Abstract
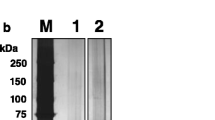
Recently, it was shown that glycoproteins with N-glycans close to the NH2 terminus can directly enter the calnexin/calreticulin cycle and bypass BiP binding. This should allow efficient secretion of glycoproteins such as factor VIII (FVIII) whose secretion is negatively affected by BiP interaction. Examination of the glycosylation pattern of the NH2 terminus of FV and FVIII revealed N-glycans at positions 23 and 27 in FV and at position 41 in FVIII. To improve FVIII secretion, a 14-amino-acid-long polypeptide with (G3) or without (G0; control) three N-linked glycosylation consensus sites was inserted upstream of the NH2 terminus of a B-domain deleted FVIII protein. Expression of G3- and G0-constructs in three different cell lines resulted in the same or even higher expression rate of protein as found for the B-domain deleted FVIII. However, as demonstrated by Western blot analysis, the G3- as well as the G0-protein variants were mainly retained inside the cells in similar amounts. Thus, glycosylation alone does not automatically lead to higher secretion rates, but must be in context to the normal structure of the FVIII protein.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkenas J, Byers PH (1997) The final stage of gene expression: chaperones and the regulation of protein fate. Am J Hum Genet 61:267–272
Becker S, Simpson JC, Pepperkok R, Heinz S, Herder C, Grez M, Seifried E, Tonn T (2004) Confocal microscopy analysis of native, full length and B-domain deleted coagulation factor VIII trafficking in mammalian cells. Thromb Haemost 92:23–35
Braakman I, Helenius J, Helenius A (1992) Manipulating disulfide bond formation and protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J 11:1717–1722
Dorner JD, Bole DG, Kaufman RJ (1987) The relationship of N-linked glycosylation and heavy chain-binding protein association with the secretion of glycoproteins. J Cell Biol 105:2665–2674
Dorner AJ, Krane MG, Kaufman RJ (1988) Reduction of endogenous GRP78 levels improves secretion of a heterologous protein in CHO cells. Mol Cell Biol 8:4063–4070
Fay PJ, Jenkins PV (2005) Mutating factor VIII: lessons from structure to function. Blood Rev 19:15–27
Haack A, Schmitt C, Poller W, Oldenburg J, Hanfland P, Brackmann HH, Schwaab R (1999) Analysis of expression kinetics and activity of a new B-domain truncated and full-length FVIII protein in three different cell lines. Ann Hematol 78:111–116
Helenius A, Aebi M (2001) Intracellular functions of N-linked glycans. Science 291:2364–2369
Jenny RJ, Pittman DD, Toole JJ, Kriz RW, Aldape RA, Hewick RM, Kaufman RJ, Mann KG (1987) Complete cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of human factor V. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:4846–4850
Kaufman RJ, Pipe SW, Tagliavacca L, Swaroop M, Moussalli M (1997) Biosynthesis, assembly and secretion of coagulation factor VIII. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 8(Suppl 2):S3–14
Marquette KA, Pittman DD, Kaufman RJ (1995) A 110-amino acid region within the A1-domain of coagulation factor VIII inhibits secretion from mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 270:10297–10303
Miao HZ, Sirachainan N, Palmer L, Kucab P, Cunningham MA, Kaufman RJ, Pipe SW (2004) Bioengineering of coagulation factor VIII for improved secretion. Blood 103:3412–3419
Molinari M, Helenius A (2000) Chaperone selection during glycoprotein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum. Science 288:331–333
Morris JA, Dorner AJ, Edwards CA, Hendershot LM, Kaufman RJ (1997) Immunoglobulin binding protein (BiP) function is required to protect cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress but is not required for the secretion of selective proteins. J Biol Chem 272:4327–4334
Nichols WC, Ginsburg D (1999) From the ER to the Golgi: insights from the study of combined factors V and VIII deficiency. Am J Hum Genet 64:1493–1498
Pipe SW, Morris JA, Shah J, Kaufman RJ (1998) Differential interaction of coagulation factor VIII and factor V with protein chaperones calnexin and calreticulin. J Biol Chem 273:8537–8544
Pipe SW (2005) The promise and challenges of bioengineered recombinant clotting factors. J Thromb Haemost 3:1692–1701
Pittman DD, Alderman EM, Tomkinson KN, Wang JH, Giles AR, Kaufman RJ (1993) Biochemical, immunological, and in vivo functional characterization of B-domain-deleted factor VIII. Blood 81:2925–2935
Pittman DD, Tomkinson KN, Kaufman RJ (1994) Post-translational requirements for functional factor V and factor VIII secretion in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 269:17329–17337
Saenko EL, Pipe SW (2006) Strategies towards a longer acting factor VIII. Haemophilia 12(Suppl 3):42–51
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, USA, pp 18.3–18.86
Schenone M, Furie BC, Furie B (2004) The blood coagulation cascade. Curr Opin Hematol 11:272–277
Srour MA, Fechner H, Wang X, Siemetzki U, Albert T, Oldenburg J, Hanfland P, Poller W, Brackmann HH, Schwaab R (2003) Regulation of human factor IX expression using doxycycline-inducible gene expression system. Thromb Haemost 90:398–405
Swaroop M, Moussalli M, Pipe SW, Kaufman RJ (1997) Mutagenesis of a potential immunoglobulin-binding protein-binding site enhances secretion of coagulation factor VIII. J Biol Chem 272:24121–24124
Wallis DD, Putnam EA, Cretoiu JS, Carmical SG, Cao SN, Thomas G, Milewicz DM (2003) Profibrillin-1 maturation by human dermal fibrobloasts: proteolytic processing and molecular chaperons. J Cell Biochem 90:641–652
Wood WI, Capon DJ, Simonsen CC, Eaton DL, Gitschier J, Keyt B, Seeburg PH, Smith DH, Hollingshead P, Wion KL, Delwart E, Tuddenham EGD, Vehar GA, Lawn RM (1984) Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature 312:330–337
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. A. Srour and J. Grupp contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srour, M.A., Grupp, J., Aburubaiha, Z. et al. Modified expression of coagulation factor VIII by addition of a glycosylation site at the N terminus of the protein. Ann Hematol 87, 107–112 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0380-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0380-9