Abstract
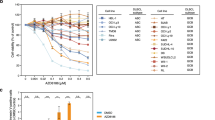
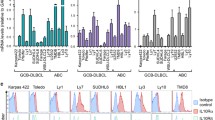
Previously, we have demonstrated that inhibition of Hedgehog pathway induces predominantly apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cell lines of activated B-cell (ABC) type but predominantly cell cycle arrest in those of germinal center (GC). Here, we explored the possibility of overcoming the resistance to apoptosis to SMO inhibitors in five DLBCL cells of GC type using the combination of the SMO inhibitor HhAntag (Genentech Inc) with the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 (Abbott Laboratories). As controls we have used two DLBCL of ABC type (OCI-LY10 and OCI-LY3). Combinatorial treatments were performed with increasing concentrations of the HhAntag with low doses (equal or less than the IC20) of ABT-737. MTS assays were used to detect changes in cell viability and Annexin-V and PARP1 cleavage assays were used to detect apoptosis. Combining low doses of ABT-737 with increasing concentrations of HhAntag in GC DLBCL cell lines resulted in significantly increase of apoptosis in comparison to treatments with the SMO inhibitor alone. We concluded that in GC DLBCL cell lines, in contrast to those of ABC type, functional inhibition of BCL2 family members is usually needed to overcome the resistance to apoptosis to SMO inhibitors. These findings provide a rationale to explore the use of SMO and BCL2 inhibitors as adjuvant therapy for treatment of DLBCL of GC type.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD (1998) New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol 16:2780–2795
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A et al (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI et al (2002) The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346:1937–1947
Savage KJ, Monti S, Kutok JL, Cattoretti G, Neuberg D, De Leval L et al (2003) The molecular signature of mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma differs from that of other diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and shares features with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 102:3871–3879
Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Choi WW, Perry KD, Smith LM, Shi X et al (2008) Addition of rituximab to standard chemotherapy improves the survival of both the germinal center B-cell-like and non-germinal center B-cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 26:4587–4594
Coiffier B (2005) Treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Curr Hematol Rep 4:7–14
Zhang H, Nimmer PM, Tahir SK, Chen J, Fryer RM, Hahn KR et al (2007) Bcl-2 family proteins are essential for platelet survival. Cell Death Differ 14:943–951
Yunis JJ, Frizzera G, Oken MM, McKenna J, Theologides A, Arnesen M (1987) Multiple recurrent genomic defects in follicular lymphoma. A possible model for cancer. N Engl J Med 316:79–84
Yang E, Korsmeyer SJ (1996) Molecular thanatopsis: a discourse on the BCL2 family and cell death. Blood 88:386–401
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2005) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116:205–219
Fesik SW (2005) Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 5:876–885
Mason KD, Khaw SL, Rayeroux KC, Chew E, Lee EF, Fairlie WD et al (2009) The BH3 mimetic compound, ABT-737, synergizes with a range of cytotoxic chemotherapy agents in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 23:2034–2041
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al (2005) An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435:677–681
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al (2006) The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 10:389–399
Singh RR, Kim JE, Davuluri Y, Drakos E, Cho-Vega JH, Amin HM et al (2010) Hedgehog signaling pathway is activated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and contributes to tumor cell survival and proliferation. Leukemia 24:1025–1036
Kim JE, Singh RR, Cho-Vega JH, Drakos E, Davuluri Y, Khokhar FA et al (2009) Sonic hedgehog signaling proteins and ATP-binding cassette G2 are aberrantly expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol 22:1312–1320
Bigelow RL, Chari NS, Unden AB, Spurgers KB, Lee S, Roop DR et al (2004) Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 mediated by the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway through gli-1. J Biol Chem 279:1197–1205
Regl G, Kasper M, Schnidar H, Eichberger T, Neill GW, Philpott MP et al (2004) Activation of the BCL2 promoter in response to Hedgehog/GLI signal transduction is predominantly mediated by GLI2. Cancer Res 64:7724–7731
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC (1994) Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 371:346–347
Singh RR, Kunkalla K, Qu C, Schlette E, Neelapu SS, Samaniego F et al (2011) ABCG2 is a direct transcriptional target of hedgehog signaling and involved in stroma-induced drug tolerance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncogene 30:4874–4886
van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ, Cloos J (2011) Cell sensitivity assays: the MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol 731:237–245
Su W, Meng F, Huang L, Zheng M, Liu W, Sun H (2012) Sonic hedgehog maintains survival and growth of chronic myeloid leukemia progenitor cells through beta-catenin signaling. Exp Hematol 40:418–427
Dierks C, Grbic J, Zirlik K, Beigi R, Englund NP, Guo GR et al (2007) Essential role of stromally induced hedgehog signaling in B-cell malignancies. Nat Med 13:944–951
Singh BN, Fu J, Srivastava RK, Shankar S (2011) Hedgehog signaling antagonist GDC-0449 (Vismodegib) inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics: molecular mechanisms. PLoS One 6:e27306
Graninger WB, Seto M, Boutain B, Goldman P, Korsmeyer SJ (1987) Expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-2-Ig fusion transcripts in normal and neoplastic cells. J Clin Invest 80:1512–1515
Schuetz JM, Johnson NA, Morin RD, Scott DW, Tan K, Ben-Nierah S et al (2012) BCL2 mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 26:1383–1390
Saito M, Novak U, Piovan E, Basso K, Sumazin P, Schneider C et al (2009) BCL6 suppression of BCL2 via Miz1 and its disruption in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:11294–11299
O'Connor L, Strasser A, O'Reilly LA, Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S et al (1998) Bim: a novel member of the BCL-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J 17:384–395
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funds from The Translational Grant of The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (to RS and FV), and K08 Physician-Scientist Award 1K08 CA143151-01 (NIH) (to FV), and SPORE Lymphoma Grant 1P50CA136411-01A1 (to FV).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary figure 1
Combining low doses of ABT-737 and increasing concentrations of HhAntag resulted in decreased cell viability in Toledo cells. Using the cell count assay Vi-Cell viability analyzer (Beckman coulter) showed that combining IC20-doses of ABT-737 with increasing concentrations of HhAntag for 48 h resulted in decreased cell viability in comparison with treatments of HhAntag alone in Toledo cells confirming the findings seen in the Annexin PI assay. The minimally lethal effect of the concentration of ABT-737 used (10 nM) for the combinatorial treatment is evident by the little decrease in the cell viability after treatment with ABT-737 alone for 48 h (left panels). (PPT 35 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunkalla, K., Liu, Y., Qu, C. et al. Functional inhibition of BCL2 is needed to increase the susceptibility to apoptosis to SMO inhibitors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of germinal center subtype. Ann Hematol 92, 777–787 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1684-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1684-6