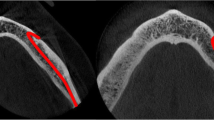
Abstract
Purpose
To determine the shape, position, vertical height, surrounding bone characteristics, and opening angle of mental foramen (MF) using dental cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
A retrospective study was performed on 663 patients. CBCT records analyzed for the shape, position, and surrounding bone measurements of the MF using Simplant 3D software (Hasselt, Belgium). Opening angle of MF was also assessed. Kruskal–Wallis and Mann–Whitney U tests were employed to test significant differences between parameters, genders and ages.
Results
All mental foramina were visualized. Regarding location, 49.2% of the MFs were located between first and second premolars, 7.7 distal and 39.7% coincident to the apex of the mandibular second premolar. The mean MF opening angle was 45.4° on the right side, and 45.9° on the left. There were no statistically differences between gender groups with regard to the opening angle degrees.
Conclusions
This study may provide useful information about variations in the position, shape and size, angle of mental foramen, which may help the practitioners to perform safer mental nerve blocks and surgical procedures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afkhami F, Haraji A, Boostani HR (2013) Radiographic localization of the mental foramen and mandibular canal. J Dent (Tehran Iran) 10:436–442
Al-Mahalawy H, Al-Aithan H, Al-Kari B, Al-Jandan B, Shujaat S (2017) Determination of the position of mental foramen and frequency of anterior loop in Saudi population. A retrospective CBCT study. Saudi Dent J 29:29–35
Alam MK, Alhabib S, Alzarea BK, Irshad M, Faruqi S, Sghaireen MG, Patil S, Basri R (2017) 3D CBCT morphometric assessment of mental foramen in Arabic population and global comparison: imperative for invasive and non-invasive procedures in mandible. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 76(2):98–104
Apinhasmit W, Methathrathip D, Chompoopong S, Sangvichien S (2006) Mental foramen in Thais: an anatomical variation related to gender and side. Surg Radiol Anat 28:529–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-006-0119-7
Bartling R, Freeman K, Kraut RA (1999) The incidence of altered sensation of the mental nerve after mandibular implant placement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Off J Am Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:1408–1412
Caglayan F, Sumbullu MA, Akgul HM, Altun O (2014) Morphometric and morphologic evaluation of the mental foramen in relation to age and sex: an anatomic cone beam computed tomography study. J Craniofac Surg 25:2227–2230. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000001080
Carruth P, He J, Benson BW, Schneiderman ED (2015) Analysis of the size and position of the mental foramen using the CS 9000 cone-beam computed tomographic unit. J Endod 41:1032–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2015.02.025
Charalampakis A, Kourkoumelis G, Psari C, Antoniou V, Piagkou M, Demesticha T, Kotsiomitis E, Troupis T (2017) The position of the mental foramen in dentate and edentulous mandibles: clinical and surgical relevance. Folia Morphologica. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.a2017.0042
Chkoura A, El Wady W (2013) Position of the mental foramen in a Moroccan population: a radiographic study. Imaging Sci Dent 43:71–75. https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.71
Chong BS, Gohil K, Pawar R, Makdissi J (2017) Anatomical relationship between mental foramen, mandibular teeth and risk of nerve injury with endodontic treatment. Clin Oral Investig 21:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1801-8
Currie CC, Meechan JG, Whitworth JM, Carr A, Corbett IP (2016) Determination of the mental foramen position in dental radiographs in 18–30 year olds. Dento maxillofac Radiol 45:20150195. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr.20150195
Gershenson A, Nathan H, Luchansky E (1986) Mental foramen and mental nerve: changes with age. Acta Anatomica 126:21–28
Goyushov S, Tozum MD, Tozum TF (2017) Accessory mental/buccal foramina: case report and review of literature. Implant Dent 26:796–801. https://doi.org/10.1097/id.0000000000000646
Greenstein G, Tarnow D (2006) The mental foramen and nerve: clinical and anatomical factors related to dental implant placement: a literature review. J Periodontol 77:1933–1943. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2006.060197
Gungor E, Aglarci OS, Unal M, Dogan MS, Guven S (2017) Evaluation of mental foramen location in the 10–70 years age range using cone-beam computed tomography. Niger J Clin Pract 20:88–92. https://doi.org/10.4103/1119-3077.178915
Igbigbi P, Lebona S (2005) The position and dimensions of the mental foramen in adult Malawian mandibles. West Afr J Med 24:184–189
Kalender A, Orhan K, Aksoy U (2012) Evaluation of the mental foramen and accessory mental foramen in Turkish patients using cone-beam computed tomography images reconstructed from a volumetric rendering program. Clin Anat 25:584–592
Khojastepour L, Mirbeigi S, Mirhadi S, Safaee A (2015) Location of MENTAL FORAMEN in a selected Iranian population: a CBCT assessment. Iran Endod J 10:117–121
Kumar V, Ludlow JB, Mol A, Cevidanes L (2007) Comparison of conventional and cone beam CT synthesized cephalograms. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 36:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr/98032356
Lipski M, Tomaszewska IM, Lipska W, Lis GJ, Tomaszewski KA (2013) The mandible and its foramen: anatomy, anthropology, embryology and resulting clinical implications. Folia Morphologica 72:285–292
Muinelo-Lorenzo J, Fernandez-Alonso A, Smyth-Chamosa E, Suarez-Quintanilla JA, Varela-Mallou J, Suarez-Cunqueiro MM (2017) Predictive factors of the dimensions and location of mental foramen using cone beam computed tomography. PloS One 12:e0179704. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179704
Orhan AI, Orhan K, Aksoy S, Ozgul O, Horasan S, Arslan A, Kocyigit D (2013) Evaluation of perimandibular neurovascularization with accessory mental foramina using cone-beam computed tomography in children. J Craniofac Surg 24:e365–369. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e3182902f49
Panjnoush M, Rabiee ZS, Kheirandish Y (2016) Assessment of location and anatomical characteristics of mental foramen, anterior loop and mandibular incisive canal using cone beam computed tomography. J Dent (Tehran Iran) 13:126–132
Patel S, Dawood A, Whaites E, Pitt Ford T (2009) New dimensions in endodontic imaging: part 1. Conventional and alternative radiographic systems. Int Endod J 42:447–462. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01530.x
Phillips JL, Weller RN, Kulild JC (1990) The mental forman: Part I. Size, orientation, and positional relationship to the mandibular second premolar. J Endod 16:221–223
Phillips JL, Weller RN, Kulild JC (1992) The mental foramen: Part III. Size and position on panoramic radiographs. J Endod 18:383–386
Prados-Frutos JC, Salinas-Goodier C, Manchon A, Rojo R (2017) Anterior loop of the mental nerve, mental foramen and incisive nerve emergency: tridimensional assessment and surgical applications. Surg Radiol Anat 39:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1690-1
Sheikhi M, Kheir MK (2016) CBCT assessment of mental foramen position relative to anatomical landmarks. Int J Dent 2016:5821048. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5821048
Solar P, Ulm C, Frey G, Matejka M (1994) A classification of the intraosseous paths of the mental nerve. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 9(3):339–344
Udhaya K, Saraladevi KV, Sridhar J (2013) The morphometric analysis of the mental foramen in adult dry human mandibles: a study on the South Indian population. J Clin Diagn Res 7:1547–1551. https://doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2013/6060.3207
Voljevica A, Talovic E, Hasanovic A (2015) Morphological and morphometric analysis of the shape, position, number and size of mental foramen on human mandibles. Acta Medica Academica 44:31–38. https://doi.org/10.5644/ama2006-124.124
von Arx T, Friedli M, Sendi P, Lozanoff S, Bornstein MM (2013) Location and dimensions of the mental foramen: a radiographic analysis by using cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod 39:1522–1528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2013.07.033
Walton JN (2000) Altered sensation associated with implants in the anterior mandible: a prospective study. J Prosthet Dent 83:443–449
Wismeijer D, van Waas MA, Vermeeren JI, Kalk W (1997) Patients’ perception of sensory disturbances of the mental nerve before and after implant surgery: a prospective study of 110 patients. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35:254–259
Zaman S, Alam MK, Yusa T, Mukai A, Shoumura M, Rahman SA, Basri R (2016) Mental foramen position using modified assessment system: an imperative landmark for implant and orthognathic surgery. J Hard Tissue Biol 25:365–370
Acknowledgements
This research study was partially supported by Implant Dentistry Research and Education Foundation, International Congress of Oral Implantologists, New Jersey, USA.
Funding
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationship with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TFT and SG designed and developed the project. SG collected the data. SG and MDT performed the analytic calculations. SG wrote the manuscript in consultation with TFT and MDT.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyushov, S., Tözüm, M.D. & Tözüm, T.F. Assessment of morphological and anatomical characteristics of mental foramen using cone beam computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat 40, 1133–1139 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2043-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2043-z