Abstract
Purpose
To explore the anatomic features of the fabella and its relationship with the common peroneal nerve and the fabellofibular ligament, so as to provide anatomical evidence for clinical diagnosis and treatment of fabella diseases in a Chinese population.
Methods
Sixty-one formalin-fixed knee specimens were obtained for anatomic dissection. Structural features of the fabella were investigated by radiological and histological tests.
Results
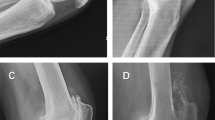
There were 53 cases (86.89%) with fabellae in the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle, including 34 bony ones (55.74%), whereas only 6 cases had fabellae in the medial head (9.84%). The fabellae were accompanied by common peroneal nerves on their surfaces in 11 cases (20.8%), and the presence of the fabella was not generally predictive of a fabellofibular ligament. As much as 57.9% of the cartilage fabellae were not visualized on radiograph. The structure of the ossified fabella is similar to a typical long bone.
Conclusions
Fabellae were mainly present in the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle in a large proportion of the Chinese population. More than half of the cartilage fabellae were not visualized on radiograph. Its clinical significance could not be ignored by physicians and anatomists.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarke AM, Matthews JG (1991) Osteoarthritis of the fabella: a fourth knee compartment? J R Coll Surg Edinb 36:58
Dannawi Z, Khanduja V, Vemulapalli K (2007) Arthroscopic excision of the fabella. J Knee Surg 20:299–301
Duncan W, Dahm D (2003) Clinical anatomy of the fabella. Clin Anat 16:448–449
Flecker H (1942) Time of appearance and fusion of ossification centers as observed by roentgenographic methods. Am J Roentgenol 47:97–159
Franceschi F, Longo UG, Ruzzini L, Leonardi F, Rojas M, Gualdi G, Denaro V (2007) Dislocation of an enlarged fabella as uncommon cause of knee pain: a case report. Knee 14:330–332
Goldenberg R, Wild E (1952) Chondromalacia fabellae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 24:688–690
Ishigooka H, Sugihara T (2004) Anatomical study of the popliteofibular ligament and surrounding structures. Orthop Sci 9:51–58
Kaplan E (1961) The fabellofibular and short lateral ligaments of the knee joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 43:169–179
Kawashima T, Takeishi H, Yoshitomi S, Ito M, Sasaki H (2007) Anatomical study of the fabella, fabellar complex and its clinical implications. Surg Radiol Anat 29:611–616
Marks P, Cameron M, Regan W (1998) Fracture of the fabella: a case of postero-lateral knee pain. Orthopedics 21:713–714
Minowa T, Murakami G, Kura H, Suzuki D, Han SH, Yamashita T (2004) Does the fabella contribute to the reinforcement of the posterolateral corner of the knee by inducing the development of associated ligaments? J Orthop Sci 9:59–65
Moorman C, LaPrade RF (2005) Anatomy and biomechanics of the posterolateral corner of the knee. J Knee Surg 18:137–145
Phukubye P, Oyedele O (2011) The incidence and structure of the fabella in a South African cadaver sample. Clin Anat 24:84–90
Pritchett J (1984) The incidence of fabellae in osteoarthrosis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66:1379–1380
Raheem O, Philpott J, Ryan W, Brien M (2007) Anatomical variations in the anatomy of the posterolateral corner of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:895–900
Robertson A, Jones SCE, Paes R, Chakrabarty G (2004) The fabella: a forgotten source of knee pain? Knee 11:243–245
Sarin VK, Erickson GM, Giori NJ (1999) Coincident development of sesamoid bones and clues to their evolution. Anat Rec 257:174–184
Seebacher JR, Inglis AE, Marshall JL, Warren RF (1982) The structure of the postero-lateral corner of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br 64:536–541
Silva JG, Chagas CAA, Torres DFM, Servidio L (2010) Morphological analysis of the fabella in Brazilians. Int J Morphol 28:105–110
Takebe K, Hirohata K (1981) Peroneal nerve palsy due to fabella. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 99:91–95
Zipple JT, Hammer RL, Loubert PV (2003) Treatment of fabella syndrome with manual therapy: a case report. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 33:33–39
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Zhang Huojun of Changhai Hospital in Shanghai for his help with radiograph investigation and instructor Guo Xiaojing of the Department of Statistics of the Second Military Medical University for her help with statistics analysis.
Conflict of interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. No funds were received in support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, SX., Dong, XL., Dang, RS. et al. Anatomic study of fabella and its surrounding structures in a Chinese population. Surg Radiol Anat 34, 65–71 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-011-0828-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-011-0828-4



