Abstract
Purpose
The human nucleus accumbens (NA), which belongs to the basal ganglia of the brain, is the main part of the ventral striatum. The purpose of our clinically oriented anatomical-radiologic study was to provide anatomical and imaging data of the human NA, primarily useful to neurosurgeons.
Methods
For our imaging study, we used cerebral magnetic resonance images (MRIs) from 26 neurosurgical patients (52 NAs). The material for our anatomic study consisted of 32 cerebral hemispheres (32 NAs) from 18 normal human brains which we have in our department (Department of Anatomy) from cadaver donors. We measured and analyzed the dimensions of the NA at specific clinically important transverse, coronal and sagittal levels.
Results
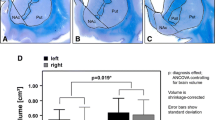
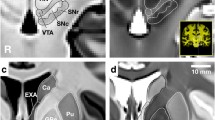
The human NA suffers from age-related but no side- or sex-related morphometric changes. In surgically important stereotactic levels this nucleus is easily identifiable on MRIs.
Conclusions
We present an anatomic guide of the NA from carefully measured data of our extensive and combined study and we hope that our work will be really helpful to neuroscientists interested in the NA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson JL, Curtis GC, Sagher O, Albucher RC, Harrigan M, Taylor SF, Martis B, Giordani B (2005) Deep brain stimulation for refractory obsessive–compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 57(5):510–516
Ahsan RL, Allom R, Gousias IS, Habib H, Turkheimer FE, Free S, Lemieux L, Myers R, Duncan JS, Brooks DJ, Koepp MJ, Hammers A (2007) Volumes, spatial extents and a probabilistic atlas of the human basal ganglia and thalamus. Neuroimage 38(2):261–270
Aouizerate B, Cuny E, Bardinet E, Yelnik J, Martin-Guehl C, Rotge JY, Rougier A, Bioulac B, Tignol J, Mallet L, Burbaud P, Guehl D (2009) Distinct striatal targets in treating obsessive–compulsive disorder and major depression. J Neurosurg 111(4):775–779
Bardinet E, Bhattacharjee M, Dormont D, Pidoux B, Malandain G, Schüpbach M, Ayache N, Cornu P, Agid Y, Yelnik J (2009) A three-dimensional histological atlas of the human basal ganglia II Atlas deformation strategy and evaluation in deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 110(2):208–219
Bewernick BH, Hurlemann R, Matusch A, Kayser S, Grubert C, Hadrysiewicz B, Axmacher N, Lemke M, Cooper-Mahkorn D, Cohen MX, Brockmann H, Lenartz D, Sturm V, Schlaepfer TE (2010) Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 67(2):110–116
Brabec J, Krásený J, Petrovický P (2003) Volumetry of striatum and pallidum in man-anatomy, cytoarchitecture, connections, MRI and aging. Sb Lek 104(1):13–65
Franzini A, Messina G, Gambini O, Muffatti R, Scarone S, Cordella R, Broggi G (2010) Deep-brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in obsessive–compulsive disorder: clinical, surgical and electrophysiological considerations in two consecutive patients. Neurol Sci 31(3):353–359
Gao G, Wang X, He S, Li W, Wang Q, Liang Q, Zhao Y, Hou F, Chen L, Li A (2003) Clinical study for alleviating opiate drug psychological dependence by a method of ablating the nucleus accumbens with stereotactic surgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 81(1–4):96–104
Greenberg BD, Malone DA, Friehs GM, Rezai AR, Kubu CS, Malloy PF, Salloway SP, Okun MS, Goodman WK, Rasmussen SA (2006) Three-year outcomes in deep brain stimulation for highly resistant obsessive–compulsive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol 31(11):2384–2393
Halpern CH, Wolf JA, Bale TL, Stunkard AJ, Danish SF, Grossman M, Jaggi JL, Grady MS, Baltuch GH (2008) Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of obesity. J Neurosurg 109(4):625–634
He F, Guan H, Zhao Z, Miao X, Zhou Q, Li L, Huang D, Liu A, Miao D (2008) Evaluation of short-term psychological functions in opiate addicts after ablating the nucleus accumbens via stereotactic surgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86(5):320–329
Huff W, Lenartz D, Schormann M, Lee SH, Kuhn J, Koulousakis A, Mai J, Daumann J, Maarouf M, Klosterkötter J, Sturm V (2010) Unilateral deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens in patients with treatment-resistant obsessive–compulsive disorder: Outcomes after one year. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 112(2):137–143
Johansen-Berg H, Gutman DA, Behrens TE, Matthews PM, Rushworth MF, Katz E, Lozano AM, Mayberg HS (2008) Anatomical connectivity of the subgenual cingulated region targeted with deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Cereb Cortex 18(6):1374–1383
Junhao T, Homykiewicz O, Kish JS (2006) Identification of a noradrenaline-rich subdivision of the human nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 96(2):349–354
Kuhn J, Lenartz D, Huff W, Lee S, Koulousakis A, Klosterkoetter J, Sturm V (2007) Remission of alcohol dependency following deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens: valuable therapeutic implications? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(10):1152–1153
Kuhn J, Lenartz D, Huff W, Mai JK, Koulousakis A, Maarouf M, Lee SH, Klosterkoetter J, Sturm V (2008) Transient manic-like episode following bilateral deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens and the internal capsule in a patient with Tourette syndrome. Neuromodul Technol Neural Interface 11(2):128–131
Kuhn J, Lenartz D, Mai JK, Huff W, Lee SH, Koulousakis A, Klosterkoetter J, Sturm V (2007) Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens and the internal capsule in therapeutically refractory Tourette-syndrome. J Neurol 254(7):963–965
Malone DA Jr, Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, Carpenter LL, Friehs GM, Eskandar EN, Rauch SL, Rasmussen SA, Machado AG, Kubu CS, Tyrka AR, Price LH, Stypulkowski PH, Giftakis JE, Rise MT, Malloy PF, Salloway SP, Greenberg BD (2009) Deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 65(4):267–275
Mantione M, van de Brink W, Schuurman PR, Denys D (2010) Smoking cessation and weight loss after chronic deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens: therapeutic and research implications: case report. Neurosurgery 66(1):E218
Mikell CB, McKhann GM, Segal S, McGovern RA, Wallenstein MB, Moore H (2009) The hippocampus and nucleus accumbens as potential therapeutic targets for neurosurgical intervention in schizophrenia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 87(4):256–265
Neto LL, Oliveira E, Correia F, Ferreira AG (2008) The human nucleus accumbens: where is it? a stereotactic, anatomical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuromodul Technol Neural Interface 11(1):13–22
Neuner I, Podoll K, Lenartz D, Sturm V, Schneider F (2009) Deep brain stimulation in the nucleus accumbens for intractable Tourette’s syndrome: follow-up report of 36 months. Biol Psychiatry 65:e5–e6
Nolte J, Angevine JB Jr (2007) The human brain in photographs and diagrams, 3rd edn. Mosby (Elsevier), Philadelphia
Okun MS, Bowers D, Springer U, Shapira NA, Malone D, Rezai AR, Nuttin B, Heilman KM, Morecraft RJ, Rasmussen SA, Greenberg BD, Foote KD, Goodman WK (2004) What’s in a “smile?” intra-operative observations of contralateral smiles induced by deep brain stimulation. Neurocase 10(4):271–279
Rauch SL, Dougherty DD, Malone D, Rezai A, Friehs G, Fischman AJ, Alpert NM, Haber SN, Stypulkowski PH, Rise MT, Rasmussen SA, Greenberg BD (2006) A functional neuroimaging investigation of deep brain stimulation in patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder. J Neurosurg 104(4):558–565
Schlaepfer TE, Cohen MX, Frick C, Kosel M, Brodesser D, Axmacher N, Joe AY, Kreft M, Lenartz D, Sturm V (2008) Deep brain stimulation to reward circuitry alleviates anhedonia in refractory major depression. Neuropsychopharmacol 33(2):368–377
Shapira NA, Okun MS, Wint D, Foote KD, Byars JA, Bowers D, Springer US, Lang PJ, Greenberg BD, Haber SN, Goodman WK (2006) Panic and fear induced by deep brain stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77(3):410–412
Sturm V, Lenartz D, Koulousakis A, Treuer H, Herholz K, Klein JC, Klosterkötter J (2003) The nucleus accumbens: a target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive–compulsive and anxiety disorders. J Chem Neuroanat 26(4):293–299
van Kuyck K, Gabriëls L, Cosyns P, Arckens L, Sturm V, Rasmussen S, Nuttin B (2007) Behavioural and physiological effects of electrical stimulation in the nucleus accumbens: a review. Acta Neurochir Suppl 97(2):375–391
Voorn P, Brady LS, Schotte A, Berendse HW, Richfield EK (1994) Evidence for two neurochemical divisions in the human nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci 6(12):1913–1916
Wu HM, Wang XL, Chang CW, Li N, Gao L, Geng N, Ma JH, Zhao W, Gao GD (2010) Preliminary findings in ablating the nucleus accumbens using stereotactic surgery for alleviating psychological dependence on alcohol. Neurosci Lett 473(2):77–81
Xia Y, Bettinger K, Shen L, Reiss AL (2007) Automatic segmentation of the caudate nucleus from human brain MR images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26(4):509–517
Yelnik J, Bardinet E, Dormont D, Malandain G, Ourselin S, Tandé D, Karachi C, Ayache N, Cornu P, Agid Y (2007) A three-dimensional, histological and deformable atlas of the human basal ganglia I atlas construction based on immunohistochemical and MRI data. Neuroimage 34(2):618–638
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mavridis, I., Boviatsis, E. & Anagnostopoulou, S. Anatomy of the human nucleus accumbens: a combined morphometric study. Surg Radiol Anat 33, 405–414 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0766-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0766-6