Abstract
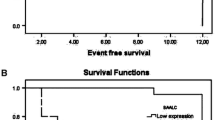
We have analyzed brain and acute leukemia, cytoplasmic (BAALC) gene expression and other genetic markers (ERG, EVI1, MN1, PRAME, WT1, FLT3, and NPM1 mutations) in 127 intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients: 98 cytogenetically normal and 29 with intermediate-risk cytogenetic alterations. High versus low BAALC expressers showed a higher refractoriness to induction treatment (31% vs 10%; p = .005), lower complete remission rate after salvage therapy (82% vs 97%; p = .010), and lower 3-year overall (23% vs 58%, p < .001) and relapse-free survival (26% vs 52%, p = .006). Similar results were found when cytogenetic subgroups were analyzed separately. Multivariate models confirmed the unfavorable prognosis of this marker. In conclusion, BAALC is a relevant prognostic marker in intermediate-risk AML.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mrozek K, Bloomfield CD (2006) Chromosome aberrations, gene mutations and expression changes, and prognosis in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology 2006:169–177
Tanner SM, Austin JL, Leone G, Rush LJ, Plass C, Heinonen K, Mrozek K, Sill H, Knuutila S, Kolitz JE, Archer KJ, Caligiuri MA, Bloomfield CD, de la Chapelle A (2001) BAALC, the human member of a novel mammalian neuroectoderm gene lineage, is implicated in hematopoiesis and acute leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13901–13906
Baldus CD, Tanner SM, Ruppert AS, Whitman SP, Archer KJ, Marcucci G, Caligiuri MA, Carroll AJ, Vardiman JW, Powell BL, Allen SL, Moore JO, Larson RA, Kolitz JE, de la Chapelle A, Bloomfield CD (2003) BAALC expression predicts clinical outcome of de novo acute myeloid leukemia patients with normal cytogenetics: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. Blood 102:1613–1618
Baldus CD, Thiede C, Soucek S, Bloomfield CD, Thiel E, Ehninger G (2006) BAALC expression and FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutations in acute myeloid leukemia patients with normal cytogenetics: prognostic implications. J Clin Oncol 24:790–797
Langer C, Radmacher MD, Ruppert AS, Whitman SP, Paschka P, Mrozek K, Baldus CD, Vukosavljevic T, Liu CG, Ross ME, Powell BL, de la Chapelle A, Kolitz JE, Larson RA, Marcucci G, Bloomfield CD (2008) High BAALC expression associates with other molecular prognostic markers, poor outcome, and a distinct gene-expression signature in cytogenetically normal patients younger than 60 years with acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) study. Blood 111:5371–5379
Bienz M, Ludwig M, Leibundgut EO, Mueller BU, Ratschiller D, Solenthaler M, Fey MF, Pabst T (2005) Risk assessment in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and a normal karyotype. Clin Cancer Res 11:1416–1424
Langer C, Marcucci G, Holland KB, Radmacher MD, Maharry K, Paschka P, Whitman SP, Mrozek K, Baldus CD, Vij R, Powell BL, Carroll AJ, Kolitz JE, Caligiuri MA, Larson RA, Bloomfield CD (2009) Prognostic importance of MN1 transcript levels, and biologic insights from MN1-associated gene and microRNA expression signatures in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: a cancer and leukemia group B study. J Clin Oncol 27:3198–3204
Marcucci G, Maharry K, Whitman SP, Vukosavljevic T, Paschka P, Langer C, Mrozek K, Baldus CD, Carroll AJ, Powell BL, Kolitz JE, Larson RA, Bloomfield CD (2007) High expression levels of the ETS-related gene, ERG, predict adverse outcome and improve molecular risk-based classification of cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol 25:3337–3343
Paschka P, Marcucci G, Ruppert AS, Whitman SP, Mrozek K, Maharry K, Langer C, Baldus CD, Zhao W, Powell BL, Baer MR, Carroll AJ, Caligiuri MA, Kolitz JE, Larson RA, Bloomfield CD (2008) Wilms tumor 1 gene mutations independently predict poor outcome in adults with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol 26:4595–4602
Breems DA, van Putten WL, de Greef GE, Van Zelderen-Bhola SL, Gerssen-Schoorl KB, Mellink CH, Nieuwint A, Jotterand M, Hagemeijer A, Beverloo HB, Lowenberg B (2008) Monosomal karyotype in acute myeloid leukemia: a better indicator of poor prognosis than a complex karyotype. J Clin Oncol 26:4791–4797
Santamaria CM, Chillon MC, Garcia-Sanz R, Perez C, Caballero MD, Ramos F, de Coca AG, Alonso JM, Giraldo P, Bernal T, Queizan JA, Rodriguez JN, Fernandez-Abellan P, Barez A, Penarrubia MJ, Balanzategui A, Vidriales MB, Sarasquete ME, Alcoceba M, az-Mediavilla J, San Miguel JF, Gonzalez M (2009) Molecular stratification model for prognosis in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 114:148–152
Krauter J, Wagner K, Schafer I, Marschalek R, Meyer C, Heil G, Schaich M, Ehninger G, Niederwieser D, Krahl R, Buchner T, Sauerland C, Schlegelberger B, Dohner K, Dohner H, Schlenk RF, Ganser A (2009) Prognostic factors in adult patients up to 60 years old with acute myeloid leukemia and translocations of chromosome band 11q23: individual patient data-based meta-analysis of the German Acute Myeloid Leukemia Intergroup. J Clin Oncol 27:3000–3006
Mrozek K, Heinonen K, Lawrence D, Carroll AJ, Koduru PR, Rao KW, Strout MP, Hutchison RE, Moore JO, Mayer RJ, Schiffer CA, Bloomfield CD (1997) Adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia and t(9; 11)(p22; q23) have a superior outcome to patients with other translocations involving band 11q23: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. Blood 90:4532–4538
Suarez L, Vidriales MB, Moreno MJ, Lopez A, Garcia-Larana J, Perez-Lopez C, Tormo M, Lavilla E, Lopez-Berges MC, de Santiago M, San Miguel JF, Orfao A (2005) Differences in anti-apoptotic and multidrug resistance phenotypes in elderly and young acute myeloid leukemia patients are related to the maturation of blast cells. Haematologica 90:54–59
Oriol A, Ribera JM, Esteve J, Guardia R, Brunet S, Bueno J, Pedro C, Llorente A, Tormo M, Besalduch J, Sanchez JM, Batlle M, Vivancos P, Carreras E, Vila JM, Julia A, Sierra J, Montserrat E, Feliu E (2004) Feasibility and results of autologous stem cell transplantation in de novo acute myeloid leukemia in patients over 60 years old. Results of the CETLAM AML-99 protocol. Haematologica 89:791–800
Chillon MC, Fernandez C, Garcia-Sanz R, Balanzategui A, Ramos F, Fernandez-Calvo J, Gonzalez M, Miguel JF (2004) FLT3-activating mutations are associated with poor prognostic features in AML at diagnosis but they are not an independent prognostic factor. Hematol J 5:239–246
Schnittger S, Schoch C, Kern W, Mecucci C, Tschulik C, Martelli MF, Haferlach T, Hiddemann W, Falini B (2005) Nucleophosmin gene mutations are predictors of favorable prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. Blood 106:3733–3739
Santamaria C, Chillon MC, Garcia-Sanz R, Balanzategui A, Sarasquete ME, Alcoceba M, Ramos F, Bernal T, Queizan JA, Penarrubia MJ, Giraldo P, San Miguel JF, Gonzalez M (2008) The relevance of preferentially expressed antigen of melanoma (PRAME) as a marker of disease activity and prognosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Haematologica 93:1797–1805
Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden V, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N, Barbany G, Cazzaniga G, Cayuela JM, Cave H, Pane F, Aerts JL, De Micheli D, Thirion X, Pradel V, Gonzalez M, Viehmann S, Malec M, Saglio G, van Dongen JJ (2003) Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia—a Europe Against Cancer program. Leukemia 17:2318–2357
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Spanish cooperative group PETHEMA (Program for the Study and Treatment of Malignant Hemopathies) for providing the treatment protocol, samples, and clinical information. This work has been partially supported by the grants PI061351 and 00/0023-00 from the Spanish “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias de la Seguridad Social”, 89/A/06 from “Gerencia Regional de Salud, Junta Castilla y León”, and CIC, IBMCC (USAL-CSIC), Spain.
Author's contributions
Santamaría C. and Chillón M. C. carried out all molecular studies and prepared the database for the final analysis. Santamaría C. performed the statistical analysis and prepared the initial version of the paper.
Garcia-Sanz R. helped in the design of the work, reviewed the database, and contributed towards the statistical analysis. He provided the pre-approval of the final version.
Pérez C., Caballero D., Mateos M. V., Ramos F., García de Coca A., Alonso J. M., Giraldo P., Bernal T., Queizán J. A., Rodriguez J. N., and Díaz-Mediavilla J. were the clinicians responsible for the patients and those who ensured the application of protocol, sampling, and the collection of clinical data.
Puig N., Balanzategui A., Sarasquete M. E., and Alcoceba M. participated in the generation of the molecular results.
San Miguel J. F. and González M. initially promoted the study and were responsible for securing financial support. Both were responsible for the group and were the persons responsible for the most important revision of the draft. González M. was the person who approved the final version to be sent to the editor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Abnormal karyotypes of AML patients included in the study (DOC 74 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santamaría, C., Chillón, M.C., García-Sanz, R. et al. BAALC is an important predictor of refractoriness to chemotherapy and poor survival in intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Ann Hematol 89, 453–458 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0864-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0864-x