Abstract
Purpose
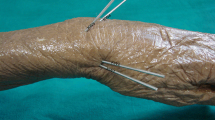
The use of percutaneous Kirschner wires for fixation of unstable fractures of the distal radius has been widely accepted as the least invasive procedure. However, the injury to the superficial branch of the radial nerve (SBRN) is common. Our purpose in this study was to develop a reliable technique to avoid damaging the SBRN.
Methods
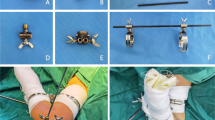
Twenty cadaver forearms were dissected to identify the SBRN distribution, and 18 forearms were used to undergo placement of three Kirschner wires (KW-A, KW-B, and KW-C). The KW-A, KW-B, and KW-C were driven in the frontal plane into the distal radius, and KW-A and KW-C through the tip of radial styloid process at different angles. The SBRN distribution and its relationship with the KW insertion were identified. Fifty-three patients with unstable distal radius fractures were fixed with external fixator and augmented with 1–3 KW, and the injury rates of SBRN were evaluated.
Results
We found a blind region of the SBRN bound by its first bifurcations into radial and ulnar branches and the line crossing the tip of the styloid process. The mean distance of the three wires (KW-A, KW-C, and KW-B) to the closest nerve branch was 4.5, 4.4, and 3.4 mm, respectively. The injury of SBRN occurred in two of 53 patients.
Conclusion
The injury rate of the SBRN can be effectively reduced when the Kirschner wire is placed along the curve AB and as in proximity to the TRSP as possible under fluoroscopic guidance. Our pinning technique is therefore reliable and practical.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams RA, Brown RA, Michael Botte (1992) The superficial branch of the radial nerve: an anatomic study with surgical implications. J Hand Surg Am 17:1037–1041
Auerbach DM, Collins ED, Kunkle KL et al (1994) The radial sensory nerve. An anatomic study. Clin Orthop Relate Res 308:241–249
Calfee RP, Shin SS, Weiss APC (2008) Neurolysis of the distal superficial radial nerve for dysaesthesia due to nerve tethering. J Hand Surg Eur 33:152–154
Cebesoy O (2008) Distal radial fracture treated with minimally invasive procedure. J Orthop Surg 14:109
Chia B, Catalano LW, Glickel SZ et al (2009) Percutaneous pinning of distal radius fractures: an anatomic study demonstrating the proximity of K-wires to structures at risk. J Hand Surg Am 34:1014–1020
Fernandez DL, Geissler WB (1991) Treatment of displaced articular fractures of the radius. J Hand Surg Am 16:375–384
Glanvill R, Boon JM, Birkholtz F et al (2006) Superficial radial nerve injury during standard K-wire fixation of uncomplicated distal radial fractures. Orthopedics 29:639–641
Glickel SZ, Catalano LW, Raia FJ et al (2008) Long-term outcomes of closed reduction and percutaneous pinning for the treatment of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am 33:1700–1705
Glickel SZ, Patel MM, Catalano LW (2006) Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning for distal radius fractures. Atlas Hand Clin 11:175–185
Gofton W, Liew A (2007) Distal radius fractures: nonoperative and percutaneous pinning treatment options. Orthop Clin North Am 38:175–185
Gutow AP (2005) Avoidance and treatment of complications of distal radius fractures. Hand Clin 21:295–305
Habernek H, Weinstabl R, Fialka C et al (1994) Unstable distal radius fractures treated by modified Kirschner wire pinning: anatomic considerations, technique, and results. J Trauma 36:83–88
Handoll HHG, Vaghela MV, Madhok R (2007) Percutaneous pinning for treating distal radial fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD006080
Hochwald NL, Levine R, Tornetta P et al (1997) The risk of Kirschner wire placement in the distal radius: a comparison of techniques. J Hand Surg Am 20:580–584
Kapoor H, Agarwal A, Dhaon BK (2000) Displaced intra-articular fractures of distal radius: a comparative evaluation of results following closed reduction, external fixation and open reduction with internal fixation. Injury 31:75–79
Kreder HJ, Hanel DP, Agel J et al (2005) Indirect reduction and percutaneous fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: a randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:829–836
Lenoble E, Dumontier C, Goutallier D et al (1995) Fracture of the distal radius. A prospective comparison between trans-styloid and Kapandji fixations. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:562–567
Ludvigsen TC, Johansen S, Svenningsen S et al (1997) External fixation versus percutaneous pinning for unstable colles’ fracture. Equal outcome in a randomized study of 60 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 68:255–258
Lundborg G, Rosen B (2004) The two-point discrimination test-time for a re-appraisal. J Hand Surg Br 29B:418–422
Mah ET, Atkinson RN (1992) Percutaneous Kirschner wire stabilization following closed reduction of colles’ fractures. J Hand Surg Br 17:55–62
Mirza A, Jupiter JB, Reinhart MK et al (2009) Fractures of the distal radius treated with cross-pin fixation and a nonbridging external fixator, the CPX system: a preliminary report. J Hand Surg Am 34:603–616
Mok D, Nikolis A, Harris PG et al (2006) The cutaneous innervation of the dorsal hand: Detailed anatomy with clinical implications. J Hand Surg Am 31:567–574
Munson GO, Gainor BJ (1981) Percutaneous pinning of distal radius fractures. J Trauma 21:1032–1035
Robson AJ, See MS, Ellis H (2008) Applied anatomy of the superficial branch of the radial nerve. Clin Anat 21:38–45
Rosati M, Bertagnini S, Digrandi G et al (2006) Percutaneous pinning for fractures of the distal radius. Acta Orthop Belg 72:138–146
Ruschel PH, Albertoni WM (2005) Treatment of unstable extra-articular distal radius fractures by modified intrafocal Kapandji method. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 9:7–16
Singh S, Trikhaa P, Twymanb R (2005) Superficial radial nerve damage due to Kirschner wiring of the radius. Injury 36:330–332
Steinberg BD, Plancher KD, Idler RS et al (1995) Percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation through the snuff box: an anatomic study. J Hand Surg Am 20:57–62
Strohm PC, Muller CA, Boll T et al (2004) Two procedures for Kirschner wire osteosynthesis of distal radial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86:2621–2628
Weil WM, Trumble TE (2005) Treatment of distal radius fractures with intrafocal (Kapandji) pinning and supplemental skeletal stabilization. Hand Clin 21:317–328
Acknowledgments
We declare that our experiments comply with the current laws of the People’s Republic of China.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflict of interest, and our research has no financial relationship with any organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zheng, X., Wang, J. et al. Reliable techniques to avoid damaging the superficial radial nerve due to percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of the distal radius fracture through the radial styloid process. Surg Radiol Anat 32, 711–717 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0652-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0652-2