Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of the hook wire system in the simultaneous localizations for multiple pulmonary nodules (PNs) before video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), and to clarify the risk factors for pneumothorax associated with the localization procedure.
Methods
Between January 2010 and February 2016, 67 patients (147 nodules, Group A) underwent simultaneous localizations for multiple PNs using a hook wire system. The demographic, localization procedure-related information and the occurrence rate of pneumothorax were assessed and compared with a control group (349 patients, 349 nodules, Group B). Multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to determine the risk factors for pneumothorax during the localization procedure.
Results
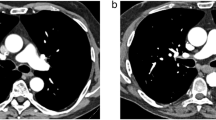
All the 147 nodules were successfully localized. Four (2.7%) hook wires dislodged before VATS procedure, but all these four lesions were successfully resected according to the insertion route of hook wire. Pathological diagnoses were acquired for all 147 nodules. Compared with Group B, Group A demonstrated significantly longer procedure time (p < 0.001) and higher occurrence rate of pneumothorax (p = 0.019). Multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that position change during localization procedure (OR 2.675, p = 0.021) and the nodules located in the ipsilateral lung (OR 9.404, p < 0.001) were independent risk factors for pneumothorax.
Conclusion
Simultaneous localizations for multiple PNs using a hook wire system before VATS procedure were safe and effective. Compared with localization for single PN, simultaneous localizations for multiple PNs were prone to the occurrence of pneumothorax. Position change during localization procedure and the nodules located in the ipsilateral lung were independent risk factors for pneumothorax.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eberth JM. Lung cancer screening with low-dose CT in the United States. J Am Coll Radiol. 2015;12(12 Pt B):1395–402.
Congregado M, Merchan RJ, Gallardo G, Ayarra J, Loscertales J. Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) lobetomy: 13 years’ experience. Surg Endosc. 2008;22(8):1852–7.
Miyoshi K, Toyooka S, Gobara H, Oto T, Mimura H, Sano Y, et al. Clinical outcomes of short hook wire and suture marking system in thoracoscopic resection for pulmonary nodules. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009;36(2):378–82.
Ichinose J, Kohno T, Fujimori S, Harano T, Suzuki S. Efficacy and complications of computed tomography-guided hook wire localization. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96(4):1203–8.
Park CH, Han K, Hur J, Lee SM, Lee JW, Hwang SH, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of pre-operative lung localization for pulmonary nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 2017;151(2):316–28.
Suzuki K, Shimohira M, Hashizume T, Ozawa Y, Sobue R, Mimura M, et al. Usefulness of CT-guided hookwire marking before video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for small pulmonary lesions. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2014;58(6):657–62.
Nakashima S, Watanabe A, Obama T, Yamada G, Takahashi H, Higami T. Need for preoperative computed tomography-guided localization in video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery pulmonary resections of metastatic pulmonary nodules. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89(1):212–8.
Chen S, Zhou J, Zhang J, Hu H, Luo X, Zhang Y, et al. Video-assisted thoracoscopic solitary pulmonary nodule resection after CT-guided hook wire localization: 43 cases report and literature review. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(6):1723–9.
Dendo S, Kanazawa S, Ando A, Hyodo T, Kouno Y, Mimura H, et al. Preoperative localization of small pulmonary lesions with a short hook wire and suture system: experience with 168 procedure. Radiology. 2002;225(2):511–8.
Li W, Wang Y, He X, Li G, Wang S, Xu L, et al. Combination of CT-guided hookwire localization and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for pulmonary nodular lesions: analasis of 103 patients. Oncol Lett. 2012;4(4):824–8.
Ciriaco P, Negri G, Puglisi A, Nicoletti R, Maschio AD, Zannini P. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for pulmonary nodules: rationale for preoperative computed tomography-guided hookwire localization. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;25(3):429–33.
Nara K, Oue T, Uehara S, Ueno T, Ibuka S, Nakahata K, et al. Efficacy of CT-guided localization followed by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in children with tiny pulmonary nodules. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2016;9(4):328–31.
Chen YR, Yeow KM, Lee JY, Su IH, Chu SY, Lee CH, et al. CT-guided hook wire localization of subpleural lung lesions for video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS). J Formos Med Assoc. 2007;106(11):911–8.
Yoshida Y, Inoh S, Murakawa T, Ota S, Masashi F, Nakajima J. Preoperative localization of small peripheral pulmonary nodules by percutaneous marking under computed tomography guidance. Interact CardioVasc Thorac Surg. 2011;13(1):25–8.
Seo JM, Lee HY, Kim HK, Choi YS, Kim J, Shim YM, et al. Factors determining successful computed tomography-guided localization of lung nodules. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;143(4):809–14.
Huang W, Ye H, Wu Y, Xu W, Tang X, Liang Y, et al. Hook wire localization of pulmonary pure ground-glass opacities for video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62(2):174–8.
Xu X, Yao Y, Shen Y, Zhang P, Zhou J. Clinical analysis of percutaneous computed tomography-guided hook wire localization of 168 small pulmonary nodules. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;100(5):1861–7.
Hanauer M, Perentes JY, Krueger T, Ris H, Bize P, Schmidt S, et al. Pre-operative localization of solitary pulmonary nodules with computed tomography-guided hook wire: report of 181 patients. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;11:5.
Horan TA, Pinheiro PM, Araújo LM, Santiago FF, Rodrigues MR. Massive gas embolism during pulmonary nodule hook wire localization. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73(5):1647–9.
Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Gobara H, Fujiwara H, Matsui Y, Sugimoto S, et al. Simultaneous multiple preoperative localizations of small pulmonary lesions using a short hook wire and suture system. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2015;38(4):971–6.
Stoeckelhuber BM, Leibecke T, Schulz E, Melchert UH, Bergmann-Koester CU, Helmberger T, et al. Radiation dose to the radiologist’s hand during continuous CT fluoroscopy-guided interventions. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2005;28(5):589–94.
Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Gobara H, Fujiwara H, Matsui Y, Miyoshi S, et al. CT fluoroscopy-guided preoperative short hook wire placement for small pulmonary lesions: evaluation of safety and identification of risk factors for pneumothorax. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(1):114–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests and no grant supports for this work.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Y., Xu, XQ., Pan, XL. et al. Retrospective Evaluation of Safety, Efficacy and Risk Factors for Pneumothorax in Simultaneous Localizations of Multiple Pulmonary Nodules Using Hook Wire System. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40, 1408–1414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1631-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1631-3