Abstract
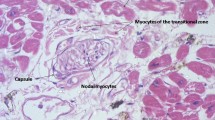
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common abnormal heart rhythm and contributes to cardiac morbidity and mortality. Electrophysiological studies with pacing have shown that AF is initiated by ectopic beats localized in the pulmonary vein (PV) walls. The aim of this work was to look for some anatomical or histological particularities to explain these ectopic beats. Ten autopsied hearts were examined (6 males, 4 females). The myocardium was studied from the left atrium to the PV. Histological sections were made from 39 PVs. Myocardial cells were localized to PV between 9 and 38 mm from the PV-atrial junction. The sleeve was composed of circularly and longitudinally oriented bundles of cardiomyocytes. The peripheral end of the myocardial sleeve was irregular. The longest myocardial sleeves were found in the superior veins and were longitudinally oriented. At the PV-atrial junction, the circular bundles were not often circumferential. PV myocardial architecture confirmed the possibility of initiating AF. This fact is important for therapeutic radiofrequency ablation and explains why PV disconnection is essential.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheung DW (1981) Electrical activity of the pulmonary vein and its interaction with the right atrium in the guinea-pig. J Physiol (Lond) 314:445–456
Cox JL (2001) Intraoperative options for treating atrial fibrillation associated with mitral valve disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 122:212–215
Ernst S, Schluter M, Ouyang F, Khanedani A, Cappato R, Hebe J, Volkmer M, Antz M, Kuck KH (1999) Modification of the substrate for maintenance of idiopathic human atrial fibrillation: efficacy of radiofrequency ablation using non-fluoroscopic catheter guidance. Circulation 100:2085–2092
Gaita FR, Lamberti F (1998) Right and left atrium radiofrequency catheter ablation in idiopathic vagal atrial fibrillation. Circulation 97:2136–2145
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Garrigue S, Takahashi A, Lavergne T, Hocini M, Peng JT, Roudaut R, Clementy J (2000) Electrophysiological end point for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation initiated from multiple pulmonary venous foci. Circulation 101:1409–1417
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Gencel L, Pradeau V, Garrigues S, Chouairi S, Hocini M, Le Metayer P, Roudaut R, Clementy J (1996) Right and left atrial radiofrequency catheter therapy of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 7:1132–1144
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Metayer P, Clementy J (1998) Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 339:659–666
Haissaguerre M, Shah DC, Jais P, Hocini M, Yamane T, Deisenhofer I, Chauvin M, Garrigue S, Clementy J (2000) Electrophysiological breakthroughs from the left atrium to the pulmonary veins. Circulation 102:2463–2465
Ho SY, Cabrera JA, Tran VH, Farre J, Anderson RH, Sanchez-Quintana D (2001) Architecture of the pulmonary veins: relevance to radiofrequency ablation. Heart 86:265–270
Jais P, Haissaguerre M, Shah DC, Chouairi S, Gencel L, Hocini M, Clementy J (1997) A focal source of atrial fibrillation treated by discrete radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 95:572–576
Jais P, Shah DC, Haissaguerre M, Takahashi A, Lavergne T, Hocini M, Garrigue S, Barold SS, Le Metayer P, Clementy J (1999) Efficacy and safety of septal and left-atrial linear ablation for atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 84:139R–146R
Masani F (1986) Node-like cells in the myocardial layer of the pulmonary vein of rats: an ultrastructural study. J Anat 145:133–142
Paes de Almeida O, Bohm CM, de Paula Carvalho M, Paes de Carvalho A (1975) The cardiac muscle in the pulmonary vein of the rat: a morphological and electrophysiological study. J Morphol 145:409–433
Poirier P, Charpy A (1911) Traité d’anatomie humaine, new edition, vol 2. Masson, Paris, pp 601–603
Shah DC, Haissaguerre M, Jais P (1999) Catheter ablation of pulmonary vein foci for atrial fibrillation. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 47 [Suppl 3]:352–356
Swartz J, Pellersels G, Silvers J (1994) A catheter-based curative approach to atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation 90:335
Tagawa M, Higuchi K, Chinushi M, Washizuka T, Ushiki T, Ishihara N, Aizawa Y (2001) Myocardium extending from the left atrium onto the pulmonary veins: a comparison between subjects with and without atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 24:1459–1463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roux, N., Havet, E. & Mertl, P. The myocardial sleeves of the pulmonary veins: potential implications for atrial fibrillation. Surg Radiol Anat 26, 285–289 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-003-0219-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-003-0219-6