Abstract
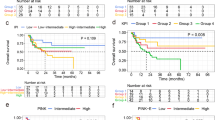
Extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) is an aggressive disease with a poor prognosis, requiring risk stratification in affected patients. We designed a new prognostic model specifically for ENKTL to identify high-risk patients who need more aggressive therapy. We retrospectively reviewed 158 patients who were newly diagnosed with ENKTL. The estimated 5-year overall survival rate was 39.4 %. Independent prognostic factors included total protein (TP) <60 g/L, fasting blood glucose (FBG) >100 mg/dL, and Korean Prognostic Index (KPI) score ≥2. We constructed a new prognostic model by combining these prognostic factors: group 1 (64 cases (41.0 %)), no adverse factors; group 2 (58 cases (37.2 %)), one adverse factor; and group 3 (34 cases (21.8 %)), two or three adverse factors. The 5-year overall survival (OS) rates of these groups were 66.7, 23.0, and 5.9 %, respectively (p < 0.001). Our new prognostic model had a better prognostic value than did the KPI model alone (p < 0.001). Our proposed prognostic model for ENKTL, including the newly identified prognostic indicators, TP and FBG, demonstrated a balanced distribution of patients into different risk groups with better prognostic discrimination compared with the KPI model alone.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe ES, Chan JK, Su IJ, Frizzera G, Mori S, Feller AC, Ho FC (1996) Report of the workshop on nasal and related extranodal angiocentric T/Natural killer cell lymphomas. Definitions, differential diagnosis, and epidemiology. Am J Surg Pathol 20(1):103–111
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J, Lister TA, Bloomfield CD (1999) World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting—Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J Clin Oncol 17(12):3835–3849
Wan M, Chow J, Lei K, Chan W (2004) Allelotyping of gastrointestinal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma. Leuk Res 28(4):339–343. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2003.08.004
Vose JM, Neumann M, Harris ME, Project IT-CL (2008) International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol 26(25):4124–4130. doi:10.1200/Jco.2008.16.4558
Ai WZ, Chang ET, Fish K, Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Keegan TH (2012) Racial patterns of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, in California: a population-based study. Br J Haematol 156(5):626–632. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08982.x
Guo H-Q, Huang G-L, Guo C-C, Pu X-X, Lin T-Y (2010) Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-221 for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Dis Markers 29(5):251–258
Al-Hakeem DA, Fedele S, Carlos R, Porter S (2007) Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Oral Oncol 43(1):4–14
Aviles A, Diaz NR, Neri N, Cleto S, Talavera A (2000) Angiocentric nasal T/natural killer cell lymphoma: a single centre study of prognostic factors in 108 patients. Clin Lab Haematol 22(4):215–220. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2257.2000.00307.x
Cheung MM, Chan JK, Lau WH, Ngan RK, Foo WW (2002) Early stage nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: clinical outcome, prognostic factors, and the effect of treatment modality. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 54(1):182–190
Chim CS, Ma SY, Au WY, Choy C, Lie AK, Liang R, Yau CC, Kwong YL (2004) Primary nasal natural killer cell lymphoma: long-term treatment outcome and relationship with the International Prognostic Index. Blood 103(1):216–221. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-05-1401
Au WY, Weisenburger DD, Intragumtornchai T, Nakamura S, Kim WS, Sng I, Vose J, Armitage JO, Liang R, Pro IPT-CL (2009) Clinical differences between nasal and extranasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a study of 136 cases from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood 113(17):3931–3937. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-10-185256
Kim TM, Park YH, Lee S-Y, Kim J-H, Kim D-W, Im S-A, Kim T-Y, Kim CW, Heo DS, Bang Y-J, Chang K-H, Kim NK (2005) Local tumor invasiveness is more predictive of survival than International Prognostic Index in stage I(E)/II(E) extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 106(12):3785–3790
Oshimi K, Kawa K, Nakamura S, Suzuki R, Suzumiya J, Yamaguchi M, Kameoka J, Tagawa S, Imamura N, Ohshima K, Kojya S, Iwatsuki K, Tokura Y, Sato E, Sugimori H, Grp N-CTS (2005) NK-cell neoplasms in Japan. Hematology 10(3):237–245. doi:10.1080/10245330400026162
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH, Lee DH, Huh J, Oh SY, Kwon H-C, Kim HJ, Lee SI, Kim JH, Park J, Oh SJ, Kim K, Jung C, Park K, Kim WS (2006) Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 24(4):612–618
Kim TM, Lee SY, Jeon YK, Ryoo BY, Cho GJ, Hong YS, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim CS, Kim S, Kim JS, Sohn SK, Song HH, Lee JL, Kang YK, Yim CY, Lee WS, Yuh YJ, Kim CW, Heo DS, Lymphoma Subcommittee of the Korean Cancer Study G (2008) Clinical heterogeneity of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: a national survey of the Korean Cancer Study Group. Ann Oncol 19(8):1477–1484
Park BB, Ryoo BY, Lee JH, Kwon HC, Yang SH, Kang HJ, Kim HJ, Oh SY, Ko YH, Huh JR, Lee SS, Nam EM, Park KW, Kim JH, Kang JH, Bang SM, Park S, Kim K, Park K, Suh C, Kim WS (2007) Clinical features and treatment outcomes of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 48(4):716–722. doi:10.1080/10428190601123989
Rodriguez J, Conde E, Gutierrez A, Arranz R, Leon A, Marin J, Bendandi M, Albo C, Caballero MD (2007) The results of consolidation with autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) in first complete remission: the Spanish Lymphoma and Autologous Transplantation Group experience. Ann Oncol 18(4):652–657. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl466
Beltran B, Quinones P, Morales D, Cotrina E, Castillo JJ (2011) Different prognostic factors for survival in acute and lymphomatous adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Leuk Res 35(3):334–339. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2010.08.006
Huang JJ, Jiang WQ, Lin TY, Huang Y, Xu RH, Huang HQ, Li ZM (2011) Absolute lymphocyte count is a novel prognostic indicator in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol 22(1):149–155. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq314
Cai Q, Luo X, Liang Y, Rao H, Fang X, Jiang W, Lin T, Lin T, Huang H (2013) Fasting blood glucose is a novel prognostic indicator for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Br J Cancer 108(2):380–386. doi:10.1038/Bjc.2012.566
Lee J, Park YH, Kim WS, Lee S-S, Ryoo B-Y, Yang SH, Park KW, Kang JH, Park JO, Lee SH, Kim K, Jung CW, Park YS, Im Y-H, Kang WK, Lee MH, Ko YH, Ahn YC, Park K (2005) Extranodal nasal type NK/T-cell lymphoma: elucidating clinical prognostic factors for risk-based stratification of therapy. Eur J Cancer 41(10):1402–1408
Kim TM, Heo DS (2009) Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: new staging system and treatment strategies. Cancer Sci 100(12):2242–2248
Luo J, Chen Y-J, Chang L-J (2012) Fasting blood glucose level and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Lung Cancer 76(2):242–247
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, Lister TA, Vose J, Grillo-Lopez A, Hagenbeek A, Cabanillas F, Klippensten D, Hiddemann W, Castellino R, Harris NL, Armitage JO, Carter W, Hoppe R, Canellos GP (1999) Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol 17(4):1244
Grillo-Lopez AJ, Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Peterson BA, Carter WD, Varns CL, Klippenstein DL, Shen CD (2000) Response criteria for NHL: importance of ‘normal’ lymph node size and correlations with response rates. Ann Oncol 11(4):399–408. doi:10.1023/A:1008332713631
Kim SJ, Kim BS, Choi CW, Choi J, Kim I, Lee YH, Kim JS (2007) Ki-67 expression is predictive of prognosis in patients with stage I/II extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Oncol 18(8):1382–1387
Watanabe T, Kinoshita T, Itoh K, Yoshimura K, Ogura M, Kagami Y, Yamaguchi M, Kurosawa M, Tsukasaki K, Kasai M, Tobinai K, Kaba H, Mukai K, Nakamura S, Ohshima K, Hotta T, Shimoyama M, Jcog LSG (2010) Pretreatment total serum protein is a significant prognostic factor for the outcome of patients with peripheral T/natural killer-cell lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma 51(5):813–821. doi:10.3109/10428191003721359
Barone BB, Yeh HC, Snyder CF, Peairs KS, Stein KB, Derr RL, Wolff AC, Brancati FL (2008) Long-term all-cause mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 300(23):2754–2764
Richardson LC, Pollack LA (2005) Therapy insight: influence of type 2 diabetes on the development, treatment and outcomes of cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2(1):48–53. doi:10.1038/Ncponc0062
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81372883 and 81001052), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (2011B031800222), Young Talents Project of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (to Cai Qingqing), Young Talents Project of Sun Yat-sen University (to Cai Qingqing), and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (8151008901000043). This research was also partly supported by the NIH through MD Anderson's Cancer Center Support Grant CA016672.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qingqing Cai, Xiaolin Luo, and Guanrong Zhang equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Q., Luo, X., Zhang, G. et al. New prognostic model for extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Hematol 93, 1541–1549 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2089-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2089-x