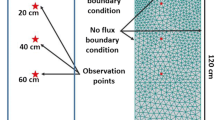
Abstract
The water productivity of wide beds is largely constrained by poor lateral infiltration. Therefore, field trials were conducted to quantify soil moisture distribution on two soils using three renovation methods [no tillage (NT), shallow cultivation (SC) and blade ploughing (BP)] and four furrow water heads. The aim was to explore strategies for improving lateral infiltration using Hydrus 2D simulation techniques. The results showed increased lateral infiltration and soil water storage with BP, increased vertical infiltration and deep drainage with SC and reduced infiltration with NT treatments. Interestingly, the maximum wetting time of a 2 m wide bed on the clay was ~20 h with NT at a 4-cm furrow water head. This seems achievable under the Australian field conditions. However, the minimum wetting time of a 1.3 m wide bed on the sandy clay loam was 15 h with BP at full furrow water head, which is difficult to manage under short Pakistani furrows with quicker irrigation times. The evaluations and graphical presentations developed can enhance decision support for the optimised irrigation management and bed width design.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adem H, Tisdall J (1984) Management of tillage and crop residues for double-cropping in fragile soils of south-eastern Australia. Soil Tillage Res 4(6):577–589
Akbar G, Hamilton G, Hussain Z, Yasin M (2007) Problems and potentials of permanent raised bed cropping systems in Pakistan. Pak J Water Resour 11(1):11–21
Akbar G, Hamilton G, Hussain Z (2009) Permanent raised bed cropping system improves water use efficiencies of wheat and maize crops, Mardan/Pakistan experience. Pak J Water Resour 13(1):17–24
Akbar G, Hamilton G, Raine S (2010) Permanent raised beds configurations and renovation methods affect crop performance. Paper presented at the 19th world congress of soil science, soil solutions for a changing world, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August, 2010
Carsel RF, Parrish RS (1988) Developing joint probability distributions of soil water retention characteristics. Water Resour Res 24(5):755–769
Connolly R, Freebairn D, Bell M, Thomas G (2001) Effects of rundown in soil hydraulic condition on crop productivity in south-eastern Queensland-a simulation study. Soil Res 39(5):1111–1129
Connolly R, Bell M, Huth N, Freebairn D, Thomas G (2002) Simulating infiltration and the water balance in cropping systems with APSIM-SWIM. Soil Res 40(2):221–242
Cook FJ, Knight JH, Humphreys E, Tisdall J, McHugh AD, Hamilton G (2008) Modelling water and solute processes and scenarios for optimization of permanent raised bed systems in China, India, Pakistan and Indonesia. Final report, vol final report. Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR), Canberra ACT 2601, Australia GPO Box 1571
Cooper J (1999) A grower survey of rotations used in the New South Wales cotton industry. Aust J Exp Agric 39(6):743–755
David R (2005) Australian synthetic daily class A pan evaporation. Queensland government, Department of Natural Resources and Mines
Eldridge D, Robson A (1997) Bladeploughing and exclosure influence soil properties in a semi-arid Australian woodland. J Range Manag 50:191–198
Hamilton G, Bakker D, Houlbrooke D, Span C (2005) Raised bed farming in Western Australia. Department of Agriculture, Western Australia, (Bulletin 4646)
Hassan I, Hussain Z, Akbar G (2005) Effect of permanent raised beds on water productivity for irrigated maize-wheat cropping system. In: Roth C, Fischer R, Meisner C (eds) Evaluation and performance of permanent raised bed cropping systems in Asia, Australia and Mexico, Griffith, NSW, Australia. ACIAR proceeding no 121, Canberra, pp 59–65
Jin H, Hongwen L, Kuhn N, Xuemin Z, Wenying L (2007) Soil loosening on permanent raised-beds in arid northwest China. Soil Tillage Res 97(2):172–183
Lucy MJ (1993) Permanent wide beds: a controlled traffic system for irrigated vertisols. Information Series-Queensland Department of Primary Industries (Australia). Department of Primary Industries, Queensland
Ma ZM, Wang FH (2005) Studies on yield and benefit of conservation tillage for wheat-corn intercropping. Paper presented at the Evaluation and performance of permanent raised bed cropping systems in Asia, Australia and Mexico, Griffith NSW, Australia
McGarry D (1995) The optimisation of soil structure for cotton production. Paper presented at the Challenging the future. World Cotton Research Conference, Brisbane, Queensland, 14–17 February 1994
McHugh A, Tullberg J, Freebairn D (2009) Controlled traffic farming restores soil structure. Soil Tillage Res 104(1):164–172
McKenzie DC (1998) SOILpak for cotton growers, 3rd edn. NSW Agriculture, Orange
McKenzie DC, Chan KY (1990) Structural improvement of compacted Vertosols. Paper presented at the soil compaction workshop, Toowoomba, Queensland
PARC (1982) Consumptive use of water for crops in Pakistan. Land and Water Resources Department, Natural Resources Division, Pakistan Agricultural Research Council, Islamabad
Rassam D, Simunek J, van Genuchten MT (2004) Modelling variably saturated flow with Hydrus-2D, vol Second edition. ND Consult, Brisbane, Australia
Richards L (1931) Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 5:318–333
Shafiq M, Hassan I, Hussain Z (2002) Influence of Irrigation methods on the productivity of summer maize under saline/sodic environment. Asian J Plant Sci 6:678–680
Shipitalo M, Dick W, Edwards W (2000) Conservation tillage and macropore factors that affect water movement and the fate of chemicals. Soil Tillage Res 53(3–4):167–183
Simunek J, Sejna M, Genuchten MT (2007) HYDRUS (2D/3D): Software package for simulating the two-and three-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. Available at www pc-progress cz (verified 20 Feb 2008) PC-Progress, Prague, Czech Republic
Šimunek J, Van Genuchten MT, Šejna M (1999) The HYDRUS-2D software package for simulating the two-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media: version 2.0. International Ground Water Modelling Centre, US Salinity Lab, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, Colorado
Singer MJ, Munns DN (1999) Soils: An introduction, 4th edn. Upper Saddle River, Prentice Hall
Smith G, Yule D, Coughlan K (1983) Soil physical factors in crop production on Vertosols in Qld. Australia paper presented at the international workshop on soils-research in the tropics, Townsville, 12–16 September
Tabuada MA, Rego ZJC, Vachaud G, Pereira LS (1995) Two-dimensional infiltration under furrow irrigation: modelling, its validation and applications. Agric Water Manag 27(2):105–123
Thomas GA, Standley J, Webb AA, Blight GW, Hunter HM (1990) Tillage and crop residue management affect vertisol properties and grain sorghum growth over 7 years in the semi-arid sub-tropics. 1. Crop residue and soil water during fallow periods. Soil Tillage Res 17(34):181–197
Thompson JA, North S (1994) Raised beds reduce winter waterlogging. Farmers’ Newsletter Large Area, vol 143. Department of Primary Industries, Australia
Tim N, House D, House N (2008) Land & water management plan, Marinya Farm, 1831 Karara Road, Cambooya. Control traffic farming, CTF solutions
Ullah MK, Habib Z, Muhammad S (2001) Spatial distribution of reference and potential evapotranspiration across the Indus Basin Irrigation Systems. Working paper 24. IWMI, Lahore, Pakistan
White SC (2007) Partial rootzone drying and deficit irrigation in cotton for use under large mobile irrigation machines. PhD, University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Ayars.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbar, G., Raine, S., McHugh, A.D. et al. Managing lateral infiltration on wide beds in clay and sandy clay loam using Hydrus 2D. Irrig Sci 33, 177–190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-014-0458-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-014-0458-9