Abstract
Background
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) has evolved to treat carotid artery disease with the intention of prevent stroke. The British Society of Interventional Radiologists developed a voluntary registry to monitor the practice of this novel procedure. We present the data from the United Kingdom (UK) CAS registry for short and long-term outcomes for symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid disease.
Methods
The UK CAS registry collected data from 1998 to 2010 from 31 hospitals across the UK for 1,154 patients. All interventions were enrolled in the registry for both asymptomatic and symptomatic patients. Initial entry forms were completed for each patient entered with data including indications, demographic data, CAS data (including stents and protection device details) and 30-day outcomes. Complications were documented. Follow-up data were collected at yearly intervals.
Results
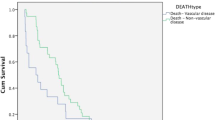
Nine hundred fifty-three (83 %) symptomatic and 201 (17 %) asymptomatic patients were enrolled into the registry. The 30-day all stroke and death rates for symptomatic patients were 5.5 and 2.2 % for those with asymptomatic disease. The 30-day mortality rate was 1.7 % for symptomatic and 0.6 % for asymptomatic patients. For symptomatic patients undergoing CAS, the 7-year all-cause mortality rate was 22.2 % and for asymptomatic patients 18.1 %. The 7-year all-cause mortality and disabling stroke rates were 25.3 and 19.4 %, respectively.
Conclusion
These data indicate that outside of the tight constraints of a randomised trial, CAS provides effective prophylaxis against stroke and death.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bockenheimer SA, Mathias K (1983) Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in arteriosclerotic internal carotid artery stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 4(3):791–792
Courtheoux P, Theron J, Tournade A et al (1987) Percutaneous endoluminal angioplasty of post endarterectomy carotid stenoses. Neuroradiology 29(2):186–189
NICE (2006) Carotid artery stent placement for carotid stenosis
Goode SD, Cleveland TJ, Gaines PA (2011) First BSIR carotid stent registry report
Johnston SC, Rothwell PM, Nguyen-Huynh MN et al (2007) Validation and refinement of scores to predict very early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack. Lancet 369(9558):283–292
NICE (2011) IPG389 carotid artery stent placement for symptomatic extracranial carotid stenosis
Naylor AR, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM et al (2002) Carotid artery disease and stroke during coronary artery bypass: a critical review of the literature. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 23(4):283–294
Brott TG, Hobson RW 2nd, Howard G et al (2010) Stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of carotid-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med 363(1):11–23
Ederle J, Dobson J, Featherstone RL et al (2010) Carotid artery stenting compared with endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis (International Carotid Stenting Study): an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 375(9719):985–997
Moore WS, Barnett HJ, Beebe HG et al (1995) Guidelines for carotid endarterectomy. A multidisciplinary consensus statement from the Ad Hoc Committee, American Heart Association. Circulation 91(2):566–579
Brown MM, Rogers J, Bland JM (2001) Endovascular versus surgical treatment in patients with carotid stenosis in the carotid and vertebral artery transluminal angioplasty study (CAVATAS): a randomised trial. Lancet 357(9270):1729–1737
Anderson HV, Rosenfield KA, White CJ et al (2010) Clinical features and outcomes of carotid artery stenting by clinical expert consensus criteria: a report from the CARE registry. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 75(4):519–525
Eckstein HH, Ringleb P, Allenberg JR et al (2008) Results of the stent-protected angioplasty versus carotid endarterectomy (SPACE) study to treat symptomatic stenoses at 2 years: a multinational, prospective, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 7(10):893–902
Keldahl ML, Park MS, Garcia-Toca M et al (2012) Does a contralateral carotid occlusion adversely impact carotid artery stenting outcomes? Ann Vasc Surg 26(1):40–45
Bonati LH, Dobson J, Algra A et al (2010) Short-term outcome after stenting versus endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis: a preplanned meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet 376(9746):1062–1073
Mas JL, Chatellier G, Beyssen B et al (2006) Endarterectomy versus stenting in patients with symptomatic severe carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 355(16):1660–1671
Reimers B, Schluter M, Castriota F et al (2004) Routine use of cerebral protection during carotid artery stenting: results of a multicenter registry of 753 patients. Am J Med 116(4):217–222
Yadav JS, Wholey MH, Kuntz RE et al (2004) Protected carotid-artery stenting versus endarterectomy in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med 351(15):1493–1501
Barbato JE, Dillavou E, Horowitz MB et al (2008) A randomized trial of carotid artery stenting with and without cerebral protection. J Vasc Surg 47(4):760–765
Macdonald S, Evans DH, Griffiths PD et al (2010) Filter-protected versus unprotected carotid artery stenting: a randomised trial. Cerebrovasc Dis 29(3):282–289
Rapp JH, Zhu L, Hollenbeck K et al (2009) Distal filtration versus flow reversal: an ex vivo assessment of the choices for carotid embolic protection. J Vasc Surg 49(5):1181–1188
Massop D, Dave R, Metzger C et al (2009) Stenting and angioplasty with protection in patients at high-risk for endarterectomy: SAPPHIRE worldwide registry first 2,001 patients. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 73(2):129–136
Gurm HS, Yadav JS, Fayad P et al (2008) Long-term results of carotid stenting versus endarterectomy in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med 358(15):1572–1579
Ederle J, Bonati LH, Dobson J et al (2009) Endovascular treatment with angioplasty or stenting versus endarterectomy in patients with carotid artery stenosis in the carotid and vertebral artery transluminal angioplasty study (CAVATAS): long-term follow-up of a randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 8(10):898–907
Mas JL, Trinquart L, Leys D et al (2008) Endarterectomy versus angioplasty in patients with symptomatic severe carotid stenosis (EVA-3S) trial: results up to 4 years from a randomised, multicentre trial. Lancet Neurol 7(10):885–892
de Donato G, Setacci C, Deloose K et al (2008) Long-term results of carotid artery stenting. J Vasc Surg 48(6):1431–1440
Hopkins LN, Myla SV, Grube E et al (2010) Carotid artery revascularisation in high-surgical-risk patients with the NexStent and the FilterWire EX/EZ: 3-year results from the CABERNET trial. Eurointervention 5(8):917–924
Fairman R, Gray WA, Scicli AP et al (2007) The CAPTURE registry: analysis of strokes resulting from carotid artery stenting in the post approval setting: timing, location, severity, and type. Ann Surg 246(4):551–556 discussion 6–8
Giacovelli JK, Egorova N, Dayal R et al (2010) Outcomes of carotid stenting compared with endarterectomy are equivalent in asymptomatic patients and inferior in symptomatic patients. J Vasc Surg 52(4):906–913
Giles KA, Hamdan AD, Pomposelli FB et al (2010) Stroke and death after carotid endarterectomy and carotid artery stenting with and without high risk criteria. J Vasc Surg 52(6):1497–1504
Gray WA, Chaturvedi S, Verta P (2009) Thirty-day outcomes for carotid artery stenting in 6,320 patients from 2 prospective, multicenter, high-surgical-risk registries. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2(3):159–166
Gray WA, Hopkins LN, Yadav S et al (2006) Protected carotid stenting in high-surgical-risk patients: the ARCHeR results. J Vasc Surg 44(2):258–268
Gray WA, Yadav JS, Verta P et al (2007) The CAPTURE registry: predictors of outcomes in carotid artery stenting with embolic protection for high surgical risk patients in the early post-approval setting. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 70(7):1025–1033
Gray WA, Yadav JS, Verta P et al (2007) The CAPTURE registry: results of carotid stenting with embolic protection in the post approval setting. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 69(3):341–348
Hopkins LN, Myla S, Grube E et al (2008) Carotid artery revascularization in high surgical risk patients with the NexStent and the Filterwire EX/EZ: 1-year results in the CABERNET trial. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 71(7):950–960
Katzen BT, Criado FJ, Ramee SR et al (2007) Carotid artery stenting with emboli protection surveillance study: thirty-day results of the CASES-PMS study. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 70(2):316–323
Mehta RH, Zahn R, Hochadel M et al (2007) Comparison of in-hospital outcomes of patients with versus without previous carotid endarterectomy undergoing carotid stenting (from the German ALKK CAS registry). Am J Cardiol 99(9):1288–1293
Pieniazek P, Musialek P, Kablak-Ziembicka A et al (2008) Carotid artery stenting with patient- and lesion-tailored selection of the neuroprotection system and stent type: early and 5-year results from a prospective academic registry of 535 consecutive procedures (TARGET-CAS). J Endovascular Ther 15(3):249–262
Safian RD, Bacharach JM, Ansel GM et al (2004) Carotid stenting with a new system for distal embolic protection and stenting in high-risk patients: the carotid revascularization with ev3 arterial technology evolution (CREATE) feasibility trial. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 63(1):1–6
Theiss W, Hermanek P, Mathias K et al (2004) Pro-CAS: a prospective registry of carotid angioplasty and stenting. Stroke 35(9):2134–2139
Theiss W, Hermanek P, Mathias K et al (2008) Predictors of death and stroke after carotid angioplasty and stenting: a subgroup analysis of the Pro-CAS data. Stroke 39(8):2325–2330
White CJ, Iyer SS, Hopkins LN et al (2006) Carotid stenting with distal protection in high surgical risk patients: the BEACH trial 30 day results. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 67(4):503–512
Wholey MH, Al-Mubarek N (2003) Updated review of the global carotid artery stent registry. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 60(2):259–266
Acknowledgments
A great many thanks to all of the clinicians who contributed data to this registry over many years and continued to provide essential follow-up data. Thanks are also due to A. Counsell, J. Saeed, M. Ireland, and S. Inglis for their help with data collection and data entry. The invaluable help of Dendrite Clinical Systems, including Robin Kinsman and Peter Walton, in setting up the registry and analyzing the data, is acknowledged and thanked.
Conflict of interest
S. Goode, T. Cleveland, and P. A. Gaines were funded by Study Grant Gore. T. Cleveland also holds a consultancy at Boston Scientific.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was conducted on behalf of the British Society of Interventional Radiologists.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goode, S.D., Cleveland, T.J. & Gaines, P.A. United Kingdom Carotid Artery Stent Registry: Short- and Long-Term Outcomes. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36, 1221–1231 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0573-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0573-7