Abstract
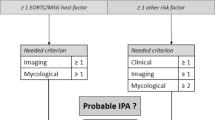
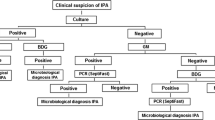
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) is a frequently fatal complication in patients with acute leukaemia. Because diagnosis is still difficult, non-invasive diagnostic criteria were recently proposed by MSG/IFICG/EORTC for study purposes. We have analysed their usefulness in the clinical management of acute leukaemic patients with pulmonary infiltrates. Twenty-seven infiltrates developed during 174 chemotherapy cycles given to 50 consecutive patients. According to diagnostic criteria, IPA was diagnosed in 42% of patients and 77.8% of pulmonary infiltrates. AML diagnosis and the first induction cycle were significant risk factors. “Proven” IPA was rare, occurring in one patient (2%). The diagnosis of “probable” IPA was made in seven patients (14%) and was strongly supported by the significant association of characteristic radiological lesions (“major” clinical criterion) with the positivity of one microbiological criterion (P = 0.026). Conversely, “possible” IPA was frequent (26%) because its pertinent diagnostic criteria were fulfilled in 48.1% of pulmonary infiltrates. However, in 84.6% of cases, the diagnosis of “possible IPA” aspecifically derived from the association of two conditions, a new pulmonary infiltrate with symptoms of lower respiratory tract infection (“minor clinical criterion”), together with the definition of “susceptible” host, which applied to 100% of our leukaemic patients. We conclude that, according to MSG/IFICG/EORTC criteria, a high number of pulmonary infiltrates would be diagnosed as IPA, but only a diagnosis of “proven/probable” IPA should be considered reliable in the clinical management of suspected IPA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denning DW (1998) Invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 26:781–805
Cornet M, Fleury L, Maslo C, Bernard JF, Brucker G (1998) Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in France: a six-years multicentric survey in the Greater Paris area. J Hosp Infect 51:288–296
Denning DW, Marinus A, Cohen J, Spence D, Herbrecht R, Pagano L, Kibbler C, Kermery V, Offner F, Cordonnier C, Jehn U, Ellis M, Collette L, Sylvester R (1998) An EORTC multicentric prospective survey of invasive aspergillosis in haematological patients: diagnosis and therapeutic outcome. EORTC Invasive Fungal Infectious Cooperative Group. J Infect 37:173–180
Nosari A, Oreste P, Cairoli R, Montillo M, Carrafiello G, Astolfi A, Muti G, Martello L, Tedeschi A, Magliano EM, Morra E (2001) Invasive aspergillosis in Haematological malignancies: clinical findings and management for intensive chemotherapy completion. Am J Hematol 68:231–236
Denning DW (1996) Therapeutic outcome in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 23:608–615
Lin S, Schranz J, Teutsch SM (2001) Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis 32:358–366
Baden LR, Rubin RH (2001) Prevention of fungal infection in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, in Preventing Opportunistic Infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Infectious Diseases Society of America, and American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Practice Guidelines and Beyond. In: Education Program Book of American Society of Hematology (ASH) pp 405–410
Stevens DA, Kan VL, Judson MA, Morrison VA, Dummer S, Denning DW, Bennett JE, Walsh TJ, Patterson TF, Pankey GA (2000) Practice guidelines for disease caused by Aspergillus. Clin Infect Dis 30:696–709
Ascioglu S, Rex JH, De Paux B, Bennett JE, Bille J, Crokaert F, Denning DW, Edwards JE, Erjavec Z, Fiere D, Lortholary O, Maertens J, Meis JF, Patterson TF, Ritter J, Selleslag D, Shah PM, Stevens DA, Walsh TJ (2002) Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin Infect Dis 34:7–14
Aliff T, Maslak P, Jurcic J, Heaney M, Cathcart K, Sepkowitz K, Weiss M (2003) Refractory Aspergillus pneumonia in patients with acute leukemia. Cancer 97:1025–1032
Nosari A, Anghilieri M, Carrafiello G, Guffanti C, Martello L, Montillo M, Muti G, Ribera S, Vanzulli A, Nichelatti M, Morra E (2003) Utility of percutaneous lung biopsy for diagnosing filamentous fungal infections in hematologic malignancies. Haematologica 88:1405–1409
Subirà M, Martino R, Rovira M, Vaquez L, Serrano D, De la Càmara (2003) Clinical applicability of the new EORTC/MSG classification for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with hematological malignancies and autopsy-confirmed invasive aspergillosis. Ann Hematol 82:80–82
Pagano L, Girmenia C, Mele L, Ricci P, Tosti ME, Nosari A, Buelli M, Picardi M, Allione B, Corvetta L, D’Antonio D, Montillo M, Melillo L, Chierichini A, Cenacchi A, Tonso A, Cudillo L, Candoni A, Svignano C, Bovini A, Martino P, Del Bavero A (2001) GIMEMA Infection Program; Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche dell’Adulto. Infections caused by filamentous fungi in patients with hematologic malignancies. A report of 391 cases by GIMEMA Infection Program. Haematologica 86:862–870
Lass Florl C, Salzer GM, Schmid T, Rabl W, Ulmer H, Dierichi MP (1999) Pulmonary Aspergillus colonization in humans and its impact on management of critically ill patients. Br J Haematol 104(4):745–747
Cornely O, Andrew JU, Karthaus M (2003) Evidence-based assessment of primary antifungal prophylaxis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 101:3365–3372
Albelda SM, Talbot GH, Gerson SL, Miller WT, Cassileth PA (1984) Role of fiberoptic bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Am J Med 76:1027–1034
Levy H, Horak DA, Tegtmeier BR, Yokota SB, Forman SJ (1992) The value of bronchoalveolar lavage and bronchial washings in the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Respir Med 86:243–248
Reichenberger F, Habicht I, Matt P, Frei R, Soler M, Bolliger CT, Dalquen P, Gratwohi A, Thmm M (1999) Diagnostic yield of bronchoscopy in histologically proven invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Bone Marrow Transplant 24:1195–1199
Tarrand JJ, Lichterfeld M, Warraich I, Luna M, Han XY, May GS, Kontoyiannis DP (2003) Diagnosis of invasive septate mould infections. A correlation of microbiological culture and histologic or cytologic examination. Am J Clin Pathol 119:854–858
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borlenghi, E., Cattaneo, C., Capucci, M.A. et al. Usefulness of the MSG/IFICG/EORTC diagnostic criteria of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in the clinical management of patients with acute leukaemia developing pulmonary infiltrates. Ann Hematol 86, 205–210 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-006-0204-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-006-0204-3