 27:1081–1088
Cortes JE, Kim DW, Pinilla-Ibarz J, le Coutre PD, Paquette R, Chuah C, Nicolini FE, Apperley JF, Khoury HJ, Talpaz M, DeAngelo DJ, Abruzzese E, Rea D, Baccarani M, Müller MC, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Lustgarten S, Rivera VM, Haluska FG, Guilhot F, Deininger MW, Hochhaus A, Hughes TP, Shah NP, Kantarjian HM (2018) Ponatinib efficacy and safety in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia: final 5-year results of the phase 2 PACE trial. Blood 132:393–404
Cortes JE, Kim DW, Pinilla-Ibarz J, le Coutre P, Paquette R, Chuah C, Nicolini FE, Apperley JF, Khoury HJ, Talpaz M, DiPersio J, DeAngelo D, Abruzzese E, Rea D, Baccarani M, Müller MC, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Wong S, Lustgarten S, Rivera VM, Clackson T, Turner CD, Haluska FG, Guilhot F, Deininger MW, Hochhaus A, Hughes T, Goldman JM, Shah NP, Kantarjian H, PACE Investigators (2013) A phase 2 trial of ponatinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med 369:1783–1796
Jabbour E, Short NJ, Ravandi F, Huang X, Daver N, DiNardo CD, Konopleva M, Pemmaraju N, Wierda W, Garcia-Manero G, Sasaki K, Cortes J, Garris R, Khoury JD, Jorgensen J, Jain N, Alvarez J, O'Brien S, Kantarjian H (2018) Combination of hyper-CVAD with ponatinib as first-line therapy for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: long-term follow-up of a single-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol 5:e618–e627
Sasaki K, Jabbour EJ, Ravandi F, Short NJ, Thomas DA, Garcia-Manero G, Daver NG, Kadia TM, Konopleva MY, Jain N, Issa GC, Jeanis V, Moore HG, Garris RS, Pemmaraju N, Cortes JE, O'Brien SM, Kantarjian HM (2016) Hyper-CVAD plus ponatinib versus hyper-CVAD plus dasatinib as frontline therapy for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a propensity score analysis. Cancer 122:3650–3656
Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Japan. Annual Report of Nationwide Survey 2018 (2018) The Japanese Data Center for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation/The Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Soverini S, De Benedittis C, Papayannidis C et al (2014) Drug resistance and BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia from the imatinib to the second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor era: the main changes are in the type of mutations, but not in the frequency of mutation involvement. Cancer 120:1002–1009
DeBoer R, Koval G, Mulkey F, Wetzler M, Devine S, Marcucci G, Stone RM, Larson RA, Bloomfield CD, Geyer S, Mullighan CG, Stock W (2016) Clinical impact of ABL1 kinase domain mutations and IKZF1 deletion in adults under age 60 with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): molecular analysis of CALGB (Alliance) 10001 and 9665. Leuk Lymphoma 57:2298–2306
Ono T, Miyawaki S, Kimura F, Kanamori H, Ohtake S, Kitamura K, Fujita H, Sugiura I, Usuki K, Emi N, Tamaki S, Aoyama Y, Kaya H, Naoe T, Tadokoro K, Yamaguchi T, Ohno R, Ohnishi K, Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group (2011) BCR-ABL1 mutations in patients with imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia by use of the PCR-Invader assay. Leuk Res 35:598–603
Nicolini FE, Basak GW, Soverini S, Martinelli G, Mauro MJ, Müller MC, Hochhaus A, Chuah C, Dufva IH, Rege-Cambrin G, Saglio G, Michallet M, Labussière H, Morisset S, Hayette S, Etienne G, Olavarria E, Zhou W, Peter S, Apperley JF, Cortes J (2011) Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients harboring T315I BCR-ABL mutated leukemias. Blood 118:5697–5700
Nicolini FE, Basak GW, Kim DW, Olavarria E, Pinilla-Ibarz J, Apperley JF, Hughes T, Niederwieser D, Mauro MJ, Chuah C, Hochhaus A, Martinelli G, DerSarkissian M, Duh MS, McGarry LJ, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE (2017) Overall survival with ponatinib versus allogeneic stem cell transplantation in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias with the T315I mutation. Cancer 123:2875–2880
Ray A, Cowan-Jacob SW, Manley PW, Mestan J, Griffin JD (2007) Identification of BCR-ABL point mutations conferring resistance to the Abl kinase inhibitor AMN107 (nilotinib) by a random mutagenesis study. Blood 109:5011–5015
Deininger M, Buchdunger E, Druker BJ (2005) The development of imatinib as a therapeutic agent for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 105:2640–2653
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, Apperley J, Slavin S, Pasquini M, Sandmaier BM, Barrett J, Blaise D, Lowski R, Horowitz M (2009) Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 15:1628–1633
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, Thomas ED (1995) 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 15:825–828
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker GE, Sale GE, Hackman R, Tsoi MS, Storb R, Donnall Thomas E (1980) Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med 69:204–217
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48:452–458
Alikian M, Gerrard G, Subramanian PG, Mudge K, Foskett P, Khorashad JS, Lim AC, Marin D, Milojkovic D, Reid A, Rezvani K, Goldman J, Apperley J, Foroni L (2012) BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutations: methodology and clinical evaluation. Am J Hematol 87:298–304
Soverini S, Bavaro L, Martelli M, de Benedittis C, Iurlo A, Orofino N, Pagano L, Criscuolo M, Bonifacio M, Scaffidi L, Sica S, Sorà F, Maino E, Rondoni M, Laginestra MA, Lunghi F, Ermacora A, D'adda M, Gugliotta G, Castagnetti F, Rosti G, Papayannidis C, Marconi G, Curti A, Miggiano MC, Galimberti S, Percesepe A, Stagno F, Sancetta R, Annunziata M, Falzetti F, Capodanno I, Pregno P, Maffioli M, Intermesoli T, di Bona E, Caocci G, Attolico I, Binotto G, Bocchia M, Angelucci E, Sgherza N, Luciano L, Mignone F, Pileri SA, Martinelli G, Cavo M (2018) Compound BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutants: prevalence, spectrum and correlation with tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in a prospective series of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia patients analyzed by next generation sequencing. Blood 132:789
Watanabe K, Minami Y, Ozawa Y, Miyamura K, Naoe T (2012) T315I mutation in Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with a highly aggressive disease phenotype: three case reports. Anticancer Res 32:1779–1783
Tachibana T, Koyama S, Andou T, Ishiyama Y, Tanaka M, Nakajima H, Kanamori H (2019) Salvage and bridging to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with ponatinib in patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Int J Hematol 109:162–168
Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M et al (2016) Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 375:740–753
Martinelli G, Boissel N, Chevallier P, Ottmann O, Gökbuget N, Topp MS, Fielding AK, Rambaldi A, Ritchie EK, Papayannidis C, Sterling LR, Benjamin J, Stein A (2017) Complete hematologic and molecular response in adult patients with relapsed/refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia following treatment with blinatumomab: results from a phase II, single-arm, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 35:1795–1802
Grupp SA, Kalos M, Barrett D, Aplenc R, Porter DL, Rheingold SR, Teachey DT, Chew A, Hauck B, Wright JF, Milone MC, Levine BL, June CH (2013) Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for acute lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med 368:1509–1518
Krishna Chandran R, Geetha N, Sakthivel KM, Suresh Kumar R, Jagathnath Krishna KMN, Sreedharan H (2019) Impact of Additional chromosomal aberrations on the disease progression of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Front Oncol 9:88
Wang W, Cortes JE, Tang G et al (2016) Risk stratification of chromosomal abnormalities in chronic myelogenous leukemia in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Blood 27:2742–2750
Akahoshi Y, Mizuta S, Shimizu H, Uchida N, Fukuda T, Kanamori H, Onizuka M, Ozawa Y, Ohashi K, Ohta S, Eto T, Tanaka J, Atsuta Y, Kako S, Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (2018) Additional cytogenetic abnormalities with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia on allogeneic stem cell transplantation in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 24:2009–2016
Ottmann OG, Pfeifer H (2009) Management of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program:371–381
Lussana F, Intermesoli T, Gianni F, Boschini C, Masciulli A, Spinelli O, Oldani E, Tosi M, Grassi A, Parolini M, Audisio E, Cattaneo C, Raimondi R, Angelucci E, Cavattoni IM, Scattolin AM, Cortelezzi A, Mannelli F, Ciceri F, Mattei D, Borlenghi E, Terruzzi E, Romani C, Bassan R, Rambaldi A (2016) Achieving molecular remission before allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: impact on relapse and long-term outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22:1983–1987
Nishiwaki S, Imai K, Mizuta S et al (2016) Impact of MRD and TKI on allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for Ph+ALL: a study from the adult ALL WG of the JSHCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 51:43–50
Tucunduva L, Ruggeri A, Sanz G, Furst S, Cornelissen J, Linkesch W, Mannone L, Ribera JM, Veelken H, Yakoub-Agha I, González Valentín ME, Schots R, Arcese W, Montesinos P, Labopin M, Gluckman E, Mohty M, Rocha V (2014) Impact of minimal residual disease on outcomes after umbilical cord blood transplantation for adults with Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: an analysis on behalf of Eurocord, Cord Blood Committee and the Acute Leukaemia working party of the European group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Br J Haematol 166:749–757
Giebel S, Czyz A, Ottmann O, Baron F, Brissot E, Ciceri F, Cornelissen JJ, Esteve J, Gorin NC, Savani B, Schmid C, Mohty M, Nagler A (2016) Use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors to prevent relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a position statement of the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Cancer 122:2941–2951
DeFilipp Z, Langston AA, Chen Z, Zhang C, Arellano ML, el Rassi F, Flowers CR, Kota VK, al-Kadhimi Z, Veldman R, Jillella AP, Lonial S, Waller EK, Khoury HJ (2016) Does post-transplant maintenance therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors improve outcomes of patients with high-risk Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia? Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 16:466–471
Pfeifer H, Wassmann B, Bethge W et al (2013) Randomized comparison of prophylactic and minimal residual disease-triggered imatinib after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for BCR-ABL1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 27:1254–1262
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all members of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and members of the Japanese Data Center for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
T.T. designed the research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. T.T., Y.N., Y.A, S.H., K.H., and S.K. supported the data analysis and manuscript preparation. N.D., N.U., T.F., M.S., M.O., S.T., M.T., and Y.M. treated patients and collected the data. M.O., T.I., J.T., and Y.A. collected and assemblied the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M.S. reports personal fees from Chugai, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Astellas, personal fees from Nippon-Shinyaku, personal fees from Ono, personal fees from MSD, personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Kyowa-Hakko Kirin, personal fees from Asahi-Kasei, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Eisai, personal fees from Otsuka, personal fees from Sumitomo Dainippon, personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees from Celgene, personal fees from Mochida, personal fees from Shire, personal fees from Mundipharma, outside the submitted work. S. H. reports stock ownership in Revorf Co.,ltd. outside the submitted work.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the data management committee of the Japanese Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and the Ethics Committee of Kanagawa Cancer Center. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
The TRUMP database includes physician-reviewed data. Observational studies based on the TRUMP database are performed with an informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 16 kb).
ESM 2
Supplementary Figure Comparison of variables according to mutation status. A The average WBC counts in the non-T315I and T315I mutation cohorts were higher compared to the no mutation cohort (p = 0.002). B The median time from diagnosis to HCT was significantly longer in the non-T315I and T315I mutation cohorts compared to the no mutation cohort (p < 0.001). C The performance status (PS) of patients at allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) was significantly higher in the T315I mutation cohort (p = 0.006, calculated by Fischer’s exact test) (PDF 62 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tachibana, T., Najima, Y., Akahoshi, Y. et al. The impacts of BCR-ABL1 mutations in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 99, 2393–2404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04212-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04212-1