Abstract
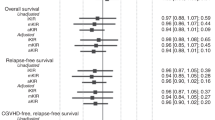
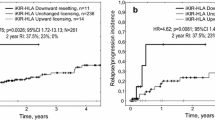
Impact of donor-recipient killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene-gene matching on transplant outcomes is still inconclusive. Recent data suggest that killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) regulated natural killer cell (NK cell) activity may contribute to graft versus leukemia (GvL) effects and graft versus host disease (GvHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). This case-control study aims to evaluate the effects of both aKIR and iKIR donor-recipient genotype matching on the outcomes of T cell replete HLA-identical sibling allo-HSCTs in a homogenous young patient population with myeloid leukemias. Five transplant outcomes including relapse rate (RR), disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS), cumulative incidences of acute GvHD (aGvHD), and chronic GvHD (cGvHD) are investigated. Out of 96 HLA-identical sibling donor-recipient pairs, 34 were matched for activating KIR (aKIR), 38 for inhibitory KIR (iKIR), and 20 for both aKIR and iKIR. Fourty-four pairs were mismatched for both iKIR and aKIR. In univariate analysis, aKIR-matching resulted with a decrease in relapse rate (RR) (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.4; p = 0.04) and an increase in disease-free survival (DFS) (HR: 0.5; p = 0.03). In addition, cGvHD ocurred less frequently in the aKIR-matched (odds ratio [OR]: 0.4; p = 0.04) or iKIR-matched (OR: 0.3; p = 0.009) cohorts. Matching for both aKIR and iKIR was also associated with a decrease in cGvHD incidence (OR: 0.3; p = 0.02). iKIR-matching had no effects on RR, OS, or DFS. Analysis of donor haplotype effects showed haplotype-BB to have a tendency towards reduced relapse rate (HR: 0.4; p = 0.08) and better OS (HR: 0.4; p = 0.04); haplotype-Bx to increase the incidence of cGvHD (OR: 4.1; p = 0.03). In multivariate analysis, DFS advantage remained significant for aKIR-matching (HR: 0.5; p = 0.04); cGvHD incidence was reduced in the presence of iKIR-match (OR: 0.3; p = 0.02) and increased in the presence of haplotype-AB and -BB donors (OR: 7.9; p = 0.02; OR: 5.1; p = 0.03, respectively). In an attempt to investigate the pathogenesis underlying KIR-matching, we searched for residual NK/T cells on day 0 peripheral blood samples of six additional recipients and noted the presence of CD3+ (7.0–91.4 × 106/L) and CD56+57+ (0.8–12.7 × 106/L) cells. In conclusion, conditioning regimen surviving recipient NK/T cells potentially influenced by KIR-matching may contribute to GvL/GvH reactions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beksac M, Dalva K (2012) Role of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor and ligand matching in donor selection. Bone Marrow Res 2012:271695–271696. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/271695
Passweg JR, Huard B, Tiercy JM, Roosnek E (2007) HLA and KIR polymorphisms affect NK-cell anti-tumor activity. Trends Immunol 28(10):437–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2007.07.008
Ljunggren HG, Karre K (1990) In search of the 'missing self': MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today 11(7):237–244
Hsu KC, Dupont B (2005) Natural killer cell receptors: regulating innate immune responses to hematologic malignancy. Semin Hematol 42(2):91–103
Venstrom JM, Pittari G, Gooley TA, Chewning JH, Spellman S, Haagenson M, Gallagher MM, Malkki M, Petersdorf E, Dupont B, Hsu KC (2012) HLA-C-dependent prevention of leukemia relapse by donor activating KIR2DS1. N Engl J Med 367(9):805–816. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1200503
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Shlomchik WD, Tosti A, Posati S, Rogaia D, Frassoni F, Aversa F, Martelli MF, Velardi A (2002) Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science 295(5562):2097–2100. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1068440
Bishara A, De Santis D, Witt CC, Brautbar C, Christiansen FT, Or R, Nagler A, Slavin S (2004) The beneficial role of inhibitory KIR genes of HLA class I NK epitopes in haploidentically mismatched stem cell allografts may be masked by residual donor-alloreactive T cells causing GVHD. Tissue Antigens 63(3):204–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0001-2815.2004.00182.x
Symons HJ, Leffell MS, Rossiter ND, Zahurak M, Jones RJ, Fuchs EJ (2010) Improved survival with inhibitory killer immunoglobulin receptor (KIR) gene mismatches and KIR haplotype B donors after nonmyeloablative, HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 16(4):533–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.11.022
Weisdorf D, Cooley S, Devine S, Fehniger TA, DiPersio J, Anasetti C, Waller EK, Porter D, Farag S, Drobyski W, Defor T, Haagenson M, Curtsinger J, Miller J (2012) T cell-depleted partial matched unrelated donor transplant for advanced myeloid malignancy: KIR ligand mismatch and outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 18(6):937–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2011.11.024
Neuchel C, Furst D, Niederwieser D, Bunjes D, Tsamadou C, Wulf G, Pfreundschuh M, Wagner E, Stuhler G, Einsele H, Schrezenmeier H, Mytilineos J (2017) Impact of donor activating KIR genes on HSCT outcome in C1-ligand negative myeloid disease patients transplanted with unrelated donors-a retrospective study. PLoS One 12(1):e0169512. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169512
Sobecks RM, Ball EJ, Maciejewski JP, Rybicki LA, Brown S, Kalaycio M, Pohlman B, Andresen S, Theil KS, Dean R, Bolwell BJ (2007) Survival of AML patients receiving HLA-matched sibling donor allogeneic bone marrow transplantation correlates with HLA-Cw ligand groups for killer immunoglobulin-like receptors. Bone Marrow Transplant 39(7):417–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705609
Giebel S, Locatelli F, Lamparelli T, Velardi A, Davies S, Frumento G, Maccario R, Bonetti F, Wojnar J, Martinetti M, Frassoni F, Giorgiani G, Bacigalupo A, Holowiecki J (2003) Survival advantage with KIR ligand incompatibility in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors. Blood 102(3):814–819. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-01-0091
Davies SM, Ruggieri L, DeFor T, Wagner JE, Weisdorf DJ, Miller JS, Velardi A, Blazar BR (2002) Evaluation of KIR ligand incompatibility in mismatched unrelated donor hematopoietic transplants. Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor. Blood 100(10):3825–3827. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-04-1197
Beelen DW, Ottinger HD, Ferencik S, Elmaagacli AH, Peceny R, Trenschel R, Grosse-Wilde H (2005) Genotypic inhibitory killer immunoglobulin-like receptor ligand incompatibility enhances the long-term antileukemic effect of unmodified allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with myeloid leukemias. Blood 105(6):2594–2600. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-04-1441
De Santis D, Bishara A, Witt CS, Nagler A, Brautbar C, Slavin S, Christiansen FT (2005) Natural killer cell HLA-C epitopes and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors both influence outcome of mismatched unrelated donor bone marrow transplants. Tissue Antigens 65(6):519–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0039.2005.00396.x
Farag SS, Bacigalupo A, Eapen M, Hurley C, Dupont B, Caligiuri MA, Boudreau C, Nelson G, Oudshoorn M, van Rood J, Velardi A, Maiers M, Setterholm M, Confer D, Posch PE, Anasetti C, Kamani N, Miller JS, Weisdorf D, Davies SM, Kir Study Group CfIB, Marrow Transplantation R (2006) The effect of KIR ligand incompatibility on the outcome of unrelated donor transplantation: a report from the center for international blood and marrow transplant research, the European blood and marrow transplant registry, and the Dutch registry. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 12(8):876–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.05.007
Brunstein CG, Wagner JE, Weisdorf DJ, Cooley S, Noreen H, Barker JN, DeFor T, Verneris MR, Blazar BR, Miller JS (2009) Negative effect of KIR alloreactivity in recipients of umbilical cord blood transplant depends on transplantation conditioning intensity. Blood 113(22):5628–5634. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-12-197467
Willemze R, Rodrigues CA, Labopin M, Sanz G, Michel G, Socie G, Rio B, Sirvent A, Renaud M, Madero L, Mohty M, Ferra C, Garnier F, Loiseau P, Garcia J, Lecchi L, Kogler G, Beguin Y, Navarrete C, Devos T, Ionescu I, Boudjedir K, Herr AL, Gluckman E, Rocha V (2009) KIR-ligand incompatibility in the graft-versus-host direction improves outcomes after umbilical cord blood transplantation for acute leukemia. Leukemia 23(3):492–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.365
Bjorklund AT, Schaffer M, Fauriat C, Ringden O, Remberger M, Hammarstedt C, Barrett AJ, Ljungman P, Ljunggren HG, Malmberg KJ (2010) NK cells expressing inhibitory KIR for non-self-ligands remain tolerant in HLA-matched sibling stem cell transplantation. Blood 115(13):2686–2694. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-229740
Cook MA, Milligan DW, Fegan CD, Darbyshire PJ, Mahendra P, Craddock CF, Moss PA, Briggs DC (2004) The impact of donor KIR and patient HLA-C genotypes on outcome following HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myeloid leukemia. Blood 103(4):1521–1526. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-02-0438
Hsu KC, Keever-Taylor CA, Wilton A, Pinto C, Heller G, Arkun K, O'Reilly RJ, Horowitz MM, Dupont B (2005) Improved outcome in HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia predicted by KIR and HLA genotypes. Blood 105(12):4878–4884. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-12-4825
McQueen KL, Dorighi KM, Guethlein LA, Wong R, Sanjanwala B, Parham P (2007) Donor-recipient combinations of group a and B KIR haplotypes and HLA class I ligand affect the outcome of HLA-matched, sibling donor hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hum Immunol 68(5):309–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2007.01.019
Stringaris K, Adams S, Uribe M, Eniafe R, Wu CO, Savani BN, Barrett AJ (2010) Donor KIR genes 2DL5A, 2DS1 and 3DS1 are associated with a reduced rate of leukemia relapse after HLA-identical sibling stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia but not other hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 16(9):1257–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.03.004
Wang H, He Y, Zhai WJ, Wang M, Zhou Z, Zhao YX, Feng SZ, Han MZ (2013) The impact of recipient HLA-Cw and donor killer immunoglobulin-like receptor genotyping on the outcome of patients receiving HLA-matched sibling donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myeloid malignancies. Swiss Med Wkly 143:w13717. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2013.13717
Verheyden S, Schots R, Duquet W, Demanet C (2005) A defined donor activating natural killer cell receptor genotype protects against leukemic relapse after related HLA-identical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 19(8):1446–1451. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403839
Faridi RM, Kemp TJ, Dharmani-Khan P, Lewis V, Tripathi G, Rajalingam R, Daly A, Berka N, Storek J, Masood Khan F (2016) Donor-recipient matching for KIR genotypes reduces chronic GVHD and missing inhibitory KIR ligands protect against relapse after Myeloablative, HLA matched hematopoietic cell transplantation. PLoS One 11(6):e0158242. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158242
Farag SS (2016) Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor ligand mismatching: to match or mismatch? Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22(2):192–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.11.1101
Yahng SA, Jeon YW, Yoon JH, Shin SH, Lee SE, Cho BS, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Lee S, Min CK, Cho SG, Kim DW, Lee JW, Min WS, Kim HJ (2016) Negative impact of unidirectional host-versus-graft killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor ligand mismatch on transplantation outcomes after Unmanipulated Haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22(2):316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.09.018
Giralt S, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Bacigalupo A, Horowitz M, Pasquini M, Sandmaier B (2009) Reduced-intensity conditioning regimen workshop: defining the dose spectrum. Report of a workshop convened by the center for international blood and marrow transplant research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 15(3):367–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.12.497
Cahn JY, Klein JP, Lee SJ, Milpied N, Blaise D, Antin JH, Leblond V, Ifrah N, Jouet JP, Loberiza F, Ringden O, Barrett AJ, Horowitz MM, Socie G, Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et Therapie C, Dana Farber Cancer I, International Bone Marrow Transplant R (2005) Prospective evaluation of 2 acute graft-versus-host (GVHD) grading systems: a joint Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et Therapie Cellulaire (SFGM-TC), Dana Farber cancer institute (DFCI), and international bone marrow transplant registry (IBMTR) prospective study. Blood 106(4):1495–1500. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-11-4557
Fraser CJ, Scott Baker K (2007) The management and outcome of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol 138(2):131–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06652.x
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, Martin P, Chien J, Przepiorka D, Couriel D, Cowen EW, Dinndorf P, Farrell A, Hartzman R, Henslee-Downey J, Jacobsohn D, McDonald G, Mittleman B, Rizzo JD, Robinson M, Schubert M, Schultz K, Shulman H, Turner M, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME (2005) National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 11(12):945–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.09.004
Parham P (2005) MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health and survival. Nat Rev Immunol 5(3):201–214. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1570
Dorak MT (2007) Role of natural killer cells and killer immunoglobulin-like receptor polymorphisms: association of HLA and KIRs. Methods Mol Med 134:123–144
Hsu KC, Chida S, Geraghty DE, Dupont B (2002) The killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genomic region: gene-order, haplotypes and allelic polymorphism. Immunol Rev 190:40–52
European Bioinformatics Institute (2016) Donor KIR B-content group calculator. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ipd/kir/donor_b_content.html
Cooley S, Weisdorf DJ, Guethlein LA, Klein JP, Wang T, Le CT, Marsh SG, Geraghty D, Spellman S, Haagenson MD, Ladner M, Trachtenberg E, Parham P, Miller JS (2010) Donor selection for natural killer cell receptor genes leads to superior survival after unrelated transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 116(14):2411–2419. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-05-283051
Bursac Z, Gauss CH, Williams DK, Hosmer DW (2008) Purposeful selection of variables in logistic regression. Source Code Biol Med 3:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0473-3-17
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Casucci M, Volpi I, Tosti A, Perruccio K, Urbani E, Negrin RS, Martelli MF, Velardi A (1999) Role of natural killer cell alloreactivity in HLA-mismatched hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 94(1):333–339
Rocha V, Ruggeri A, Spellman S, Wang T, Sobecks R, Locatelli F, Askar M, Michel G, Arcese W, Iori AP, Purtill D, Danby R, Sanz GF, Gluckman E, Eapen M, Eurocord, Cord Blood Committee Cellular Therapy Immunobiology Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, Netcord, and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (2016) Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor-ligand matching and outcomes after unrelated cord blood transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22(7):1284–1289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2016.04.007
Beksac K, Beksac M, Dalva K, Karaagaoglu E, Tirnaksiz MB (2015) Impact of "Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor /Ligand" Genotypes on Outcome following Surgery among Patients with Colorectal Cancer: Activating KIRs Are Associated with Long-Term Disease Free Survival. PLoS One 10(7):e0132526
Stewart CA, Laugier-Anfossi F, Vely F, Saulquin X, Riedmuller J, Tisserant A, Gauthier L, Romagne F, Ferracci G, Arosa FA, Moretta A, Sun PD, Ugolini S, Vivier E (2005) Recognition of peptide-MHC class I complexes by activating killer immunoglobulin-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(37):13224–13229. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0503594102
Shah N (2015) Activating KIR: iN Kase of KIR-ligand mismatch. Blood 125(20):3045–3046. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-03-634733
Wu X, Yao Y, Bao X, Zhou H, Tang X, Han Y, Ma X, Liu Y, Chen J, Zhou H, Jing S, Gu B, Xu Y, Sun A, He J, Wu D (2015) KIR2DS4 and its variant KIR1D are associated with acute graft-versus-host disease, cytomegalovirus, and overall survival after sibling-related HLA-matched transplantation in patients with donors with KIR gene haplotype a. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22(2):220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.10.004
Middleton D, Gonzalez-Galarza F, Meenagh A, Gourraud PA (2010) Diversity of KIR genes, alleles and haplotypes. In: Zimmer J (ed) Natural Killer Cells. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 63–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02309-5_3
Elmaagacli AH, Ottinger H, Koldehoff M, Peceny R, Steckel NK, Trenschel R, Biersack H, Grosse-Wilde H, Beelen DW (2005) Reduced risk for molecular disease in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia after transplantation from a KIR-mismatched donor. Transplantation 79(12):1741–1747
Bachanova V, Weisdorf DJ, Wang T, Marsh SG, Trachtenberg E, Haagenson MD, Spellman SR, Ladner M, Guethlein LA, Parham P, Miller JS, Cooley SA (2016) Donor KIR B genotype improves progression-free survival of non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients receiving unrelated donor transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22(9):1602–1607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2016.05.016
Acknowledgements
Funda Gungor and Klara Dalva performed the laboratory analysis. Meral Beksac designed the research and selected subjects to be included in the study. Ugur Sahin and Celalettin Ustun analyzed the data. Ugur Sahin and Meral Beksac wrote the paper.
Authors are thankful to Dr. Daniel J. Weisdorf for his most valuable suggestions about the statistical approaches and critical review of the manuscript. We also would like to thank Atilla Halil Elhan and Ryan Shanley for their suggestions during data analysis; Dr. Erden Atilla and Didem Civit for their help in formation of the patient database.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and good clinical practice guidelines and was approved by the local institutional review board of Ankara University Medical School. Written informed consents were obtained from all participants prior to enrollment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary materials
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahin, U., Dalva, K., Gungor, F. et al. Donor-recipient killer immunoglobulin like receptor (KIR) genotype matching has a protective effect on chronic graft versus host disease and relapse incidence following HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 97, 1027–1039 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3274-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3274-0