Abstract
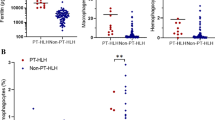
Although hemophagocytic syndrome (HS) featuring secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) has a grave prognosis, little is known about the natural course of the disease. Patients who showed the clinical features of HLH as well as tissue-proven hemophagocytosis when seen at Asan Medical Center between 1999 and 2010 were included in this analysis. Patients with proven lymphoma were excluded. The median age of our 23 study patients was 49 years. Epstein–Barr virus was suspected to have caused HS in 16 (70%) patients and hepatitis A virus in one patient. Twenty-two patients were treated, 13 according to the HLH protocol and nine using immunosuppressive agents such as corticosteroid and/or cyclosporine. Five patients undertook allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) during their treatment-dependent relapse (n = 4) or responsive status (n = 1). After the median follow-up of 180 days, 17 (74%) died and six (26%) were alive. The median time from initial presentation until death was 41 days among those patients who died. The serum fibrinogen level ≥166 mg/dL determined at the initial visit was significantly associated with the survival time according to univariate analysis. The low histiocyte proportion in bone marrow and early initiation of treatment tended to correlate with a favorable outcome. On multivariate analysis, serum fibrinogen ≥166 mg/dL (hazard ratio, 0.175, P = 0.018) was an independent clinical factor for determining the patient survival time. Despite appropriate patient management, the outcome of HS featuring HLH was grave. The serum fibrinogen level at the initial presentation was significant, and selected patients obtained some benefit from allogeneic HCT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janka GE (2007) Hemophagocytic syndromes. Blood Rev 21(5):245–253. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2007.05.001
Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski J, Janka G (2007) HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Canc 48(2):124–131. doi:10.1002/pbc.21039
Henter JI, Elinder G, Ost A (1991) Diagnostic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. The FHL Study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Semin Oncol 18(1):29–33
Henter JI, Arico M, Elinder G, Imashuku S, Janka G (1998) Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 12(2):417–433
Janka G, Imashuku S, Elinder G, Schneider M, Henter JI (1998) Infection- and malignancy-associated hemophagocytic syndromes. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 12(2):435–444
Rouphael NG, Talati NJ, Vaughan C, Cunningham K, Moreira R, Gould C (2007) Infections associated with haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis 7(12):814–822. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70290-6
Arlet JB, Le TH, Marinho A, Amoura Z, Wechsler B, Papo T, Piette JC (2006) Reactive haemophagocytic syndrome in adult-onset Still’s disease: a report of six patients and a review of the literature. Ann Rheum Dis 65(12):1596–1601. doi:10.1136/ard.2005.046904
Fukaya S, Yasuda S, Hashimoto T, Oku K, Kataoka H, Horita T, Atsumi T, Koike T (2008) Clinical features of haemophagocytic syndrome in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases: analysis of 30 cases. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(11):1686–1691. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken342
Finkielman JD, Grinberg AR, Paz LA, Plana JL, Benchetrit GA, Nicastro MA, Roncoroni AJ (1996) Case report: reactive hemophagocytic syndrome associated with disseminated strongyloidiasis. Am J Med Sci 312(1):37–39
Takahashi N, Chubachi A, Kume M, Hatano Y, Komatsuda A, Kawabata Y, Yanagiya N, Ichikawa Y, Miura AB, Miura I (2001) A clinical analysis of 52 adult patients with hemophagocytic syndrome: the prognostic significance of the underlying diseases. Int J Hematol 74(2):209–213
Kaito K, Kobayashi M, Katayama T, Otsubo H, Ogasawara Y, Sekita T, Saeki A, Sakamoto M, Nishiwaki K, Masuoka H, Shimada T, Yoshida M, Hosoya T (1997) Prognostic factors of hemophagocytic syndrome in adults: analysis of 34 cases. Eur J Haematol 59(4):247–253
Sonke GS, Ludwig I, van Oosten H, Baars JW, Meijer E, Kater AP, de Jong D (2008) Poor outcomes of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in non-Japanese adult patients. Clin Infect Dis 47(1):105–108. doi:10.1086/588790
Henter JI, Arico M, Egeler RM, Elinder G, Favara BE, Filipovich AH, Gadner H, Imashuku S, Janka-Schaub G, Komp D, Ladisch S, Webb D (1997) HLH-94: a treatment protocol for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. HLH study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med Pediatr Oncol 28(5):342–347. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-911X(199705)28:5<342::AID-MPO3>3.0.CO;2-H
Ahn JS, Rew SY, Shin MG, Kim HR, Yang DH, Cho D, Kim SH, Bae SY, Lee SR, Kim YK, Kim HJ, Lee JJ (2010) Clinical significance of clonality and Epstein-Barr virus infection in adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Am J Hematol 85(9):719–722. doi:10.1002/ajh.21795
Shabbir M, Lucas J, Lazarchick J, Shirai K (2011) Secondary hemophagocytic syndrome in adults: a case series of 18 patients in a single institution and a review of literature. Hematol Oncol 29(2):100–106. doi:10.1002/hon.960
Imashuku S, Teramura T, Tauchi H, Ishida Y, Otoh Y, Sawada M, Tanaka H, Watanabe A, Tabata Y, Morimoto A, Hibi S, Henter JI (2004) Longitudinal follow-up of patients with Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica 89(2):183–188
Ohga S, Kudo K, Ishii E, Honjo S, Morimoto A, Osugi Y, Sawada A, Inoue M, Tabuchi K, Suzuki N, Ishida Y, Imashuku S, Kato S, Hara T (2010) Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Japan. Pediatr Blood Canc 54(2):299–306. doi:10.1002/pbc.22310
Horne A, Trottestam H, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Gadner H, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, Webb D, Janka G, Henter JI (2008) Frequency and spectrum of central nervous system involvement in 193 children with haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Br J Haematol 140(3):327–335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06922.x
Jin YK, Xie ZD, Yang S, Lu G, Shen KL (2010) Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective study of 78 pediatric cases in mainland of China. Chin Med J (Engl) 123(11):1426–1430
Imashuku S, Kuriyama K, Sakai R, Nakao Y, Masuda S, Yasuda N, Kawano F, Yakushijin K, Miyagawa A, Nakao T, Teramura T, Tabata Y, Morimoto A, Hibi S (2003) Treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (EBV-HLH) in young adults: a report from the HLH study center. Med Pediatr Oncol 41(2):103–109. doi:10.1002/mpo.10314
Fukunaga A, Nakamura F, Yoshinaga N, Inano S, Maruyama W, Hirata H, Arima N (2011) Successful treatment with combined chemotherapy of two adult cases of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in recipients of umbilical cord blood cell transplantation. Int J Hematol 93(4):551–554. doi:10.1007/s12185-011-0792-0
Sovinz P, Schwinger W, Lackner H, Benesch M, Moser A, Raicht A, Zobel G, Urban C (2010) Severe epstein-barr virus encephalitis with hemophagocytic syndrome: rapid clearance of virus following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from a seropositive donor. Pediatr Infect Dis J 29(6):553–556. doi:10.1097/INF.0b013e3181d1de1d
Cesaro S, Locatelli F, Lanino E, Porta F, Di Maio L, Messina C, Prete A, Ripaldi M, Maximova N, Giorgiani G, Rondelli R, Arico M, Fagioli F (2008) Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective analysis of data from the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology Oncology (AIEOP). Haematologica 93(11):1694–1701. doi:10.3324/haematol.13142
Sato E, Ohga S, Kuroda H, Yoshiba F, Nishimura M, Nagasawa M, Inoue M, Kawa K (2008) Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Epstein-Barr virus-associated T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disease in Japan. Am J Hematol 83(9):721–727. doi:10.1002/ajh.21247
Lin TF, Ferlic-Stark LL, Allen CE, Kozinetz CA, McClain KL (2011) Rate of decline of ferritin in patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis as a prognostic variable for mortality. Pediatr Blood Canc 56(1):154–155. doi:10.1002/pbc.22774
Gabay C, Kushner I (1999) Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 340(6):448–454. doi:10.1056/NEJM199902113400607
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant (KG2010-10) Basic Research in Medicine, Korean Institute of Medicine & GlaxoSmithKline, Seoul, Korea.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, HS., Kim, DY., Lee, JH. et al. Clinical features of adult patients with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis from causes other than lymphoma: an analysis of treatment outcome and prognostic factors. Ann Hematol 91, 897–904 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-011-1380-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-011-1380-3