Abstract
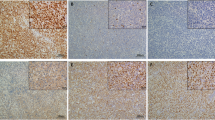
Apoptosis-related proteins play an important role in lymphoma cell death during chemotherapy. In our study, we investigated the prognostic significance of CD95, BCL2, and P53 expression in extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). We examined 71 patients with extranodal NHL [45 diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) and 26 mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas (MALTLs)], 35 male and 36 female, with a median age of 65.8 years. The most common site of origin was the stomach (N = 31). Paraffin-embedded specimens were analyzed immunohistochemically for CD95, BCL2, and P53 expression. Multivariate analysis revealed that in DLBCLs, positive CD95 and negative BCL2 expression were independent prognostic factors for overall survival. We reached the same conclusion for MALTLs, with positive CD95 and negative P53 expression. In DLBCLs, the 5-year overall survival rate was 71.5% for the CD95-positive cases and 35% for the CD95-negative cases (p = 0.004) and the 5-year overall survival was significantly better in BCL2-negative cases (70.8%) when compared to BCL2-positive cases (37%; p = 0.009). In MALTLs, the 5-year overall survival rate for the CD95-positive and CD95-negative groups was 89.5% and 42.9%, respectively (p = 0.004) and the 5-year overall survival rate was 50% for the P53-positive cases and 88.9% for the P53-negative cases (p = 0.016). In conclusion, positive CD95 expression proved to be a good prognostic factor of overall survival in both extranodal DLBCLs and MALTLs. In contrast, positive expression of BCL2 and P53 was found to be unfavorably associated with survival in extranodal DLBCLs and MALTLs, respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feller AC, Diebold J (2004) Histopathology of nodal and extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. 3rd, completely rev. and updated ed. Springer, Berlin, p 186
Irisarri M, Plumas J, Bonnefoix T et al (2000) Resistance to CD95-mediated apoptosis through constitutive c-FLIP expression in a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma B cell line. Leukemia 14:2149–2158
Troeger A, Glouchkova L, Escherich G et al (2008) Reduced expression of defective modulation of TNF receptor/ligand family molecules on proB-ALL blasts. Klin Pediatr 220:353–357
Griffith TS, Yu X, Herndon JM, Green DR, Ferguson TA (1996) CD95-induced apoptosis of lymphocytes in an immune-privileged cite induces immunological tolerance. Immunity 5:7–16
Landowski TH, Moscinski L, Burke R (2001) CD95 antigen mutations in hematopoietic malignancies (review). Leuk Lymphoma 42:835–846
Wilson WH, Teruya-Feldstein J, Fest T (1997) Relationship of P53, BCL2, and tumor proliferation to clinical drug resistance in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Blood 89:601–609
Harris SL, Levine AJ (2005) The P53 pathway: positive and negative feedback loops (review). Oncogene 24:2899–2908
Steele RJ, Lane DP (2005) P53 in cancer: a paradigm for modern management of cancer (review). Surg 3:197–205
Kroemer G (1997) The proto-oncogene BCL2 and its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med 3:614–620
Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ (1998) BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 16:395–419
Pazella F, Turley H, Kuzu I, Tungekar MF, Dunnill MS, Pierce CB et al (1993) BCL2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med 329:690–694
Pazella F, Gatter K (1995) What is the value of BCL2 protein detection for histopathologists? Histopathology 26:89–93
Wohlfart S, Sebinger D, Gruber P (2004) FAS (CD95) mutations are rare in gastric MALT lymphoma but occur more frequently in primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphomas DLBCL. Am J Pathol 164:1081–1089
Imamura J, Miyoshi I, Koeffler HP (1994) P53 in hematologic malignancies. Blood 84:2412–2421
Hernandez L, Fest T, Cazorla M et al (1996) P53 gene mutations and protein overexpression are associated with aggressive variants of mantle cell lymphomas. Blood 87:3351–3359
Li Y, Raffo AJ, Drew L, Mao Y (2003) FAS-mediated apoptosis is dependent on wild-type P53 status in human cancer cells expressing a temperature-sensitive P53 mutant alanine-143. Cancer Res 63:1527–1533
Das GC, Holiday D, Gallardo R, Haas C (2001) Taxol-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis: dose-response relationship in lung cancer cells of different wild-type P53 status and under isogenic condition. Cancer Lett 165:147–153
Stewart ZA, Tang LJ, Pietenpol JA (2001) Increased P53 phosphorylation after microtubule disruption is mediated in a microtubule inhibitor- and cell-specific manner. Oncogene 20:113–124
Makin G, Hickman JA (2000) Apoptosis and cancer chemotherapy. Cell Tissue Res 301:143–152
Piris MA, Pezella F, Martinez-Montero JC et al (1994) P53 and BCL2 expression in high-grade B-cell lymphomas: correlation with survival time. Br J Cancer 69:337–341
Reed JC (1995) Regulation of apoptosis by BCL2 family proteins and its role in cancer and chemoresistance. Curr Opin Oncol 7:541–546
Hermine O, Haioun C, Lepage E (1996) Prognostic significance of BCL2 protein expression in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte (GELA). Blood 87:265–272
Miyashita T, Reed JC (1993) BCL2 oncoprotein blocks chemotherapyinduced apoptosis in a human leukemia cell line. Blood 81:151–157
Iwai K, Miyawaki T, Takizawa T (1994) Differential expression of BCL2 and susceptibility to anti-Fas-mediated cell death in peripheral blood lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils. Blood 84:1201–1208
Yoshino T, Kondo E, Cao L (1994) Inverse expression of BCL2 protein and FAS antigen in lympho-blasts in peripheral blood T and B lymphocytes. Blood 83:1856–1861
Nguyen PL, Harris NL, Ritz J, Robertson MJ (1996) Expression of CD95 antigen and BCL2 protein in non Hodgkin's lymphomas and Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol 148:847–853
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the collaboration of the technical staff of the Pathology Department.
Authorship and disclosures
AC was the principal investigator and analyzed the data. IV and NP participated in the scoring of immunohistochemical results. GT and GA participated in the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatzitolios, A., Venizelos, I., Tripsiannis, G. et al. Prognostic significance of CD95, P53, and BCL2 expression in extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Hematol 89, 889–896 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-0945-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-0945-x