Abstract
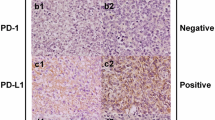
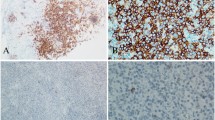
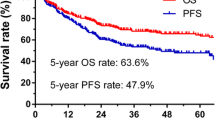
Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) are new therapeutic targets in cancer immunotherapy. The aim of this study was to investigate the clinicopathological characteristics of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in extranodal natural killer/T‑cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL). We performed PD-1 and PD-L1 immunostaining in 79 ENKTL biopsy samples and retrospectively analyzed medical records of all 79 patients from four tertiary referral hospitals. The expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 by tumor cells and/or infiltrating immune cells was evaluated. The expression rates of PD-L1 in tumor cells and infiltrating immune cells were 79.7 and 78.5 %, respectively, whereas PD-1 in tumor cells and infiltrating immune cells were 1.3 and 11.4 %. The PD-L1 positivity in tumor cells and infiltrating immune cells was significantly associated with low international prognostic index (IPI) (P = 0.044 and 0.037, respectively). Patients with normal range of serum lactate dehydrogenase demonstrated a significantly higher PD-L1 positivity in tumor cells (P = 0.020). PD-L1-positive patients had a trend toward better overall survival compared with that in patients with PD-L1-negative in tumor cells and infiltrating immune cells (P = 0.498 and 0.435, respectively). The expression rate of PD-L1 was up to 79.7 % in ENKTL, while PD-1 expression rate was very low. This is the first report describing the clinicopathological features and survival outcome according to expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 in ENKTL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huh J (2012) Epidemiologic overview of malignant lymphoma. Korean J Hematol 47(2):92–104
Suh C, Kim WS, Kim JS, Park B-B (2013) Review of the clinical research conducted by the Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma of the Korean Society of Hematology Lymphoma Working Party. Blood Res 48(3):171–177
Jaffe ES (2009) The 2008 WHO classification of lymphomas: implications for clinical practice and translational research. Hematology/the Education Program of the American Society of Hematology American Society of Hematology Education Program: 523-531. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2009.1.523
Chen BJ, Chapuy B, Ouyang J, Sun HH, Roemer MG, Xu ML, Yu H, Fletcher CD, Freeman GJ, Shipp MA, Rodig SJ (2013) PD-L1 expression is characteristic of a subset of aggressive B-cell lymphomas and virus-associated malignancies. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 19(13):3462–3473. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-0855
Hamid O, Carvajal RD (2013) Anti-programmed death-1 and anti-programmed death-ligand 1 antibodies in cancer therapy. Expert opinion on biological therapy 13(6):847–861. doi:10.1517/14712598.2013.770836
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Atkins MB, Leming PD, Spigel DR, Antonia SJ, Horn L, Drake CG, Pardoll DM, Chen L, Sharfman WH, Anders RA, Taube JM, McMiller TL, Xu H, Korman AJ, Jure-Kunkel M, Agrawal S, McDonald D, Kollia GD, Gupta A, Wigginton JM, Sznol M (2012) Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. The New England journal of medicine 366(26):2443–2454. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1200690
Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, Schuster SJ, Millenson MM, Cattry D, Freeman GJ, Rodig SJ, Chapuy B, Ligon AH, Zhu L, Grosso JF, Kim SY, Timmerman JM, Shipp MA, Armand P (2015) PD-1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. New England Journal of Medicine 372(4):311–319. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411087
Kim SJ (2015) Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma (CISL): a model of multicenter collaboration for lymphoma studies in Korea. Blood Res 50(4):187–188. doi:10.5045/br.2015.50.4.187
A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (1993) The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. The New England journal of medicine 329(14):987–994. doi:10.1056/nejm199309303291402
Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Jaccard A, Chng WJ, Lim ST, Hong H, Park Y, Chang KM, Maeda Y, Ishida F, Shin D-Y, Kim JS, Jeong SH, Yang D-H, Jo J-C, Lee G-W, Choi CW, Lee W-S, Chen T-Y, Kim K, Jung S-H, Murayama T, Oki Y, Advani R, d’Amore F, Schmitz N, Suh C, Suzuki R, Kwong YL, Lin T-Y, Kim WS A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. The Lancet Oncology 17 (3):389-400. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00533-1
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, Ishida Y, Tsubata T, Yagita H, Honjo T (1996) Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. International immunology 8(5):765–772
Andorsky DJ, Yamada RE, Said J, Pinkus GS, Betting DJ, Timmerman JM (2011) Programmed death ligand 1 is expressed by non-hodgkin lymphomas and inhibits the activity of tumor-associated T cells. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 17(13):4232–4244. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-2660
Bouvard V, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C, Galichet L, Cogliano V (2009) A review of human carcinogens—Part B: biological agents. The Lancet Oncology 10(4):321–322
Green MR, Rodig S, Juszczynski P, Ouyang J, Sinha P, O’Donnell E, Neuberg D, Shipp MA (2012) Constitutive AP-1 activity and EBV infection induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin lymphomas and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders: implications for targeted therapy. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 18(6):1611–1618. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1942
Paydas S, Bagir E, Seydaoglu G, Ercolak V, Ergin M (2015) Programmed death-1 (PD-1), programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), and EBV-encoded RNA (EBER) expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. Annals of hematology 94(9):1545–1552. doi:10.1007/s00277-015-2403-2
Koh YW, Jeon YK, Yoon DH, Suh C, Huh J (2015) Programmed death 1 expression in the peritumoral microenvironment is associated with a poorer prognosis in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4622-5
Roncador G, Garcia Verdes-Montenegro JF, Tedoldi S, Paterson JC, Klapper W, Ballabio E, Maestre L, Pileri S, Hansmann ML, Piris MA, Mason DY, Marafioti T (2007) Expression of two markers of germinal center T cells (SAP and PD-1) in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 92(8):1059–1066
Yuan CM, Vergilio JA, Zhao XF, Smith TK, Harris NL, Bagg A (2005) CD10 and BCL6 expression in the diagnosis of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: utility of detecting CD10+ T cells by flow cytometry. Human pathology 36(7):784–791. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2005.05.008
Ree HJ, Kadin ME, Kikuchi M, Ko YH, Suzumiya J, Go JH (1999) Bcl-6 expression in reactive follicular hyperplasia, follicular lymphoma, and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with hyperplastic germinal centers: heterogeneity of intrafollicular T-cells and their altered distribution in the pathogenesis of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Human pathology 30(4):403–411
Huang B, Chen L, Bao C, Sun C, Li J, Wang L, Zhang X (2015) The expression status and prognostic significance of programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 in gastrointestinal tract cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. OncoTargets and therapy 8:2617–2625. doi:10.2147/ott.s91025
Wu P, Wu D, Li L, Chai Y, Huang J (2015) PD-L1 and survival in solid tumors: a meta-analysis. PloS one 10(6), e0131403. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0131403
Hawkes EA, Grigg A, Chong G (2015) Programmed cell death-1 inhibition in lymphoma. The Lancet Oncology 16(5):e234–245. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70103-8
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Ulsan University Hospital (Biomedical Research Center Promotion Fund; Grant no. 2015-1).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 61 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, JC., Kim, M., Choi, Y. et al. Expression of programmed cell death 1 and programmed cell death ligand 1 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Hematol 96, 25–31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2818-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2818-4