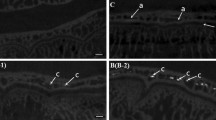
Abstract
Background
Intraosseous vessels play an important role in regeneration of bone. However, the anatomy of the intraosseous vessels in humans has not been clearly delineated due to inadequate method of stereoscopically investigating vessels surrounded by bone tissues.
Purpose
This study was to investigate the feasibility of simple CT scanning with barium sulphate perfusion to detect intraosseous vessels in humans.
Methods
Two freshly obtained feet from a patient who required a double amputation were used in this study. One foot was perfused with barium sulfate and then scanned by CT (CT method). The other foot was processed using vascular corrosion casting (traditional method). Intraosseous vessels in both specimens were compared.
Results
The anatomical distributions of the calcaneal intraosseous vessels were similar as assessed by the CT and traditional methods. However, in comparison to traditional method, the CT method allows the preservation of the surrounding bone tissue, which is important for analyzing the relationship between intraosseous vessels and the surrounding bone structures, and the visualization of a special vascular structure called the sinusoid cluster.
Conclusion
Simple CT scanning with barium sulfate perfusion may be a practical and adequate method for stereoscopically detecting the morphology and distribution of the intraosseous vessels.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT(A):
-
Computed tomography (angiography)
- MRA:
-
Magnetic Resonance angiography
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
References
Andermahr J, Helling HJ, Rehm KE, Koebke Z (1999) The vascularization of the os calcaneum and the clinical consequences. Clin Orthop Relat Res 363:212–218
Brookes M (1960) Sequelae of experimental partial ischemia in long bones of the rabbit. J Anat 94:552–561
Fei J, Peyrin F, Malaval L, Vico L, Lafage-Proust MH (2010) Imaging and quantitative assessment of long bone vascularization in the adult rat using micro-computed tomography. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 293:215–224
Giuvărăşteanu I (2007) Scanning electron microscopy of vascular corrosion casts—standard method for studying microvessels. Rom J Morphol Embryol 48:257–261
Lu W, Dong Z, Liu Z, Fu W, Peng Y, Chen S, Xiao T, Xie H, Du G, Deng B, Zhang X (2010) Detection of microvasculature in rat hind limb using synchrotron radiation. J Surg Res 164:193–199
Machens HG, Grzybowski S, Bucsky B, Spanholtz T, Niedworok C, Maichle A, Stöckelhuber B, Condurache A, Liu F, Egana JT, Kaun M, Mailänder P, Aach T (2006) A technique to detect and to quantify fasciocutaneous blood vessels in small laboratory animals ex vivo. J Surg Res 131:91–96
Miller AN, Prasarn ML, Dyke JP, Helfet DL, Lorich DG (2011) Quantitative assessment of the vascularity of the talus with gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:1116–1121
Møller JF, Robertsen K, Bünger C, Hansen ES (1997) Improved method for examination of microvascular structures in bone tissue. Clin Orthop Relat Res 334:15–23
Morini S, Pannarale L, Franchitto A, Donati S, Gaudio E (1999) Microvascular features and ossification process in the femoral head of growing rats. J Anat 195:225–233
Pazzaglia UE, Congiu T, Ranchetti F, Salari M, Dell’Orbo C (2010) Scanning electron microscopy study of bone intracortical vessels using an injunction and fractured surfaces technique. Anat Sci Int 85:31–37
Quinodoz P, Quinodoz M, Nussbaum JL, Montandon D, Pittet B (2002) Barium sulphate and soft-tissue radiology: allying the old and the new for the investigation of animal cutaneous microcirculation. Br J Plast Surg 55:664–666
Rath B, Notermans HP, Frank D, Walpert J, Deschner J, Luering CM, Koeck FX, Koebke J (2009) Arterial anatomy of the hallucal sesamoids. Clin Anat 22:755–760
Rath B, Notermans HP, Franzen J, Knifka J, Walpert J, Frank D, Koebke J (2009) The microvascular anatomy of the metatarsal bones a plastination study. Surg Radiol Anat 31:271–277
Schneider P, Krucker T, Meyer E, Ulmann-Schuler A, Weber B, Stampanoni M, Müller R (2009) Simultaneous 3D visualization and quantification of marine bone and bone vasculature using micro-computed tomography and vascular replica. Microsc Res Techn 72:690–701
Shereff MJ, Yang QM, Kummer FJ, Frey CC, Greenidge N (1991) Vascular anatomy of the fifth metatarsal. Foot Ankle 11:350–353
Sider KL, Song J, Davies JE (2010) A new bone vascular perfusion compound for the simultaneous analysis of bone and vascular structure. Microsc Res Tech 73:665–672
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Yang joins the first author.
M. Yang and L. Yang contributed equally to this work. They do not have any controversy on this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Yang, L. A simple method to detect human intraosseous vascular structures: using the calcaneus as an example. Surg Radiol Anat 34, 839–846 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-0964-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-0964-5