Abstract
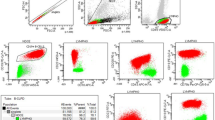
Zeta-associated protein 70 (ZAP-70), determined by flow cytometry, has been advocated a surrogate marker of immunoglobulin (Ig)VH unmutated status in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The aim of the current study was to test the applicability of an easy flow cytometry protocol for ZAP-70 measurement in CLL samples. Samples from 61 CLL patients and 44 normal subjects were analyzed using a commercial ZAP-70 monoclonal antibody (1E7.2 clone) conjugated with phycoerythrin (PE) and Alexa 488 fluorochromes. Modifications of the published methods led to the structure of a simplified in-house method of ZAP-70 measurement. A three-color approach was used with CD19, CD3 gating comparing with the isotype control provided by the same manufacturer. The cutoff levels for ZAP-70 positivity were defined from a receiver operator characteristic curve in relation to the IgVH mutational status and from the ln normalized mean value +2 SD of normal controls. Using the 20% cutoff value for ZAP-70 positivity in CLL patients defined by the literature, ZAP-PE had a sensitivity of 55% and a specificity of 98% in predicting the IgVH mutational status, whereas the corresponding values for ZAP-Alexa were 55% and 84%, respectively. Using the 7% cutoff value for CD38 positivity, the sensitivity was 55%, whereas the specificity was 76%. ZAP-70-positive patients showed a shorter time to disease progression in comparison with ZAP-70-negative patients (p<0.001). In conclusion, the 100% specific prediction of mutational status is accompanied by reduced sensitivity, thus limiting ZAP-70’s applicability either as a single marker or combined with CD38 for the assessment of the mutational status of CLL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibrahim S, Keating M, Do KA, O’Brien S, Huh YO, Jilani I, Lerner S, Kantarjian HM, Albitar M (2001) CD38 expression as an important prognostic factor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 98:181–186
Durig J, Naschar M, Schmucker U, Renzing-Kohler K, Holter T, Huttmann A, Duhrsen U (2002) CD38 expression is an important prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leukemia 16:30–35
Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Dohner K, Bentz M, Lichter M (1999) Chromosome aberrations in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: reassessment based on molecular cytogenetic analysis. J Mol Med 77:266–281
Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK (1999) Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 94:1848–1854
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL, Buchbinder A, Budman D, Dittmar K, Kolitz J, Lichtman SM, Schulman P, Vinciguerra VP, Rai KR, Ferrarini M, Chiorazzi N (1999) IgV gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 94:1840–1847
Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Barry TS, Wright G, Davis RE, Henrickson SE, Zhao H, Ibbotson RE, Orchard JA, Davis Z, Stetler-Stevenson M, Raffeld M, Arthur DC, Marti GE, Wilson WH, Hamblin TJ, Oscier DG, Staudt LM (2003) ZAP-70 expression identifies a chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype with unmutated immunoglobulin genes, inferior clinical outcome, and distinct gene expression profile. Blood 101:4944–4951
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M, Marce S, Lopez-Guillermo A, Campo E, Montserrat E (2003) ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate marker for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 348:1764–1775
Durig J, Nuckel H, Cremer M, Fuhrer A, Halfmeyer K, Fandrey J, Moroy T, Klein-Hitpass L, Duhrsen U (2003) ZAP-70 is a prognostic factor in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 17:2426–2434
Orchard JA, Ibbotson RE, Davis Z, Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Thomas PW, Hamblin TJ, Staudt LM, Oscier DG (2004) ZAP-70 expression and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Lancet 363:105–111
Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, Chen L, Keating MJ, Gribben JG, Neuberg DS, Flinn IW, Rai KR, Byrd JC, Kay NE, Greaves A, Weiss A, Kipps TJ (2004) ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 351:893–901
Schroers R, Griesinger F, Trumper L, Haase D, Kulle B, Klein-Hitpass L, Sellmann L, Duhrsen U, Durig J (2005) Combined analysis of ZAP-70 and CD38 expression as a predictor of disease progression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 19:750–758
Chan AC, Iwashima M, Turck CW, Weiss A (1992) ZAP-70: a 70 kd protein tyrosine-kinase that associates with the TCR ζ chain. Cell 71:649–662
Rosenwald A, Alizadeh AA, Widhopf G, Simon R, Davis RE, Yu X, Yang L, Pickeral OK, Rassenti LZ, Powell J, Botstein D, Byrd JC, Grever MR, Cheson BD, Chiorazzi N, Wilson WH, Kipps TJ, Brown PO, Staudt LM (2001) Relation of gene expression phenotype to immunoglobulin mutation genotype in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 194:1639–1647
Nolz JC, Tschumper RC, Pittner BT, Darce JR, Kay NE, Jelinek DF (2005) ZAP-70 is expressed by a subset of normal human B-lymphocytes displaying an activated phenotype. Leukemia 19:1018–1024
Schweighoffer E, Vanes L, Mathiot A, Nakamura T, Tybulewicz VL (2003) Unexpected requirement for ZAP-70 in pre-B cell development and allelic exclusion. Immunity 18:523–533
Chen L, Apgar J, Huynh L, Dicker F, Giago-McGahan T, Rassenti L, Weiss A, Kipps T (2005) ZAP-70 directly enhances IgM signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 105:2036–2041
Nedellec S, Renaudineau Y, Bordron A, Berthou C, Porakishvili N, Lydyard PM, Pers JO, Youinou P (2005) B cell response to surface IgM cross-linking identifies different prognostic groups of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. J Immunol 174:3749–3756
Castro J, Prada C, Loria O, Kamal A, Chen L, Burrows F, Kipps T (2005) ZAP-70 is a novel conditional heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) client: inhibition of Hsp90 leads to ZAP-70 degradation, apoptosis and impaired signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 106:2506–2512
Orchard J, Ibbotson R, Best G, Parker A, Oscier D (2005) ZAP-70 in B cell malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma 46:1689–1698
Richardson SJ, Matthews C, Catherwood MA, Alexander HD, Carey BS, Farrugia J, Gardiner A, Mould S, Oscier D, Copplestone JA, Prentice AG (2006) ZAP-70 expression is associated with enhanced ability to respond to migratory and survival signals in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL). Blood 107:3584–3592
Hamblin AD, Hamblin TJ (2005) Functional and prognostic role of ZAP-70 in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9:1165–1178
Gibbs G, Bromidge T, Howe D, Hopkins J, Johnson S (2005) Comparison of flow cytometric methods for the measurement of ZAP-70 expression in the routine diagnostic laboratory. Clin Lab Haematol 27:258–266
Bakke AC, Purtzer Z, Leis J, Huang J (2005) A robust ratio metric method for analysis of Zap-70 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Cytometry B Clin Cytom. DOI 10.1002/cyto.b.20079
Matutes E, Owusu-Ankomah K, Morilla R, Garcia MJ, Houlihan A, Que TH, Catovsky D (1994) The immunological profile of B cell disorders and proposal for a scoring system for the diagnosis for CLL. Leukemia 8:1640–1645
Del Giudice I, Morilla A, Osuji N, Matutes E, Morilla R, Burford A, Maravelaki S, Owusu-Ankomah K, Swansbury J, A’hern R, Brito-Babapulle V, Catovsky D (2005) Zeta-chain associated protein 70 and CD38 combined predict the time to first treatment in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 104:2124–2132
Ghia P, Stamatopoulos K, Belessi C, Moreno C, Stella S, Guida G, Michel A, Crespo M, Laoutaris N, Montserrat E, Anagnostopoulos A, Dighiero G, Fassas A, Caligaris-Cappio F, Davi F (2005) Geographic patterns and pathogenetic implications of IGHV gene usage in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: the lesson of the IGHV3-21 gene. Blood 105:1678–1685
Ghia P, Guida G, Stella S, Gottardi D, Geuna M, Strola G, Scielzo C, Caligaris-Cappio F (2003) The pattern of CD38 expression defines a distinct subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients at risk of disease progression. Blood 101:1262–1269
Binet JL, Caligaris-Cappio F, Catovsky D, Cheson B, Davis T, Dighiero G, Dohner H, Hallek M, Hillmen P, Keating M, Montserrat E, Kipps TG, Rai K (2005) Perspectives of the use of new diagnostic tools in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 107:859–861
Del Poeta G, Del Principe MI, Consalvo MA, Maurillo L, Buccisano F, Venditti A, Mazzone C, Bruno A, Gianni L, Capelli G, Lo Coco F, Cantonetti M, Gattei V, Amadori S (2005) The addition of rituximab to fludarabine improves clinical outcome in untreated patients with ZAP-70-negative chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 104:2743–2752
Kim SZ, Chow KU, Kukoc-Zivojnov N, Boehrer S, Brieger A, Steimle-Grauer SA, Harder L, Hoelzer D, Mitrou PS, Weidmann E (2004) Expression of ZAP-70 protein correlates with disease stage in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is associated with, but not generally restricted to, non-mutated Ig VH status. Leuk Lymphoma 45:2037–2045
Orchard J, Ibbotson R, Best G, Parker A, Oscier D (2005) ZAP-70 in B cell malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma 46:1689–1698
Laurenti L, Petlickovski A, Rumi C, Gobessi S, Piccioni P, Tarnani M, Puggioni P, Marietti S, Sica S, Leone G, Efremov DG (2005) Comparison of ZAP-70/Syk mRNA levels with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status and disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 90:1533–1540
Krober A, Bloehdorn J, Hafner S, Buhler A, Seiler T, Kienle D, Winkler D, Bangerter M, Schlenk RF, Benner A, Lichter P, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S (2006) Additional genetic high-risk features such as 11q deletion, 17p deletion, and V3-21 usage characterize discordance of ZAP-70 and VH mutation status in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 24:969–975
Herishanu Y, Kay S, Rogowski O, Pick M, Naparstek E, Deutsch VR, Polliack A (2005) T-cell ZAP-70 overexpression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) correlates with CLL cell ZAP-70 levels, clinical stage and disease progression. Leukemia 19:1289–1291
Kiaii S, Choudhury A, Mozaffari F, Kimby E, Osterborg A, Mellstedt H (2005) Signaling molecules and cytokine production in T cells of patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL): comparison of indolent and progressive disease. Med Oncol 22:291–302
Kay S, Pick M, Herishanu Y, Rogowsky O, Baron S, Naparstek E, Polliack A, Deutsch V (2004) A novel flow cytometry analysis method for the quantitation of zap-70 expression in B-CLL cells. Hematology J 5(S):S24
Admirand JH, Rassidakis GZ, Abruzzo LV, Valbuena JR, Jones D, Jeffrey Medeiros L (2004) Immunohistochemical detection of ZAP-70 in 341 cases of non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma. Mod Pathol 17:954–961
Wang J, Young L, Win W, Taylor CR (2005) Distribution and ZAP-70 expression of WHO lymphoma categories in Shanxi, China: a review of 447 cases using a tissue microarray technique. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 13:323–332
Vener C, Gianelli U, Cortelezzi A, Fracchiolla NS, Somalvico F, Savi F, Pasquini MC, Bosari S, Deliliers GL (2006) ZAP-70 immunoreactivity is a prognostic marker of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 47:245–251
Corcoran M, Parker A, Orchard J, Davis Z, Wirtz M, Schmitz OJ, Oscier D (2005) ZAP-70 methylation status is associated with ZAP-70 expression status in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 90:1078–1088
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Passam, F., Tachynopoulou, V., Skoumi, D. et al. Feasibility of an easily applicable method of ZAP-70 measurement in chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the routine flow cytometry setting: a methodological approach. Ann Hematol 85, 795–805 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-006-0159-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-006-0159-4