Abstract
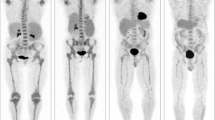
The percentage of myeloma cells in bone marrow is subsequently an important index of disease in patients with multiple myeloma (MM). Bone marrow myeloma cells can be detected by strong CD38/CD138 positivity and light scatter characteristics using flow cytometry. The aim of the study was to evaluate the relationship between the degree of Tc-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) uptake and the percentage of CD38/CD138 expressing myeloma cells in the bone marrow of patients with MM. A total of 15 patients with MM (mean age: 61.7±2.4 years; 7 F and 8 M) were included in the study. Tc-99m MIBI imaging was obtained 20 min after injection of 740 MBq Tc-99m MIBI. Planar spot images of the pelvis and thorax were acquired. The uptake of Tc-99m MIBI in the bone marrow was evaluated using a qualitative and also a semiquantitative scoring system for the bone marrow in areas that included the proximal femurs, anterior iliac crest, and sternum. In all patients, flow cytometry was performed for assessing the percentage of CD38/CD138 expressing myeloma cells in the bone marrow samples. There was a statistically significant positive correlation between the percentage of CD38/CD138 expressing plasma cells in bone marrow and both mean qualitative (r=0.689, p=0.005) and semiquantitative (r=0.669, p=0.006) results of Tc-99m MIBI uptake. In conclusion, our results indicate that increased Tc-99m MIBI uptake of bone marrow is related to the percentage of plasma cell infiltration of bone marrow. Tc-99m MIBI bone marrow imaging may be a useful tool for predicting the levels of myeloma cells in bone marrow of patients with MM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams B, Fataar A, Nizami M (1996) Technetium-99m-sestamibi uptake in myeloma. J Nucl Med 37:1001–1002
Alexandrakis M, Kyriakou D, Passam F, Koukouraki S, Karkavitsas N (2001) Value of Tc-99m sestamibi scintigraphy in the detection of bone lesions in multiple myeloma: comparison with Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate. Ann Hematol 80:349–353
Biassoni L, Tirovola E, Kaleva N, Kouykin V, Britton K (1995) Myeloma imaging with Tc99m-MIBI. Eur J Nucl Med 22:856
Catalano L, Pace L, Califano C, Pinto A, De Renzo A, Di Gennaro F, Del Vecchio S, Fonti R, Salvatore M, Rotoli B (1999) Detection of myeloma lesions by technetium-99m-sestaMIBI scintigraphy. Haematologica 84:119–124
Chilosi M, Adami F, Lestani M, Montagna L, Cimarosto L, Semenzato G, Pizzolo G, Menestrina F (1999) CD138/syndecan-1: a useful immunohistochemical marker of normal and neoplastic plasma cells on routine trephine bone marrow biopsies. Mod Pathol 12:1101–1106
Chiu M, Kronauge J, Piwnika-Worms D (1990) Effect of mitochondrial and plasma membrane potentials on accumulation of hexakis (2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile)-technetium (I) in cultured mouse fibroblast. J Nucl Med 31:1646–1653
Chun K, Cho I, Won K, Lee K, Lee H, Hyun M, Hayashida K (2001) Comparison of Tc-99m sestamibi and TI-201 uptake in multiple myeloma. Clin Nucl Med 26:212–215
Delmon-Moingeon L, Piwnica-Worms D, Van den Abbeele A, Holman L, Davidson A, Jones A (1990) Uptake of cation hexakis (2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile)-technetium-99m by human carcinoma cell line in vitro. Cancer Res 50:2198–2202
Dhodapkar M, Sanderson R (1999) Syndecan-1 (CD 138) in myeloma and lymphoid malignancies: a multifunctional regulator of cell behaviour within the tumor microenvironment. Leuk Lymphoma 34:35–43
el-Shirbiny A, Yeung H, Imbriaco M, Michaeli J, Macapinlac H, Larson S (1997) Technetium-99m-MIBI versus fluorine-18-FDG in diffuse multiple myeloma. J Nucl Med 38:1208–1210
Foldes I, Levay A, Stotz G (1993) Comparative scanning of thyroid nodules with technetium-99m pertechnetate and technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile. Eur J Nucl Med 20:330–333
Fonti R, Del Vecchio S, Zannetti A, De Renzo A, Di Gennaro F, Catalano L, Califano C, Pace L, Rotoli B, Salvatore M (2001) Bone marrow uptake of 99mTc-MIBI in patients with multiple myeloma. Eur J Nucl Med 28:214-220
Hussein M, Juturi J, Lieberman I (2002) Multiple myeloma: present and future. Curr Opin Oncol 14:31–35
Muller S, Guth-Tougelidis B, Creutzig H (1987) Imaging of malignant tumours with Tc-99m-MIBI SPECT (abstract). J Nucl Med 28:562
Pace L, Catalano L, Pinto A, De Renzo A, Di Gennaro F, Califano C, Del Vecchio S, Rotoli B, Salvatore M (1998) Different patterns of technetium-99m sestamibi uptake in multiple myeloma. Eur J Nucl Med 25:714–720
Pace L, Catalano L, Del Vecchio S, Di Gennaro F, De Renzo A, Sica G, Califano C, Tedesco N, Borrelli G, Rotoli B, Salvatore M (2001) Predictive value of technetium-99m sestamibi in patients with multiple myeloma and potential role in the follow-up. Eur J Nucl Med 28:304–312
Palmedo H, Biersack H, Lastoria S, Maublant J, Prats S, Stegner H, Bourgeois P, Hustinx R (1998) Scintimammography with technetium 99m-methoxyisobutylisonitrile: results of a prospective European multicentre trial. Eur J Nucl Med 25:375–385
Piwnica-Worms D, Kronauge J, Chiu M (1990) Uptake and retention of hexakis (2-methoxyisobutyl isonitrile) technetium (I) in cultured chick myocardial cells. Mitochondrial and plasma membrane potential dependence. Circulation 82:1826–1838
Piwnika-Worms D (1993) Functional imaging of multidrug-resistant P-glycoprotein with an organo-technetium complex. Cancer Res 53:977–984
Rawstron A, Owen R, Davies F, Johnson R, Jones R, Richards S, Evans P, Child J, Smith G, Jack A, Morgan G (1997) Circulating plasma cells in multiple myeloma: characterization and correlation with disease stage. Br J Haematol 97:46–55
Soderlund V, Jonsson C, Bauer H, Brosjo O, Jacobsson H (1997) Comparison of technetium-99m-MIBI and technetium-99m-tetrofosmin uptake by musculoskeletal sarcomas. J Nucl Med 38:682–686
Svaldi M, Tappa C, Gebert U, Bettini D, Fabris PFF, Osele L, Mitterer M (2001) Technetium-99m-sestamibi scintigraphy: an alternative approach for diagnosis and follow-up of active myeloma lesions after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 80:393–397
Tedder T, Clement L, Cooper M (1984) Discontinuous expression of a membrane antigen (HB-7) during B lymphocyte differentiation. Tissue Antigens 24:140–149
Tirovola E, Biassoni L, Britton K, Kaleva N, Kouykin V, Malpas J (1996) The use of 99mTc-MIBI scanning in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer 74:1815–1820
Wackers F, Berman D, Maddahi J, Watson D, Beller G, Strauss H, Boucher C, Picard M, Holman B, Fridrich R (1989) Technetium-99m hexakis 2-methoxyisobutyl isonitrile: human biodistribution, dosimetry, safety, and preliminary comparison to thallium-201 for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 30:301–311
Yokogami K, Kawano H, Moriyama T, Uehara H, Sameshima T, Oku T, Goya T, Wakisaka S, Nagamachi S, Jinnouchi S, Tamura S (1998) Application of SPET using technetium-99m sestamibi in brain tumours and comparison with expression of the MDR-1 gene: is it possible to predict the response to chemotherapy in patients with gliomas by means of 99mTc-sestamibi SPET. Eur J Nucl Med 25:401–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00277-003-0742-x
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AK, İ., Aslan, V., Vardareli, E. et al. Tc-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile bone marrow imaging for predicting the levels of myeloma cells in bone marrow in multiple myeloma: correlation with CD38/CD138 expressing myeloma cells. Ann Hematol 82, 88–92 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-002-0600-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-002-0600-2