Abstract
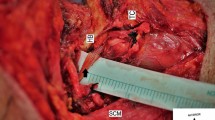
The objective of the present work was to investigate the laryngeal branching pattern of the inferior laryngeal nerve (ILN) in detail before the branches entered the larynx. In 49 specimens 96 sides were examined for this project, including 27 males and 22 female cadavers. In 7 sides (7.3%, 5 on the left and 2 on the right) the ILN passed as a single trunk into the larynx below the inferior constrictor muscle. In 82 sides (85.4%, 40 on the left and 42 on the right) two laryngeal branches originated from the nerve. The nerve divided either just before entering the larynx (58.3%, 24 on the left and 32 on the right) or 15–32 mm below the inferior constrictor muscle (27.1%, 16 on the left and 10 on the right). In 69 sides (71.8%), the anterior and/or posterior laryngeal branches subdivided into one or two sub-branches. The anterior (observed in 49 sides, 51%) and posterior laryngeal branches supplied all intrinsic laryngeal muscles except the cricothyroid muscle and the mucosa below the vocal cords, respectively, while their sub-branches reached the cricopharyngeal part of the inferior constrictor muscle, esophagus and/or the thyroid gland. In 7 sides (7.3%, 4 on the left and 3 on the right) the nerve divided into three laryngeal branches. In conclusion, the branching pattern of the nerve may be important pitfalls of the thyroidal and laryngeal surgery. Owing to this the surgeon should keep in mind the risk of extra laryngeal division of the nerve and not confuse laryngeal and extra laryngeal branches.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardito G, Revelli L, D’Alatri, Lerro V, Guidi ML, Ardito F (2004) Revised anatomy of the recurrent laryngeal nerves. Am J Surg 187:249–253
Armstrong WG, Hinton JW (1951) Multiple divisions of the recurrent laryngeal nerve; an anatomic study. Arch Surg 62:532–599
Berlin DD (1935) The recurrent laryngeal nerves in total ablation of the normal thyroid gland—an anatomical and surgical study. Surg Gynecol Obstet 60:19–26
Hisham A, Lukman MR (2002) Recurrent laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery: a critical appriasal. ANZ J Surg 72:887–889
International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (1977) Nomina Anatomica. 4th edn. Exerpta Medica, Amsterdam, p A88
International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (1983) Nomina Anatomica, 5th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p A75
Keros P, Nemanic D (1967) The terminal branching of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Pract Otorhinolaryngol 29:5–10
Kratz RC (1973) The identification and protection of the laryngeal motor nerve during thyroid and laryngeal surgery. A new microsurgical technique. Laryngoscope 83:59–78
Moreau S, De Rugy MG, Babin E, Salame E, Delmas P, Valdazzo A (1998) The recurrent laryngeal nerve: related vascular anatomy. Laryngoscope 108:1351–1353
Nguyen M, Junien-Lavillauroy C, Faure C (1989) Anatomical interarytenoid anterior branch of the recurrent (inferior) laryngeal nerve. Surg Radiol Anat 11:123–127
Rueger RS (1972) The superior laryngeal nerve and interarytenoid muscle in humans. An anatomical study. Laryngoscope 82:2008–2031
Schweizer V, Dörfl J (1997) The anatomy of the inferior laryngeal nerve. Clin Otolaryngol 22:362–369
Sturniolo G, D’Alia C, Tonante A, Gagliano E, Taranto F, Lo Schiavo MG (1999) The recurrent laryngeal nerve related to thyroid surgery. Am J Surg 177(6):485–488
Sun SQ, Zhao J, Lu H, He GQ, Ran JH, Peng XH (2001) An anatomical study of the recurrent laryngeal nerve: its branching patterns and relationship to the inferior thyroid artery. Surg Radiol Anat 23:363–369
Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister LH (1995) Gray’s Anatomy. 37th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 1116–1118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yalçın, B., Tuğcu, H., Cantürk, N. et al. Laryngeal branching pattern of the inferior laryngeal nerve, before entering the larynx. Surg Radiol Anat 28, 339–342 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-006-0118-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-006-0118-8