Abstract
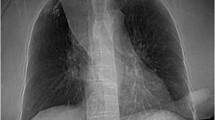
Iatrogenic injuries of the superior vena cava during endovascular treatments are a rare but life-threatening complication. According to the literature, treatment is mostly surgical. Herein we present the case of a patient undergoing venoplasty for a malignant superior vena cava syndrome. During balloon venoplasty the vessel wall perforated, leading to mediastinal as well as pericardial hemorrhage and cardiopulmonary shock. The lesion was effectively treated by an immediate reinflation of the venoplasty balloon followed by resuscitation and implantation of a covered stent. This procedure substantiates, first, the usefulness of interventional radiological methods for acute central venous hemorrhages and, second, the necessity to be adequately prepared for complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathias K, Jäger H, Willaschek J et al (1998) Interventional radiology in central venous obstructions. Dilatation-stent-implantation-thrombolysis. Radiologe 38(7):606–613
Nagata T, Makutani S, Uchida H et al (2007) Follow-up results of 71 patients undergoing metallic stent placement for the treatment of a malignant obstruction of the superior vena cava. CardiVasc Interv Radiol 30(5):959–967
Mansour M, Kamper L, Altenburg A et al (2008) Radiological central vein treatment in vascular access. J Vasc Access 9(2):85–101
Kamper L, Krüger K, Altenburg A et al (2008) Venous interventions. Part 2: thromboses of the upper torso and mesenteric veins. Radiologe 11 [Epub ahead of print]
Oshima K, Takahashi T, Ishikawa S et al (2006) Superior vena cava rupture caused during balloon dilation for treatment of SVC syndrome due to repetitive catheter ablation—a case report. Angiology 57(2):247–249
Brown KT, Getrajdman GI (2005) Balloon dilation of the superior vena cava (SVC) resulting in SVC rupture and pericardial tamponade: a case report and brief review. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 28(3):372–376
Kee ST, Kinoshita L, Razavi MK et al (1998) Superior vena cava syndrome: treatment with catheter-directed thrombolysis and endovascular stent placement. Radiology 206(1):187–193
Martin M, Baumgartner I, Kolb M et al (2002) Fatal pericardial tamponade after Wallstent implantation for malignant superior vena cava syndrome. J Endovasc Ther 9(5):680–684
Samuels LE, Nyzio JB, Entwistle JW (2007) Superior vena cava rupture during balloon angioplasty and stent placement to relieve superior vena cava syndrome: a case report. Heart Surg Forum 10(1):E78–E80
Burket MW (2003) Challenging cases: superior vena cava rupture. Endovasc Today 2:11–13
Boardman P, Ettles DF (2000) Cardiac tamponade: a rare complication of attempted stenting in malignant superior vena cava obstruction. Clin Radiol 55(8):645–647
Warshauer DM, Archer RK, Selzman CH et al (2007) Case 115: aortic pseudoaneurysm from penetrating superior vena cava stent. Radiology 243(3):901–904
Kappert U, Schulz CG, Waldow T et al (2006) Perforation of the ascending aorta: a late complication of superior vena cava stenting. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 54(1):63–65
Brant J, Peebles C, Kalra P et al (2001) Hemopericardium after superior vena cava stenting for malignant SVC obstruction: the importance of contrast-enhanced CT in the assessment of postprocedural collapse. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 24(5):353–355
Recto MR, Bousamra M, Yeh T Jr (2002) Late superior vena cava perforation and aortic laceration after stenting to treat superior vena cava syndrome secondary to fibrosing mediastinitis. J Invas Cardiol 14(10):624–629
Smith SL, Manhire AR, Clark DM (2001) Delayed spontaneous superior vena cava perforation associated with a SVC Wallstent. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 24(4):286–287
Evans J, Saba Z, Rosenfeld H et al (2000) Aortic laceration secondary to palmaz stent placement for treatment of superior vena cava syndrome. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 49(2):163–166
Azizzadeh A, Villa MA, Miller CC 3rd et al (2007) Endovascular repair of an iatrogenic superior vena caval injury: a case report. J Vasc Surg 46:569–571
Anaya-Ayala JE, Charlton-Ouw KM, Kaiser CL et al (2009) Successful emergency endovascular treatment for superior vena cava injury. Ann Vasc Surg 23(1):139–141
Schneider JR, Alonzo MJ, Hahn D (2006) Successful endovascular management of an acute iliac venous injury during lumbar discectomy and anterior spinal fusion. J Vasc Surg 44(6):1353–1356
Erzurum VZ, Shoup M, Borge M et al (2003) Inferior vena cava endograft to control surgically inaccessible hemorrhage. J Vasc Surg 38(6):1437–1439
Castelli P, Caronno R, Piffaretti G et al (2005) Emergency endovascular repair for traumatic injury of the inferior vena cava. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 28(6):906–908
Watarida S, Nishi T, Furukawa A et al (2002) Fenestrated stent-graft for traumatic juxtahepatic inferior vena cava injury. J Endovasc Ther 9(1):134–137
Martin M, Baumgartner I, Kolb M et al (2002) Fatal pericardial tamponade after Wallstent implantation for malignant superior vena cava syndrome. J Endovasc Ther 9:680–684
Bayer O, Schummer C, Richter K et al (2006) Implication of the anatomy of the pericardial reflection on positioning of central venous catheters. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 20(6):777–780
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansour, M., Altenburg, A. & Haage, P. Successful Emergency Stent Implantation for Superior Vena Cava Perforation During Malignant Stenosis Venoplasty. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32, 1312–1316 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9587-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9587-6