Abstract
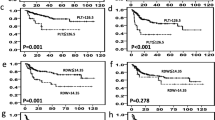
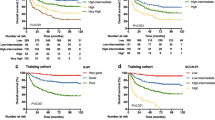
Few studies have examined the prognostic impact of blood markers [other than the five factors in the enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI)] in elderly patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). We retrospectively analyzed 391 DLBCL patients receiving rituximab plus anthracycline-containing chemotherapy to examine the prognostic impact of simple blood markers. The NCCN-IPI was more accurate for discriminating prognoses than the original IPI. Multivariate analysis identified platelet count (<100,000/μl) and albumin (<3.5 g/dl) levels as significantly associated with lower overall survival (OS), independently of the NCCN-IPI. These parameters stratified patients into three risk groups: platelet–albumin (PA) score low (platelet count ≥100,000/μl, albumin ≥3.5 g/dl, n = 243); intermediate (platelet count <100,000/μl, albumin ≥3.5 g/dl or platelet count ≥100,000/μl, albumin <3.5 g/dl, n = 125); and high (platelet count <100,000/μl, albumin <3.5 g/dl, n = 23). The 5-year OS rates were 81.5, 48.6, and 20.2 %, respectively (p < 0.001). Notably, most patients with a low platelet count (n = 30) were stratified into the high-risk subgroup, suggesting that platelet count was prognostic for high-risk patients with a dismal outcome. In elderly patients (n = 291), the prognostic value of the NCCN-IPI might be diminished because the low-risk category was excluded; however, the PA score was predictive of survival: the 5-year OS rates for PA score low (n = 171), intermediate (n = 101), and high (n = 19) groups were 77.6, 47.9, and 19.0 %, respectively (p < 0.001). Platelet count and albumin levels are useful prognostic factors, and their combined use can predict survival, even in elderly patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
The International non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project (1993) A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 329(14):987–994. doi:10.1056/nejm199309303291402
Ziepert M, Hasenclever D, Kuhnt E, Glass B, Schmitz N, Pfreundschuh M, Loeffler M (2010) Standard International prognostic index remains a valid predictor of outcome for patients with aggressive CD20+ B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. Journal of Clinical Oncology : Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 28(14):2373–2380. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.26.2493
Zhou Z, Sehn LH, Rademaker AW, Gordon LI, Lacasce AS, Crosby-Thompson A, Vanderplas A, Zelenetz AD, Abel GA, Rodriguez MA, Nademanee A, Kaminski MS, Czuczman MS, Millenson M, Niland J, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM, Friedberg JW, Winter JN (2014) An enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the rituximab era. Blood 123(6):837–842. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-09-524108
Huang CE, Chen YY, Lu CH, Chen PT, Lee KD, Chen CC (2015) Validation of an enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) in an Asian cohort of patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 94(6):1063–1065. doi:10.1007/s00277-014-2293-8
Melchardt T, Troppan K, Weiss L, Hufnagl C, Neureiter D, Trankenschuh W, Hopfinger G, Magnes T, Deutsch A, Neumeister P, Hackl H, Greil R, Pichler M, Egle A (2015) A modified scoring of the NCCN-IPI is more accurate in the elderly and is improved by albumin and beta2 -microglobulin. Br J Haematol 168(2):239–245. doi:10.1111/bjh.13116
Aoki K, Tabata S, Yonetani N, Matsushita A, Ishikawa T (2013) The prognostic impact of absolute lymphocyte and monocyte counts at diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. Acta Haematol 130(4):242–246. doi:10.1159/000350484
Cao Y, Shi YX, Chen JO, Tan YT, Cai YC, Luo HY, Qiu MZ, Cai XY, Jin Y, Sun YL, Jiang WQ (2012) Serum C-reactive protein as an important prognostic variable in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Tumour Biology : The Journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 33(4):1039–1044. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0337-z
Bairey O, Shacham-Abulafia A, Shpilberg O, Gurion R (2015) Serum albumin level at diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: an important simple prognostic factor. Hematol Oncol. doi:10.1002/hon.2233
Legouffe E, Rodriguez C, Picot MC, Richard B, Klein B, Rossi JF, Commes T (1998) C-reactive protein serum level is a valuable and simple prognostic marker in non Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 31(3–4):351–357. doi:10.3109/10428199809059228
Chen LP, Lin SJ, Yu MS (2012) Prognostic value of platelet count in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 12(1):32–37. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2011.09.215
Markovic O, Popovic L, Marisavljevic D, Jovanovic D, Filipovic B, Stanisavljevic D, Matovina-Brko G, Hajder J, Matkovic T, Zivkovic R, Stanisavljevic N, Todorovic M, Petrovic D, Mihaljevic B (2014) Comparison of prognostic impact of absolute lymphocyte count, absolute monocyte count, absolute lymphocyte count/absolute monocyte count prognostic score and ratio in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Eur J Intern Med 25(3):296–302. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2014.01.019
Wilcox RA, Ristow K, Habermann TM, Inwards DJ, Micallef IN, Johnston PB, Colgan JP, Nowakowski GS, Ansell SM, Witzig TE, Markovic SN, Porrata L (2011) The absolute monocyte and lymphocyte prognostic score predicts survival and identifies high-risk patients in diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 25(9):1502–1509. doi:10.1038/leu.2011.112
Aoki K, Takahashi T, Tabata S, Kurata M, Matsushita A, Nagai K, Ishikawa T (2013) Efficacy and tolerability of reduced-dose 21-day cycle rituximab and cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisolone therapy for elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 54(11):2441–2447. doi:10.3109/10428194.2013.780654
Tsimberidou AM, O’Brien S, Khouri I, Giles FJ, Kantarjian HM, Champlin R, Wen S, Do KA, Smith SC, Lerner S, Freireich EJ, Keating MJ (2006) Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with Richter’s syndrome treated with chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy with or without stem-cell transplantation. Journal of Clinical Oncology : Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 24(15):2343–2351. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.05.0187
Parry-Jones N, Matutes E, Gruszka-Westwood AM, Swansbury GJ, Wotherspoon AC, Catovsky D (2003) Prognostic features of splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes: a report on 129 patients. Br J Haematol 120(5):759–764
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(3):452–458. doi:10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Yamauchi T, Tasaki T, Tai K, Ikegaya S, Takagi K, Negoro E, Kishi S, Yoshida A, Iwasaki H, Ueda T (2015) Prognostic effect of peripheral blood cell counts in advanced diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP-like chemotherapy: a single institution analysis. Oncol Lett 9(2):851–856. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2716
Binet JL, Auquier A, Dighiero G, Chastang C, Piguet H, Goasguen J, Vaugier G, Potron G, Colona P, Oberling F, Thomas M, Tchernia G, Jacquillat C, Boivin P, Lesty C, Duault MT, Monconduit M, Belabbes S, Gremy F (1981) A new prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia derived from a multivariate survival analysis. Cancer 48(1):198–206
Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, Chanana AD, Levy RN, Pasternack BS (1975) Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 46(2):219–234
Kantarjian HM, Dixon D, Keating MJ, Talpaz M, Walters RS, McCredie KB, Freireich EJ (1988) Characteristics of accelerated disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer 61(7):1441–1446
Kook H, Hwang TJ, Yang DW, Moon JD (1991) Therapeutic results and prognostic predictors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Cox regression analysis. J Korean Med Sci 6(4):348–354
Donadieu J, Auclerc MF, Baruchel A, Leblanc T, Landman-Parker J, Perel Y, Michel G, Cornu G, Bordigoni P, Sommelet D, Leverger G, Hill C, Schaison G (1998) Critical study of prognostic factors in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: differences in outcome are poorly explained by the most significant prognostic variables. Fralle Group. French Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Study Group. Br J Haematol 102(3):729–739
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403(6769):503–511. doi:10.1038/35000501
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI, Gascoyne RD, Muller-Hermelink HK, Smeland EB, Giltnane JM, Hurt EM, Zhao H, Averett L, Yang L, Wilson WH, Jaffe ES, Simon R, Klausner RD, Powell J, Duffey PL, Longo DL, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Sanger WG, Dave BJ, Lynch JC, Vose J, Armitage JO, Montserrat E, Lopez-Guillermo A, Grogan TM, Miller TP, LeBlanc M, Ott G, Kvaloy S, Delabie J, Holte H, Krajci P, Stokke T, Staudt LM (2002) The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346(25):1937–1947. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012914
Gutierrez-Garcia G, Cardesa-Salzmann T, Climent F, Gonzalez-Barca E, Mercadal S, Mate JL, Sancho JM, Arenillas L, Serrano S, Escoda L, Martinez S, Valera A, Martinez A, Jares P, Pinyol M, Garcia-Herrera A, Martinez-Trillos A, Gine E, Villamor N, Campo E, Colomo L, Lopez-Guillermo A (2011) Gene-expression profiling and not immunophenotypic algorithms predicts prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. Blood 117(18):4836–4843. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-12-322362
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Kasahara Memorial Foundation for Medical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures involving human participants were undertaken in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments (or comparable ethical standards). The nature of the study meant that the requirement for informed consent was waived.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ochi, Y., Kazuma, Y., Hiramoto, N. et al. Utility of a simple prognostic stratification based on platelet counts and serum albumin levels in elderly patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 96, 1–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2819-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2819-3