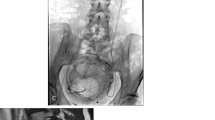
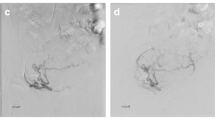
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether the size, location, or number of fibroids affects therapeutic efficacy or complications of uterine artery embolization (UAE). Patients with symptomatic uterine fibroids (n = 101) were treated by selective bilateral UAE using 500- to 710-μm polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles. Baseline measures of clinical symptoms, sonography, and MRI taken before the procedure were compared to those taken 1, 3, 6, and 12 months later. Complications and outcomes were analyzed for associations with fibroid size, location, and number. Reductions in mean fibroid volume were similar in patients with single (66.6 ± 21.5%) and multiple (67.4 ± 25.0%) fibroids (p-value = 0.83). Menstrual improvement occurred in patients with single (93.3%) and multiple (72.2%) fibroids (p = 0.18). Changes in submucosal and other fibroids were not significantly different between the two groups (p’s > 0.56). Linear regression analysis between primary fibroid volume as independent variable and percentage reduction of fibroid volume after 1 year yielded an R2 of 0.083 and the model coefficient was not statistically significant (p = 0.072). Multivariate regression models revealed no statistically or clinically significant coefficients or odds ratios for three independent variables (primary fibroid size, total number, and fibroid location) and all outcome variables (percent reduction of uterus and fibroid volumes in 1 year, improvement of clinical symptoms [menstrual, bulk related, and urinary] in 1 year, and complications after UAE). In conclusion, neither the success rate nor the probability of complications was affected by the primary fibroid size, location, or total number of fibroids.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Good-Sampson JA (1912) The blood supply of uterine myomata. Surg Gynecol Obstet 14:215–230
Ravina JH, Herbreteau D, Ciraru-Vigneron N et al (1995) Arterial embolisation to treat uterine myomata. Lancet 346:671–672
Worthington-Kirsch RL (2005) Uterine artery embolization for fibroid disease is not experimental. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28(2):150–152
Hutchins FL, Worthington-Kirsch RL, Berkowitz RP (1999) Selective uterine artery embolization as primary treatment for symptomatic Leiomyoma uteri: a review of 305 consecutive eases. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc 6:279–284
Walker WJ, Pelage JP (2002) Uterine artery embolisation for symptomatic fibroids: clinical results in 400 women with imaging followup. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 109:1262–1272
Pron G, Bennett J, Common A et al (2003) The Ontario Uterine Fibroid Embolization Trial. Part 2. Uterine fibroid reduction and symptom relief after uterine artery embolization for fibroids. Fertil Steril 79:120–127
Pinto I, Chimeno P, Romo A et al (2003) Uterine fibroids: uterine artery embolization versus abdominal hystereetomy for treatment, a prospective, randomized, and controlled elinical trial. Radiology 226:425–431
Spies JB, Bruno J, Czeyda-Pommersheim F et al (2005) Long-term outcome of uterine artery embolization of leiomyomata. 106(5; Pt 1):933–939
Katsumori T, Nakajima K, Mihara T (2003) Is a large fibroid a high-risk factor for uterine artery embolization? AJR 181(5):1309–1314
Ruta DA, Garratt AM, Chadha YC et al (1995). Assessment of patients with menorrhagia: How valid is a structured clinical history as a measure of health status? Qual Life Res 4(1):33–40
Firouznia K, Ghanaati H, Sanaati M et al (2004) A case of massive uterine bleeding due to fibroid expulsion after uterine artery embolization: control of bleeding by re-embolization. Iran J Radiol 2:79–82
Goodwin SC, McLucas B, Lee M et al (1999) Uterine artery embolization for the treatment of uterine leiomyomata: midterm results. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:1159–1165
Jha RC, Spies JB (2001) Uterine artery embolization for leiomyomata: resource use and cost estimation. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:571–574
Worthington-Kirsch R, Popky G, Hutchins F (1998) Uterine arterial embolization for the management of leiomyomas: quality–of-life assessment and clinical response. Radiology 208:625–629
Watson GMT, Walker WJ (2002) Uterine artery embolization for the treatment of symptomatic fibroids in 114 Women: reduction in size of the fibroids and women’s views of the success of the treatment. BJOG 109:129–135
Goodwin Sc, Vedantham S, Mclucas B et al (1997) Preliminary experience with uterine artery embolization for uterus fibroids. J Vasc Interv Radiol 8:517–526
Spies JB, Myers ER, Worthington-Kirsch R et al (2005) FIBROID Registry Investigators. The FIBROID Registry: symptom and quality-of-life status 1 year after therapy. Obstet Gynecol 106(6):1309–1318
Roth AR, Spies JB, Walsh SM et al (2000) Pain after uterine artery embolization for leiomyomata: Can its severity be predicted and does severity predict outcome? J Vasc Interv Radiol 11(8):1047–1052
Volkers NA, Hehenkamp WJ, Birnie E et al (2006) Uterine artery embolization in the treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroid tumors (EMMY trial): periprocedural results and complications. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(3):471–480
Spies JB, Roth AR, Jha RC (2002) Leiomyomata treated with uterine artery embolization: factors associated with successful symptom and imaging outcome. Radiology 222(1):45–52
Zhou SK, Li SB, Zhang ZS (2003) Influential factors to therapeutic efficacy of uterine artery embolization in the treatment of uterine fibroids. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28(4):409–411
Rajan DK, Beecroft JR, Clark TW et al (2004) Risk of intrauterine infectious complications after uterine artery embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:1415–1421
Kroncke TJ, Gauruder-Burmester A, Scheurig C et al (2005) Transarterial embolization for uterine fibroids: clinical success rate and results of magnetic resonance imaging. Rofo 177(1):89–98
Jha R, Ascher S, Imaoka I et al (2000) Symptomatic fibroleiomyomata: MR imaging of the uterus before and after uterine arterial embolization. Radiology 217:228–235
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr. Bakhshandeh for his cooperation in statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Firouznia, K., Ghanaati, H., Sanaati, M. et al. Uterine Artery Embolization in 101 Cases of Uterine Fibroids: Do Size, Location, and Number of Fibroids Affect Therapeutic Success and Complications?. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31, 521–526 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9288-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9288-y