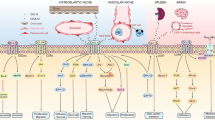
Abstract
Chemokines are centrally involved in leukocyte migration, homing and haematopoiesis. Besides these physiological aspects, their role in pathological processes especially with respect to solid tumour and haematological neoplasias is well established. In this context, the focus was set here on disclosing their contribution in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL), which is regarded as the most characteristic low-grade lymphoma. Up to now, it has been demonstrated that several chemokines are involved in migration of B-CLL cells to lymph nodes, secondary lymphoid organs and bone marrow. Moreover, some chemokines are known to have an anti-apoptotic effect and thus contribute to the survival of B-CLL cells. By interfering with both of these aspects, new therapeutic targets for this yet incurable disease may be developed. Furthermore, a correlation can be drawn between the concentration of some chemokines in patients’ serum, the expression of their respective receptors on B-CLL cells and well-established predictive clinical parameters. Consequently, further systematic investigation of the chemokine network may lead to the identification of new diagnostic and prognostic markers. This review focuses on the impact of chemokines and their receptors on B-CLL pathophysiology and points out potential implications for both treatment and diagnosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, Hebert CA, Horuk R, Matsushima K, Miller LH, Oppenheim JJ, Power CA (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 52:145–176
Balkwill F (2004) Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer 4:540–550
Raman D, Baugher PJ, Thu YM, Richmond A (2007) Role of chemokines in tumor growth. Cancer Lett 256:137–165
Broxmeyer HE (2008) Chemokines in hematopoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol 15:49–58
Pistoia V, Corcione A, Dallegri F, Ottonello L (2006) Lymphoproliferative disorders and chemokines. Curr Drug Targets 7:81–90
Pals ST, de Gorter DJ, Spaargaren M (2007) Lymphoma dissemination: the other face of lymphocyte homing. Blood 110:3102–3111
Burger JA, Burkle A (2007) The CXCR4 chemokine receptor in acute and chronic leukaemia: a marrow homing receptor and potential therapeutic target. Br J Haematol 137:288–296
Kipps TJ (2000) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr Opin Hematol 7:223–234
Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 352:804–815
Burger M, Hartmann T, Krome M, Rawluk J, Tamamura H, Fujii N, Kipps TJ, Burger JA (2005) Small peptide inhibitors of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor (CD184) antagonize the activation, migration, and antiapoptotic responses of CXCL12 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 106:1824–1830
Binsky I, Haran M, Starlets D, Gore Y, Lantner F, Harpaz N, Leng L, Goldenberg DM, Shvidel L, Berrebi A, Bucala R, Shachar I (2007) IL-8 secreted in a macrophage migration-inhibitory factor- and CD74-dependent manner regulates B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13408–13413
Hu C, Xiong J, Zhang L, Huang B, Zhang Q, Li Q, Yang M, Wu Y, Wu Q, Shen Q, Gao Q, Zhang K, Sun Z, Liu J, Jin Y, Tan J (2004) PEG10 activation by co-stimulation of CXCR5 and CCR7 essentially contributes to resistance to apoptosis in CD19+ CD34+ B cells from patients with B cell lineage acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cell Mol Immunol 1:280–294
Alfonso-Perez M, Lopez-Giral S, Quintana NE, Loscertales J, Martin-Jimenez P, Munoz C (2006) Anti-CCR7 monoclonal antibodies as a novel tool for the treatment of chronic lymphocyte leukemia. J Leukoc Biol 79:1157–1165
Morabito F, Merendino RA, Penna G, Cuzzola M, Stelitano C, Callea V, Di Pasquale G, Minciullo PL, Gangemi S (2005) The CX3C chemokine fractalkine (CX3CL1) is detectable in serum of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with lymph node involvement. Acta Haematol 113:152–154
Ghobrial IM, Bone ND, Stenson MJ, Novak A, Hedin KE, Kay NE, Ansell SM (2004) Expression of the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR7 and disease progression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/ small lymphocytic lymphoma. Mayo Clin Proc 79:318–325
Ocana E, Delgado-Perez L, Campos-Caro A, Munoz J, Paz A, Franco R, Brieva JA (2007) The prognostic role of CXCR3 expression by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Haematologica 92:349–356
Kara IO, Sahin B, Gunesacar R (2007) Expression of soluble CD27 and interleukins-8 and -10 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with disease stage and prognosis. Adv Ther 24:29–40
Jones D, Benjamin RJ, Shahsafaei A, Dorfman DM (2000) The chemokine receptor CXCR3 is expressed in a subset of B-cell lymphomas and is a marker of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 95:627–632
Tachibana K, Hirota S, Iizasa H, Yoshida H, Kawabata K, Kataoka Y, Kitamura Y, Matsushima K, Yoshida N, Nishikawa S, Kishimoto T, Nagasawa T (1998) The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature 393:591–594
Zou YR, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, Taniuchi I, Littman DR (1998) Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 393:595–599
Ma Q, Jones D, Borghesani PR, Segal RA, Nagasawa T, Kishimoto T, Bronson RT, Springer TA (1998) Impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, and derailed cerebellar neuron migration in CXCR4- and SDF-1-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:9448–9453
Burger JA, Kipps TJ (2002) Chemokine receptors and stromal cells in the homing and homeostasis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leuk Lymphoma 43:461–466
Burger JA, Burger M, Kipps TJ (1999) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express functional CXCR4 chemokine receptors that mediate spontaneous migration beneath bone marrow stromal cells. Blood 94:3658–3667
Mohle R, Failenschmid C, Bautz F, Kanz L (1999) Overexpression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia is associated with increased functional response to stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1). Leukemia 13:1954–1959
Burger JA, Tsukada N, Burger M, Zvaifler NJ, Dell'Aquila M, Kipps TJ (2000) Blood-derived nurse-like cells protect chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from spontaneous apoptosis through stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 96:2655–2663
Durig J, Schmucker U, Duhrsen U (2001) Differential expression of chemokine receptors in B cell malignancies. Leukemia 15:752–756
Zeng Z, Samudio IJ, Munsell M, An J, Huang Z, Estey E, Andreeff M, Konopleva M (2006) Inhibition of CXCR4 with the novel RCP168 peptide overcomes stroma-mediated chemoresistance in chronic and acute leukemias. Mol Cancer Ther 5:3113–3121
Calandra G, McCarty J, McGuirk J, Tricot G, Crocker SA, Badel K, Grove B, Dye A, Bridger G (2008) AMD3100 plus G-CSF can successfully mobilize CD34+ cells from non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Hodgkin’s disease and multiple myeloma patients previously failing mobilization with chemotherapy and/or cytokine treatment: compassionate use data. Bone Marrow Transplant 41:331–338
Wong D, Korz W (2008) Translating an antagonist of chemokine receptor CXCR4: from bench to bedside. Clin Cancer Res 14:7975–7980
Burger JA, Peled A (2009) CXCR4 antagonists: targeting the microenvironment in leukemia and other cancers. Leukemia 23:43–52
Tsutsumi H, Tanaka T, Ohashi N, Masuno H, Tamamura H, Hiramatsu K, Araki T, Ueda S, Oishi S, Fujii N (2007) Therapeutic potential of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 antagonists as multifunctional agents. Biopolymers 88:279–289
Bennett F, Rawstron A, Plummer M, de Tute R, Moreton P, Jack A, Hillmen P (2007) B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells show specific changes in membrane protein expression during different stages of cell cycle. Br J Haematol 139:600–604
Redondo-Munoz J, Escobar-Diaz E, Samaniego R, Terol MJ, Garcia-Marco JA, Garcia-Pardo A (2006) MMP-9 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia is up-regulated by alpha4beta1 integrin or CXCR4 engagement via distinct signaling pathways, localizes to podosomes, and is involved in cell invasion and migration. Blood 108:3143–3151
Barretina J, Junca J, Llano A, Gutierrez A, Flores A, Blanco J, Clotet B, Este JA (2003) CXCR4 and SDF-1 expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and stage of the disease. Ann Hematol 82:500–505
Dao-Ung LP, Sluyter R, Fuller SJ, Taper J, Wiley JS (2004) CXCR4 but not CXCR3 expression correlates with lymphocyte counts in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol 83:326–327
Richardson SJ, Matthews C, Catherwood MA, Alexander HD, Carey BS, Farrugia J, Gardiner A, Mould S, Oscier D, Copplestone JA, Prentice AG (2006) ZAP-70 expression is associated with enhanced ability to respond to migratory and survival signals in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). Blood 107:3584–3592
di Celle PF, Carbone A, Marchis D, Zhou D, Sozzani S, Zupo S, Pini M, Mantovani A, Foa R (1994) Cytokine gene expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: evidence of constitutive interleukin-8 (IL-8) mRNA expression and secretion of biologically active IL-8 protein. Blood 84:220–228
di Celle FP, Mariani S, Riera L, Stacchini A, Reato G, Foa R (1996) Interleukin-8 induces the accumulation of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by prolonging survival in an autocrine fashion. Blood 87:4382–4389
Secchiero P, Corallini F, Barbarotto E, Melloni E, di Iasio MG, Tiribelli M, Zauli G (2006) Role of the RANKL/RANK system in the induction of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells. J Cell Physiol 207:158–164
Secchiero P, di Iasio MG, Gonelli A, Barbarotto E, Melloni E, Tiribelli M, Chiaruttini C, Zauli G (2007) Differential gene expression induction by TRAIL in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells showing high versus low levels of Zap-70. J Cell Physiol 213:229–236
Horuk R (2009) Chemokine receptor antagonists: overcoming developmental hurdles. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:23–33
Zhao X, Li F, Town JR, Zhang X, Wang W, Gordon JR (2007) Humanized forms of the CXCR1/CXCR2 antagonist, bovine CXCL8((3-74))K11R/G31P, effectively block ELR-CXC chemokine activity and airway endotoxemia pathology. Int Immunopharmacol 7:1723–1731
Gonsiorek W, Fan X, Hesk D, Fossetta J, Qiu H, Jakway J, Billah M, Dwyer M, Chao J, Deno G, Taveras A, Lundell DJ, Hipkin RW (2007) Pharmacological characterization of Sch527123, a potent allosteric CXCR1/CXCR2 antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:477–485
Chapman RW, Minnicozzi M, Celly CS, Phillips JE, Kung TT, Hipkin RW, Fan X, Rindgen D, Deno G, Bond R, Gonsiorek W, Billah MM, Fine JS, Hey JA (2007) A novel, orally active CXCR1/2 receptor antagonist, Sch527123, inhibits neutrophil recruitment, mucus production, and goblet cell hyperplasia in animal models of pulmonary inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:486–493
Busch-Petersen J (2006) Small molecule antagonists of the CXCR2 and CXCR1 chemokine receptors as therapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Curr Top Med Chem 6:1345–1352
Parfienczyk A, Kiersnowska-Rogowska B, Rogowski F (2003) Cytokine and adhesion molecule concentrations in blood of patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with regard to disease progression. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst 48:90–94
Wierda WG, Johnson MM, Do KA, Manshouri T, Dey A, O’Brien S, Giles FJ, Kantarjian H, Thomas D, Faderl S, Lerner S, Keating M, Albitar M (2003) Plasma interleukin 8 level predicts for survival in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 120:452–456
Molica S, Vitelli G, Levato D, Levato L, Dattilo A, Gandolfo GM (1999) Clinico-biological implications of increased serum levels of interleukin-8 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 84:208–211
Ohl L, Henning G, Krautwald S, Lipp M, Hardtke S, Bernhardt G, Pabst O, Forster R (2003) Cooperating mechanisms of CXCR5 and CCR7 in development and organization of secondary lymphoid organs. J Exp Med 197:1199–1204
Muller G, Hopken UE, Lipp M (2003) The impact of CCR7 and CXCR5 on lymphoid organ development and systemic immunity. Immunol Rev 195:117–135
Reif K, Ekland EH, Ohl L, Nakano H, Lipp M, Forster R, Cyster JG (2002) Balanced responsiveness to chemoattractants from adjacent zones determines B-cell position. Nature 416:94–99
Burkle A, Niedermeier M, Schmitt-Graff A, Wierda WG, Keating MJ, Burger JA (2007) Overexpression of the CXCR5 chemokine receptor, and its ligand, CXCL13 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 110:3316–3325
Cyster JG (1999) Chemokines and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Science 286:2098–2102
Lopez-Giral S, Quintana NE, Cabrerizo M, Alfonso-Perez M, Sala-Valdes M, De Soria VG, Fernandez-Ranada JM, Fernandez-Ruiz E, Munoz C (2004) Chemokine receptors that mediate B cell homing to secondary lymphoid tissues are highly expressed in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphomas with widespread nodular dissemination. J Leukoc Biol 76:462–471
Chunsong H, Yuling H, Li W, Jie X, Gang Z, Qiuping Z, Qingping G, Kejian Z, Li Q, Chang AE, Youxin J, Jinquan T (2006) CXC chemokine ligand 13 and CC chemokine ligand 19 cooperatively render resistance to apoptosis in B cell lineage acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia CD23+ CD5+ B cells. J Immunol 177:6713–6722
Ticchioni M, Essafi M, Jeandel PY, Davi F, Cassuto JP, Deckert M, Bernard A (2007) Homeostatic chemokines increase survival of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through inactivation of transcription factor FOXO3a. Oncogene 26:7081–7091
Willimann K, Legler DF, Loetscher M, Roos RS, Delgado MB, Clark-Lewis I, Baggiolini M, Moser B (1998) The chemokine SLC is expressed in T cell areas of lymph nodes and mucosal lymphoid tissues and attracts activated T cells via CCR7. Eur J Immunol 28:2025–2034
Burgstahler R, Kempkes B, Steube K, Lipp M (1995) Expression of the chemokine receptor BLR2/EBI1 is specifically transactivated by Epstein–Barr virus nuclear antigen 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 215:737–743
Birkenbach M, Josefsen K, Yalamanchili R, Lenoir G, Kieff E (1993) Epstein–Barr virus-induced genes: first lymphocyte-specific G protein-coupled peptide receptors. J Virol 67:2209–2220
Till KJ, Lin K, Zuzel M, Cawley JC (2002) The chemokine receptor CCR7 and alpha4 integrin are important for migration of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells into lymph nodes. Blood 99:2977–2984
Gary-Gouy H, Sainz-Perez A, Marteau JB, Marfaing-Koka A, Delic J, Merle-Beral H, Galanaud P, Dalloul A (2007) Natural phosphorylation of CD5 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells and analysis of CD5-regulated genes in a B cell line suggest a role for CD5 in malignant phenotype. J Immunol 179:4335–4344
Qin S, Rottman JB, Myers P, Kassam N, Weinblatt M, Loetscher M, Koch AE, Moser B, Mackay CR (1998) The chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR5 mark subsets of T cells associated with certain inflammatory reactions. J Clin Invest 101:746–754
Trentin L, Agostini C, Facco M, Piazza F, Perin A, Siviero M, Gurrieri C, Galvan S, Adami F, Zambello R, Semenzato G (1999) The chemokine receptor CXCR3 is expressed on malignant B cells and mediates chemotaxis. J Clin Invest 104:115–121
Lazzeri E, Romagnani P (2005) CXCR3-binding chemokines: novel multifunctional therapeutic targets. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord 5:109–118
Wijtmans M, Verzijl D, Leurs R, de Esch IJ, Smit MJ (2008) Towards small-molecule CXCR3 ligands with clinical potential. ChemMedChem 3:861–872
van Wanrooij EJ, de Jager SC, van Es T, de Vos P, Birch HL, Owen DA, Watson RJ, Biessen EA, Chapman GA, van Berkel TJ, Kuiper J (2008) CXCR3 antagonist NBI-74330 attenuates atherosclerotic plaque formation in LDL receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:251–257
Walser TC, Rifat S, Ma X, Kundu N, Ward C, Goloubeva O, Johnson MG, Medina JC, Collins TL, Fulton AM (2006) Antagonism of CXCR3 inhibits lung metastasis in a murine model of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 66:7701–7707
Imai T, Hieshima K, Haskell C, Baba M, Nagira M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Takagi S, Nomiyama H, Schall TJ, Yoshie O (1997) Identification and molecular characterization of fractalkine receptor CX3CR1, which mediates both leukocyte migration and adhesion. Cell 91:521–530
Bazan JF, Bacon KB, Hardiman G, Wang W, Soo K, Rossi D, Greaves DR, Zlotnik A, Schall TJ (1997) A new class of membrane-bound chemokine with a CX3C motif. Nature 385:640–644
Ferrer A, Ollila J, Tobin G, Nagy B, Thunberg U, Aalto Y, Vihinen M, Vilpo J, Rosenquist R, Knuutila S (2004) Different gene expression in immunoglobulin-mutated and immunoglobulin-unmutated forms of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 153:69–72
Andreasson U, Ek S, Merz H, Rosenquist R, Andersen N, Jerkeman M, Dictor M, Borrebaeck CA (2008) B cell lymphomas express CX3CR1 a non-B cell lineage adhesion molecule. Cancer Lett 259:138–145
Inoue A, Hasegawa H, Kohno M, Ito MR, Terada M, Imai T, Yoshie O, Nose M, Fujita S (2005) Antagonist of fractalkine (CX3CL1) delays the initiation and ameliorates the progression of lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Rheum 52:1522–1533
Streit WJ, Davis CN, Harrison JK (2005) Role of fractalkine (CX3CL1) in regulating neuron–microglia interactions: development of viral-based CX3CR1 antagonists. Curr Alzheimer Res 2:187–189
D'Orlando O, Gri G, Cattaruzzi G, Merluzzi S, Betto E, Gattei V, Pucillo C (2007) Outside inside signalling in CD40-mediated B cell activation. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 21:49–62
Schonbeck U, Libby P (2001) The CD40/CD154 receptor/ligand dyad. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:4–43
Granger DN, Vowinkel T, Petnehazy T (2004) Modulation of the inflammatory response in cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 43:924–931
Luczynski W, Stasiak-Barmuta A, Piszcz J, Ilendo E, Kowalczuk O, Krawczuk-Rybak M (2007) B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia-derived dendritic cells stimulate allogeneic T-cell response and express chemokines involved in T-cell migration. Neoplasma 54:527–535
Ghia P, Circosta P, Scielzo C, Vallario A, Camporeale A, Granziero L, Caligaris-Cappio F (2005) Differential effects on CLL cell survival exerted by different microenvironmental elements. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 294:135–145
Burger JA, Quiroga MP, Hartmann E, Burkle A, Wierda WG, Keating MJ, Rosenwald A (2009) High-level expression of the T-cell chemokines CCL3 and CCL4 by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells in nurselike cell cocultures and after BCR stimulation. Blood 113:3050–3058
Deaglio S, Vaisitti T, Aydin S, Ferrero E, Malavasi F (2006) In-tandem insight from basic science combined with clinical research: CD38 as both marker and key component of the pathogenetic network underlying chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 108:1135–1144
Elhabazi A, Marie-Cardine A, Chabbert-de Ponnat I, Bensussan A, Boumsell L (2003) Structure and function of the immune semaphorin CD100/SEMA4D. Crit Rev Immunol 23:65–81
Kumanogoh A, Kikutani H (2003) Roles of the semaphorin family in immune regulation. Adv Immunol 81:173–198
Acknowledgement
This study is supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) grant no. BU/1159/4-1 (to M.B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröttner, P., Leick, M. & Burger, M. The role of chemokines in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: pathophysiological aspects and clinical impact. Ann Hematol 89, 437–446 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0876-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0876-6