Abstract
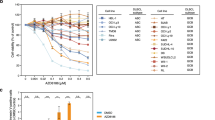
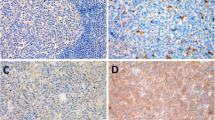
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) represents the most common subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and accounts for approximately 30 % of newly diagnosed lymphoid neoplasms in Western countries, and 40–50 % in China. A better understanding of the biology of DLBCL is needed for the development of potential therapeutic agents that target specific intracellular pathways. In this study, expression of the important components of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway and their clinical significance were investigated in 73 DLBCL cases. The effect of rituximab alone or combined with the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitor rapamycin was further evaluated in the DLBCL cell lines. A total of 73 patients were identified, including 45 men and 28 women aged 18 to 78 years (median age 50 years). Of these patients, p-AKT was positive in 40 cases (54.8 %), p-p70S6K in 34 cases (46.6 %), and p-4E-BP1 in 33 cases (45.2 %). Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway was related to poor disease outcome in DLBCL patients treated with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) but not in those treated with rituximab-CHOP. Rituximab combined with rapamycin synergically downregulated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Western blot analysis revealed a baseline activation status of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in DLBCL cell lines, with high levels of p-AKT, p-mTOR, in addition to downstream molecules p-p70S6K and p-4E-BP1. The results indicate that the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is a potentially important signaling route and an unfavorable prognostic factor for DLBCL. Patients with PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation experience a more rapidly deteriorating clinical course with poor treatment response and decreased survival time. Addition of rituximab could downregulate PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation, reversing its negative effect on chemotherapy-treated patients. In addition, our results indicate that the combination of rituximab and inhibition of the activated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway could be a promising target for DLBCL therapeutic intervention in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (2001) World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumors of hematopoetic and lymphoid tissues. IARC, Lyon
Li JM, Wang L, Shen Y et al (2007) Rituximab in combination with CHOP chemotherapy for the treatment of diffuse large B cell lymphoma in Chinese patients. Ann Hematol 86:639–645
Mey U, Hitz F, Lohri A, Pederiva S, Taverna C, Tzankov A, Meier O, Yeow K, Renner C (2012) Diagnosis and treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Swiss Med Wkly 142:0. doi:10.4414/smw.2012.13511
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE et al (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC et al (2002) The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 20:1937–1947
Uddin S, Hussain AR, Siraj AK et al (2006) Role of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival. Blood 108:4178–4186
Wanner K, Hipp S, Oelsner M, Ringshausen I, Bogner C, Peschel C, Decker T (2006) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition induces cell cycle arrest in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells and sensitises DLBCL cells to rituximab. Br J Haematol 134:475–484
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296:1655–1657
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, Franklin RA, McCubrey JA (2003) Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 17:590–603
Morgensztern D (2005) McLeod HL.PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16:797–803
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E, Braziel RM, Jaffe ES et al (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103:275–282
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, Lister TA, Vose J, Grillo-López A, Hagenbeek A et al (1999) Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol 17:1244
Friedberg JW (2011) Relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2011:498–505
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129:1261–1274
Fillmore GC, Wang Q, Carey MJ, Kim CH, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Lim MS (2005) Expression of Akt (protein kinase B) and its isoforms in malignant lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma 46:1765–1773
Hasselblom S, Hansson U, Olsson M et al (2010) High immunohistochemical expression of p-AKT predicts inferior survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. Br J Haematol 149(4):560–568
Cartron G, Dacheux L, Salles G, Solal-Celigny P, Bardos P, Colombat P, Watier H (2002) Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood 99:754–758
Suzuki E, Umezawa K, Bonavida B (2007) Rituximab inhibits the constitutively activated PI3K-Akt pathway in B-NHL cell lines: involvement in chemosensitization to drug-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 26:6184–6193
Ansell SM, Tang H, Kurtin PJ et al (2011) Temsirolimus and rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 12(4):361–368
Fingar DC, Blenis J (2004) Target of rapamycin (TOR): an integrator of nutrient and growth factor signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 23:3151–3171
Gera JF, Mellinghoff IK, Shi Y, Rettig MB, Tran C, Hsu JH, Sawyers CL, Lichtenstein AK (2004) AKT activity determines sensitivity to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors by regulating cyclin D1 and c-myc expression. J Biol Chem 279:2737–2746
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Shanghai Commission of Science and Technology (grants 44107025 and 05DZ19317), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 30570777 and 30750335), the Chinese National High Tech Program (grant 863:2006AA02A301), the Shanghai Commission of Science and Technology (grants 08410708800 and 11140901200), and the Program for Outstanding Young Teachers in Universities of Shanghai (JDY09084).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, ZZ., Xia, ZG., Wang, AH. et al. Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: clinical significance and inhibitory effect of rituximab. Ann Hematol 92, 1351–1358 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1770-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1770-9