Abstract
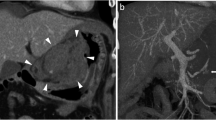
Glucagon is often used in radiology to decrease bowel motility for enhanced imaging, including visceral digital subtraction angiography. We present a case in which branch hepatic artery vasospasm followed the intravenous administration of glucagon during visceral angiography.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redd DC (1997) Diagnostic pharmacoangiography. In: Baum S (ed) Abrams’ angiography, 4th ed. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 49–65
Dotevall G, Kock N (1963) The effect of glucagon on intestinal motility in man. Gastroenterology 45:364–367
Mochiki E, Suzuki H, Takenoshita S, et al. (1998) Mechanism of inhibitory effect of glucagon on gastrointestinal motility and cause of side effects of glucagon. J Gastroenterol 33:835–841
Maglinte D, Caudill L, Krol K, et al. (1982) The minimum effective dose of glucagon in upper gastrointestinal radiography. Gastrointest Radiol 7:119–122
Miller R, Chernish S, Brunelle, et al. (1978) Double-blind radiographic study of dose response to intravenous glucagon for hypotonic duodenography. Radiology 127:55–59
Madden J, Ludewig R, Wangensteen S (1971) Effects of glucagon on the splanchnic and the systemic circulation. Am J Surg 122:85–90
Richardson P (1982) Physiological regulation of the hepatic circulation. Fed Proc 41:2111–2116
Kawasaki T, Carmichael F, Saldivia V, et al. (1990) Relationship between portal venous and hepatic arterial blood flows: spectrum of response. Am J Physiol 259:1010–1018
Ross G (1970) Regional circulatory effects of pancreatic glucagon. Br J Pharmacol 38:735–742
Fasth S, Hulten L (1971) The effect of glucagon on intestinal motility and blood flow. Acta Physiol Scand 83:169–173
Estall JL, Drucker DJ (2006) Glucagon and glucagon-like peptide receptors as drug targets. Curr Pharm Des 12:1731–1750
Gardiner SM, March PA, Kemp PA, et al. (2006) Mesenteric vasoconstriction and hindquarters vasodilation accompany the pressor actions of exendin-4 in conscious rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:852–859
Joseph JM, Doenz F, Mosimann F (1994) Standing waves:differential diagnosis of fibromuscular disease. Helv Chir Acta 60:897–899
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dziedzic, T.S., Smith, T.P. Glucagon-Induced Vasospasm of Hepatic Artery Branches During Visceral Angiography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31 (Suppl 2), 30–33 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9172-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9172-9