Abstract
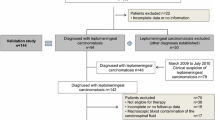
Conventional cytology (CC) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fails to demonstrate malignant cells in up to 45 % of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or lymphoblastic lymphoma (ALL/LL) in whom occult leptomeningeal disease is present. Flow cytometry (FCM) is considered more sensitive than CC, but clinical implications of CC negativity/CC positivity are not yet established. CSF samples from 38 adult patients with newly diagnosed ALL/LL were examined. Five (13 %) and nine (24 %) specimens were CC positive-FC positive (FCMpos/CCpos) and CC negative-FC positive (CCneg/FCMpos), respectively. The remaining 24 (63 %) samples were double negative (CCneg/FCMneg) (p = 0.001). CCneg/FCMpos patients showed a significantly shorter overall survival (OS) compared to CCneg/FCMneg ones. In multivariate analysis, the status of single FCM positivity was demonstrated to affect independently duration of OS (p = 0.005). In conclusion, FCM significantly improves detection of leptomeningeal occult localization in ALL/LL and appears to anticipate an adverse outcome. Further prospective studies on larger series are needed to confirm this preliminary observation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas X, Le QH (2008) Central nervous system involvement in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology 13:293–302
Fiere D, Lepage E, Sebban C, Boucheix C, Gisselbrecht VJP, Varet B, Broustet A, Cahn JY, Rigal-Huquet et al (1993) Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a multicentric randomized trial testing bone marrow transplantation as postremission therapy. J Clin Oncol 11:1990–2001
Ahluwalia MS, Wallace PK, Peereboom DM (2012) Flow cytometry as a diagnostic tool in lymphomatous or leukemic meningitis. Cancer 118(7):1747–1753
Quijano S, Lopez A, Sancho JM, Panizo C, Debén G, Castilla C, García-Vela JA, Salar A, Alonso-Vence N, Gonzalez-Barca E, Penalver FJ, Plaza-Villa JJ, Morado M, García-Marco AJ, Briones J, Ferrer S, Capote J, Concepción N, Orfao A (2009) Identification of leptomeningeal disease in aggressive B-cell non Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: improved sensitivity of flow cytometry. J Clin Oncol 27:1462–1469
French CA, Dorfman DM, Shaheen G, Cibas ES (2000) Diagnosing lymphoproliferative disorders involving the cerebrospinal fluid: increased sensitivity using flow cytometric analysis. Diagn Cytopathol 23:369–374
Hegde U, Filie AC, Little RF, Janik JE, Grant N, Steinberg SM, Dunleavy K, Jaffe ES, Abati A, Stetler-Stevenson M, Wilson WH (2005) High incidence of occult leptomeningeal disease detected by flow cytometry in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas at risk for central nervous system involvement: The role of flow cytometry versus cytology. Blood 105:496–502
Benevolo G, Stacchini A, Spina M, Ferreri AJ, Arras M, Bellio L, Botto B, Bulian P, Cantonetti M, Depaoli L, Di Renzo N, Di Rocco A, Evangelista A, Franceschetti S, Godio L, Mannelli F, Pavone V, Pioltelli P, Vitolo U, Pogliani EM, Linfomi FI (2012) Final results of a multicenter trial addressing role of CSF flow cytometric analysis in NHL patients at high risk for CNS dissemination. Blood 120(16):3222–3228
Craig FE, Foon KA (2008) Flow cytometric immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood 111:3941–3967
Bromberg JE, Breems DA, Kraan J, Bikker J, van der Holt B, Smitt PS, van den Bent MJ, van’t Veer M, Gratama JW (2007) CSF flow cytometry greatly improves diagnostic accuracy in CNS hematologic malignancies. Neurology 68:1674–1679
Annino L, Vignetti M, Paoloni FP et al (2009) Treatment of adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): an update of the GIMEMA experience. Blood 114:3097a
Kantarjian HM, O’Brien S, Smith TL, Cortes J, Giles FJ, Beran M, Pierce S, Huh Y, Andreeff M, Koller C, Ha CS, Keating MJ, Murphy S, Freireich EJ (2000) Results of treatment with hyper-CVAD, a dose-intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 18:547–561
Kantarjian H, Thomas D, O’Brien S, Cortes J, Giles F, Jeha S, Bueso-Ramos CE, Pierce S, Shan J, Koller C, Beran M, Keating M, Freireich EJ (2004) Long-term follow-up results of hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone (Hyper-CVAD), a dose-intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 101:2788–2801
Mahmoud HH, Rivera GK, Hancock ML, Krance RA, Kun LE, Behm FG, Ribeiro RC, Sandlund JT, Crist WM, Pui CH (1993) Low leukocyte counts with blast cells in cerebrospinal fluid of children with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. New Engl J Med 329:314–319
Di Noto R, Scalia G, Abate G, Gorrese M, Pascariello C, Raia M, Morabito P, Capone F, Cl P, Mirabelli P, Mariotti E, Del Vecchio L (2008) Critical role of multidimensional flow cytometry in detecting occult leptomeningeal disease in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Leuk Res 32:1196–1199
Mitri Z, Siddiqui MT, El Rassi F, Holden JT, Heffner LT, Langston A, Waller EK, Winton E, McLemore M, Bernal-Mizrachi L, Jaye D, Arellano M, Khoury HJ (2013) Sensitivity and specificity of, cerebrospinal fluid flow cytometry for the diagnosis of leukemic meningitis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma Oct 18 [epub ahead of print]
Sayed D, Badrawy H, Ali AM, Shaker S (2009) Immunophenotyping and immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement analysis in cerebrospinal fluid of paediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Res 33:655–661
Scrideli CA, Queiroz RP, Takayanagui OM, Bernardes JE, Melo EV, Tone LT (2004) Molecular diagnosis of leukemic cerebrospinal fluid cells in children with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 89(8):1013–1015
Pui CH, Howard SC (2008) Current management and challenges of malignant disease in the CNS in paediatric leukemia. Lancet Oncol 9:257–268
Martínez-Laperche C, Gómez-García AM, Lassaletta Á, Moscardó C, Vivanco JL, Molina J, Fuster JL, Couselo JM, de Toledo SJ, Bureo E, Madero L, Ramírez M (2013) Detection of occult cerebrospinal fluid involvement during maintenance therapy identifies a group of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia at high risk for relapse. Am J Hematol 88(5):359–364
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Del Principe, M.I., Buccisano, F., Cefalo, M. et al. High sensitivity of flow cytometry improves detection of occult leptomeningeal disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoblastic lymphoma. Ann Hematol 93, 1509–1513 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2080-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-014-2080-6