Abstract
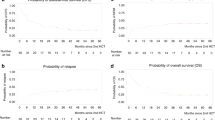
Different RIC regimens were evaluated prior to allo-HSCT in different hematological malignancies. We conducted this prospective study in adult patients with various hematological malignancies in order to evaluate the toxicity and efficacy of treosulfan-based conditioning, followed by allo-HSCT from 10/10 HLA-identical unrelated donors. Conditioning included treosulfan 12 g/m2/day i.v. (day −6 to day −4), fludarabine 30 mg/m2/day i.v. (day −6 to day −2), and ATG 2.5 mg/kg/day (day −2 to day −1). PBSC were used as HSC source. We included 56 patients (29 AML, 9 MM, 8 MDS, 6 CLL, 3 ALL, and 1 CML) with a median age of 57 years (18–65.5). Fifty-four (96%) patients engrafted; the cumulative incidence of aGVHD grade ≥II at 3 months reached 31%. The cumulative incidence of cGVHD at 18 months was 34% limited and 8% extensive. The median overall survival (OS) was not reached with a 3-year probability of 52%. The cumulative incidence of relapse at 3 years was 25%, and the cumulative incidence of transplant-related mortality (TRM) at 12 and 24 months was 20% and 23%, respectively. Treosulfan appears to be a good alternative for conditioning of MUD transplant patients with promising results in terms of OS, relapse, and TRM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yakoub-Agha I, Mesnil F, Kuentz M, Boiron JM, Ifrah N, Milpied N, Chehata S, Esperou H, Vernant JP, Michallet M, Buzyn A, Gratecos N, Cahn JY, Bourhis JH, Chir Z, Raffoux C, Socie G, Golmard JL, Jouet JP (2006) Allogeneic marrow stem-cell transplantation from human leukocyte antigen-identical siblings versus human leukocyte antigen-allelic-matched unrelated donors (10/10) in patients with standard-risk hematologic malignancy: a prospective study from the French Society of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Cell Therapy. J Clin Oncol 24(36):5695–5702
Weisdorf DJ, Anasetti C, Antin JH, Kernan NA, Kollman C, Snyder D, Petersdorf E, Nelson G, McGlave P (2002) Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia: comparative analysis of unrelated versus matched sibling donor transplantation. Blood 99(6):1971–1977
Michallet M, Sobh M, Milligan D, Morisset S, Niederwieser D, Koza V, Ruutu T, Russell NH, Verdonck L, Dhedin N, Vitek A, Boogaerts M, Vindelov L, Finke J, Dubois V, van Biezen A, Brand R, de Witte T, Dreger P (2010) The impact of HLA matching on long-term transplant outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for CLL: a retrospective study from the EBMT registry. Leukemia 24(10):1725–1731
Flomenberg N, Baxter-Lowe LA, Confer D, Fernandez-Vina M, Filipovich A, Horowitz M, Hurley C, Kollman C, Anasetti C, Noreen H, Begovich A, Hildebrand W, Petersdorf E, Schmeckpeper B, Setterholm M, Trachtenberg E, Williams T, Yunis E, Weisdorf D (2004) Impact of HLA class I and class II high-resolution matching on outcomes of unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation: HLA-C mismatching is associated with a strong adverse effect on transplantation outcome. Blood 104(7):1923–1930
Dini G, Cancedda R, Locatelli F, Bosi A, Bandini G, Alessandrino EP, Porta F, Uderzo C, Messina C, Fagioli F, Arcese W, Marenco P, Fanin R, Falda M, Soligo D, La Nasa G, Giardini C, Pession A, Scime R, Di Bartolomeo P, Bruno B, Garbarino L, Lamparelli T, Giorgiani G, Lanino E, Manzitti C, Bacigalupo A (2001) Unrelated donor marrow transplantation: an update of the experience of the Italian Bone Marrow Group (GITMO). Haematologica 86(5):451–456
Bierman PJ, Sweetenham JW, Loberiza FR Jr, Taghipour G, Lazarus HM, Rizzo JD, Schmitz N, van Besien K, Vose JM, Horowitz M, Goldstone A (2003) Syngeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a comparison with allogeneic and autologous transplantation—The Lymphoma Working Committee of the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry and the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. J Clin Oncol 21(20):3744–3753
Anderson JE, Litzow MR, Appelbaum FR, Schoch G, Fisher LD, Buckner CD, Petersen FB, Crawford SW, Press OW, Sanders JE et al (1993) Allogeneic, syngeneic, and autologous marrow transplantation for Hodgkin's disease: the 21-year Seattle experience. J Clin Oncol 11(12):2342–2350
Khouri IF, Keating MJ, Saliba RM, Champlin RE (2002) Long-term follow-up of patients with CLL treated with allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation. Cytotherapy 4(3):217–221
Bearman SI, Appelbaum FR, Buckner CD, Petersen FB, Fisher LD, Clift RA, Thomas ED (1988) Regimen-related toxicity in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol 6(10):1562–1568
Balduzzi A, Valsecchi MG, Silvestri D, Locatelli F, Manfredini L, Busca A, Iori AP, Messina C, Prete A, Andolina M, Porta F, Favre C, Ceppi S, Giorgiani G, Lanino E, Rovelli A, Fagioli F, De Fusco C, Rondelli R, Uderzo C (2002) Transplant-related toxicity and mortality: an AIEOP prospective study in 636 pediatric patients transplanted for acute leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 29(2):93–100
Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E, Kapelushnik Y, Aker M, Cividalli G, Varadi G, Kirschbaum M, Ackerstein A, Samuel S, Amar A, Brautbar C, Ben-Tal O, Eldor A, Or R (1998) Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood 91(3):756–763
Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I, Wang X, Braunschweig I, Ippolitti C, Claxton D, Donato M, Bruton J, Cohen A, Davis M, Andersson BS, Anderlini P, Gajewski J, Kornblau S, Andreeff M, Przepiorka D, Ueno NT, Molldrem J, Champlin R (2001) Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood 97(3):631–637
Gropp M, Meier W, Hepp H (1998) Treosulfan as an effective second-line therapy in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 71(1):94–98
Casper J, Wolff D, Knauf W, Blau IW, Ruutu T, Volin L, Wandt H, Schafer-Eckart K, Holowiecki J, Giebel S, Aschan J, Zander AR, Kroger N, Hilgendorf I, Baumgart J, Mylius HA, Pichlmeier U, Freund M (2010) Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with hematologic malignancies after dose-escalated treosulfan/fludarabine conditioning. J Clin Oncol 28(20):3344–3351
Markiewicz M, Wojciechowska M, Wylezol I, Giebel S, Wozniczka K, Wojnar J, Mendek-Czajkowska E, Holowiecki J (2005) First two successful unrelated donor bone marrow transplantations for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in Poland. Ann Transplant 10(3):26–30
Kroger N, Shimoni A, Zabelina T, Schieder H, Panse J, Ayuk F, Wolschke C, Renges H, Dahlke J, Atanackovic D, Nagler A, Zander A (2006) Reduced-toxicity conditioning with treosulfan, fludarabine and ATG as preparative regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) in elderly patients with secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Bone Marrow Transplant 37(4):339–344
Shimoni A, Hardan I, Shem-Tov N, Rand A, Yerushalmi R, Nagler A (2007) Fludarabine and treosulfan: a novel modified myeloablative regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation with effective antileukemia activity in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma 48(12):2352–2359
Casper J, Knauf W, Kiefer T, Wolff D, Steiner B, Hammer U, Wegener R, Kleine HD, Wilhelm S, Knopp A, Hartung G, Dolken G, Freund M (2004) Treosulfan and fludarabine: a new toxicity-reduced conditioning regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 103(2):725–731
Schmidt-Hieber M, Blau IW, Trenschel R, Andreesen R, Stuhler G, Einsele H, Kanz L, Keilholz U, Marinets O, Beelen DW, Fauser AA, Volin L, Ruutu T, Uharek L, Fietz T, Knauf W, Hopfenmuller W, Thiel E, Freund M, Casper J (2007) Reduced-toxicity conditioning with fludarabine and treosulfan prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 39(7):389–396
Blau IW, Schmidt-Hieber M, Leschinger N, Goldner H, Knauf W, Hopfenmuller W, Thiel E, Blau O (2007) Engraftment kinetics and hematopoietic chimerism after reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine and treosulfan before allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 86(8):583–589
Baronciani D, Rambaldi A, Iori AP, Di Bartolomeo P, Pilo F, Pettinau M, Depau C, Mico C, Santarone S, Angelucci E (2008) Treosulfan/fludarabine as an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant conditioning regimen for high-risk patients. Am J Hematol 83(9):717–720
Bernardo ME, Zecca M, Piras E, Vacca A, Giorgiani G, Cugno C, Caocci G, Comoli P, Mastronuzzi A, Merli P, La Nasa G, Locatelli F (2008) Treosulfan-based conditioning regimen for allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with thalassaemia major. Br J Haematol 143(4):548–551
Ruutu T, Volin L, Beelen DW, Trenschel R, Finke J, Schnitzler M, Holowiecki J, Giebel S, Markiewicz M, Uharek L, Blau IW, Kienast J, Stelljes M, Larsson K, Zander AR, Gramatzki M, Repp R, Einsele H, Stuhler G, Baumgart J, Mylius HA, Pichlmeier U, Freund M, Casper J (2011) Reduced-toxicity conditioning with treosulfan and fludarabine in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myelodysplastic syndromes: final results of an international prospective phase II trial. Haematologica 96(9):1344–1350
Lapierre V, Oubouzar N, Auperin A, Tramalloni D, Tayebi H, Robinet E, Kuentz M, Blaise D, Hartmann O, Herve P, Tiberghien P (2001) Influence of the hematopoietic stem cell source on early immunohematologic reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation. Blood 97(9):2580–2586
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, Lerner KG, Thomas ED (1974) Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 18(4):295–304
Zutter MM, Martin PJ, Sale GE, Shulman HM, Fisher L, Thomas ED, Durnam DM (1988) Epstein–Barr virus lymphoproliferation after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 72(2):520–529
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life tables. J Royal Stat Soc B 34:187–220
de Lima M, Anagnostopoulos A, Munsell M, Shahjahan M, Ueno N, Ippoliti C, Andersson BS, Gajewski J, Couriel D, Cortes J, Donato M, Neumann J, Champlin R, Giralt S (2004) Nonablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning regimens in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: dose is relevant for long-term disease control after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 104(3):865–872
Shimoni A, Hardan I, Shem-Tov N, Rand A, Herscovici C, Yerushalmi R, Nagler A (2007) Comparison between two fludarabine-based reduced-intensity conditioning regimens before allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: fludarabine/melphalan is associated with higher incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease and non-relapse mortality and lower incidence of relapse than fludarabine/busulfan. Leukemia 21(10):2109–2116
Dasgupta RK, Rule S, Johnson P, Davies J, Burnett A, Poynton C, Wilson K, Smith GM, Jackson G, Richardson C, Wareham E, Stars AC, Tollerfield SM, Morgan GJ (2006) Fludarabine phosphate and melphalan: a reduced intensity conditioning regimen suitable for allogeneic transplantation that maintains the graft versus malignancy effect. Bone Marrow Transplant 37(5):455–461
Dix SP, Wingard JR, Mullins RE, Jerkunica I, Davidson TG, Gilmore CE, York RC, Lin LS, Devine SM, Geller RB, Heffner LT, Hillyer CD, Holland HK, Winton EF, Saral R (1996) Association of busulfan area under the curve with veno-occlusive disease following BMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 17(2):225–230
Curtis RE, Travis LB, Rowlings PA, Socie G, Kingma DW, Banks PM, Jaffe ES, Sale GE, Horowitz MM, Witherspoon RP, Shriner DA, Weisdorf DJ, Kolb HJ, Sullivan KM, Sobocinski KA, Gale RP, Hoover RN, Fraumeni JF Jr, Deeg HJ (1999) Risk of lymphoproliferative disorders after bone marrow transplantation: a multi-institutional study. Blood 94(7):2208–2216
Mohty M, Labopin M, Balere ML, Socie G, Milpied N, Tabrizi R, Ifrah N, Hicheri Y, Dhedin N, Michallet M, Buzyn A, Cahn JY, Bourhis JH, Blaise D, Raffoux C, Esperou H, Yakoub-Agha I (2010) Antithymocyte globulins and chronic graft-vs-host disease after myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation from HLA-matched unrelated donors: a report from the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire. Leukemia 24(11):1867–1874
Baron F, Maris MB, Sandmaier BM, Storer BE, Sorror M, Diaconescu R, Woolfrey AE, Chauncey TR, Flowers ME, Mielcarek M, Maloney DG, Storb R (2005) Graft-versus-tumor effects after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning. J Clin Oncol 23(9):1993–2003
Klumpp TR, Herman JH, Ulicny J, Emmons RV, Martin ME, Mangan KF (2006) Lack of effect of donor–recipient ABO mismatching on outcome following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 38(9):615–620
Kanda J, Ichinohe T, Matsuo K, Benjamin RJ, Klumpp TR, Rozman P, Blumberg N, Mehta J, Sohn SK, Uchiyama T (2009) Impact of ABO mismatching on the outcomes of allogeneic related and unrelated blood and marrow stem cell transplantations for hematologic malignancies: IPD-based meta-analysis of cohort studies. Transfusion 49(4):624–635
Nemecek ER, Guthrie KA, Sorror ML, Wood BL, Doney KC, Hilger RA, Scott BL, Kovacsovics TJ, Maziarz RT, Woolfrey AE, Bedalov A, Sanders JE, Pagel JM, Sickle EJ, Witherspoon R, Flowers ME, Appelbaum FR, Deeg HJ (2011) Conditioning with treosulfan and fludarabine followed by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for high-risk hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 17(3):341–350
Blaise D, Farnault L, Faucher C, Marchetti N, Furst S, El Cheikh J, Ladaique P, Vey N, Bouabdallah R, Stoppa AM, Lemarie C, Calmels B, Prebet T, Castagna L, Chabannon C, Mohty M, Esterni B (2010) Reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabin, oral busulfan, and thymoglobulin allows long-term disease control and low transplant-related mortality in patients with hematological malignancies. Exp Hematol 38(12):1241–1250
Kroger N, Bornhauser M, Ehninger G, Schwerdtfeger R, Biersack H, Sayer HG, Wandt H, Schafer-Eckardt K, Beyer J, Kiehl M, Zander AR (2003) Allogeneic stem cell transplantation after a fludarabine/busulfan-based reduced-intensity conditioning in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol 82(6):336–342
Conflict of interest
J Baumgart is an employee of medac GmbH. All the other authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michallet, M., Sobh, M., Milpied, N. et al. Phase II prospective study of treosulfan-based reduced-intensity conditioning in allogeneic HSCT for hematological malignancies from 10/10 HLA-identical unrelated donor. Ann Hematol 91, 1289–1297 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1429-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1429-y